Multi-semantic security map construction, use and scheduling method for AGV navigation scheduling
A map construction and multi-semantic technology, applied to road network navigators, image analysis, and re-radiation, can solve problems such as path tracking failure, positioning drift cannot be effectively detected, and steering wheel damage, etc., to achieve the goal of accelerating data computing efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
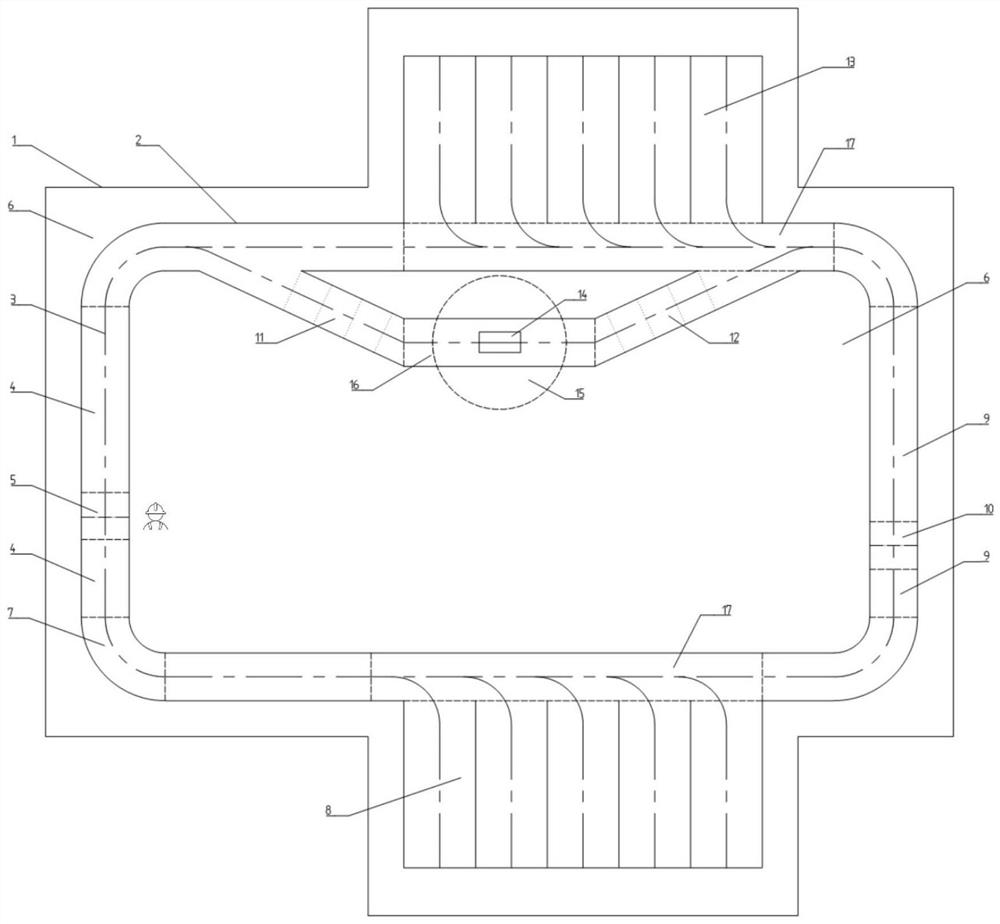
[0073] Such as figure 1 Shown, AGV navigation dispatching described in the present invention uses the multi-semantic safety map construction method, comprises the following steps:
[0074] S1. Use vehicle-mounted auxiliary drawing data software to collect key points of the path;
[0075] S2. Use map software to process the data collected in step S1, remove irregular noise data, and perform down-sampling at positions with higher data density;
[0076] S3. Using the geometric attributes of the route points and map elements to fit the route to form a continuous driving route;
[0077] S4. Establishing the structural relationship between the lane boundary and the driving path;
[0078] S5. According to the requirements of the scene, use map elements to perform multi-semantic area segmentation on the lane;
[0079] S6. Set different constraint information according to different regional semantics and establish a structural relationship with the lane to constrain the operating st...
Embodiment 2
[0087] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a method for using the map constructed by the above-mentioned multi-semantic safe map construction method for AGV navigation scheduling, specifically:
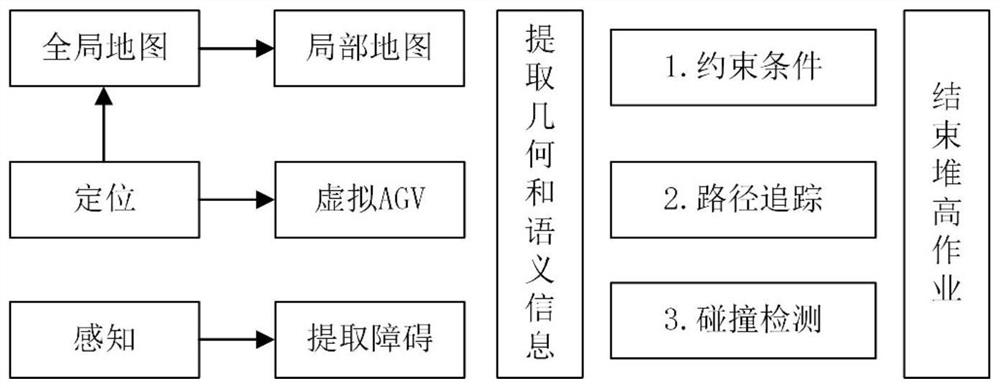
[0088] T1, AGV map module loads and extracts map data;
[0089] T2. The map module interpolates the key nodes of the driving path according to the constraints to form a smooth lane guideline 3;
[0090] T3. Use the bounding box to process the map area elements;
[0091] T4. Use kd-tree to establish the structural organization relationship between each map element;
[0092] T5. The positioning module releases the positioning information of the laser radar in real time, and informs other modules of the system of the position and heading information of the AGV;
[0093] T6. The AGV map module periodically releases the local map 15 data within a certain radius of the AGV's environment according to the positioning information released by the positioning module, so as to ...
Embodiment 3
[0124] On the basis of Embodiment 2, a method for scheduling AGVs is provided, including the following steps:
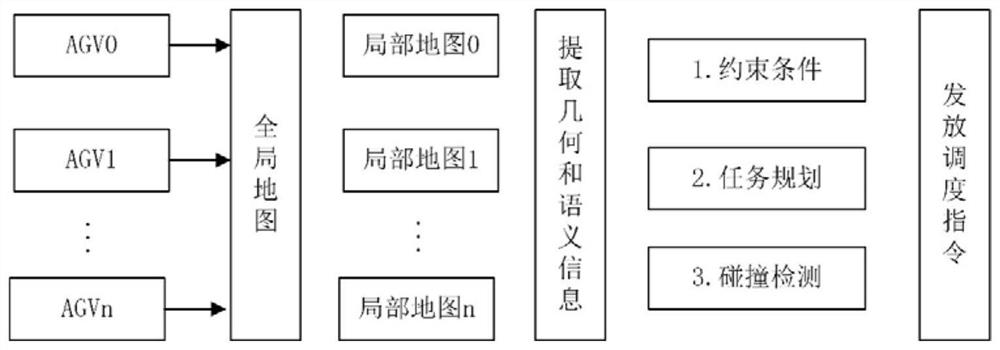
[0125] D1. According to the lane information and constraint information of the map, the server uses the planning algorithm (using the existing algorithm, such as the improved Dijkstra, A * 、D * Algorithm) to plan the optimal task path for each AGV and send scheduling instructions;
[0126] D2. The map module of the server publishes the local map information of each AGV in real time according to the status and perception information of each AGV;
[0127] D3. The server detects the local map information of each AGV. When some AGVs are relatively close, the status information and geometric contour information of other AGVs will appear in the local map perspective of the current AGV. For the AGVs in the current local map 15 Collision detection is carried out between them, avoiding global detection, and improving detection efficiency and safety.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com