An electric assisted repeated deep drawing device
A technology of electric auxiliary and forming devices, which is applied in the direction of feeding devices, positioning devices, storage devices, etc., can solve problems such as residual stress, difficult bottom drawing, cracking, etc., achieve high forming efficiency, less labor time-consuming, and improve forming extreme effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
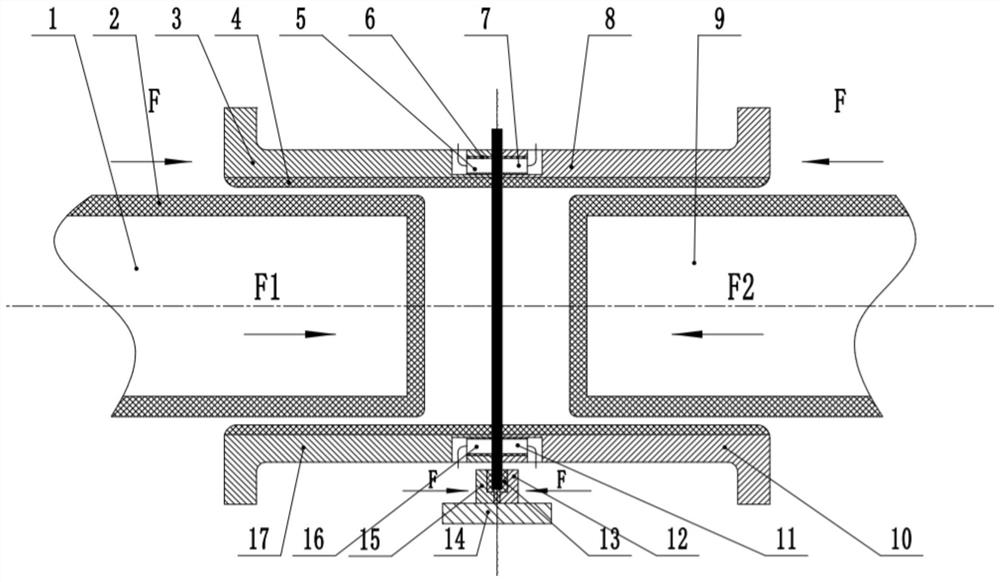
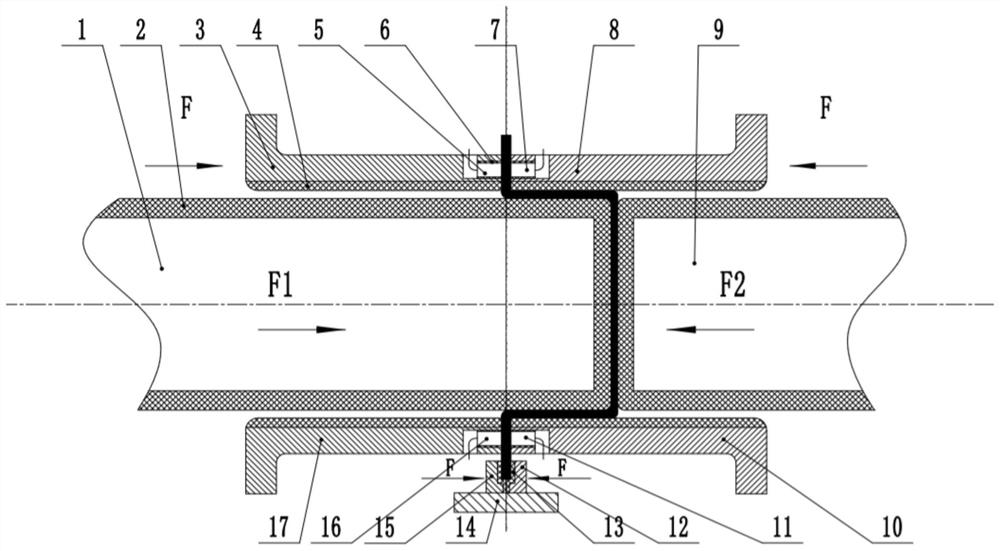
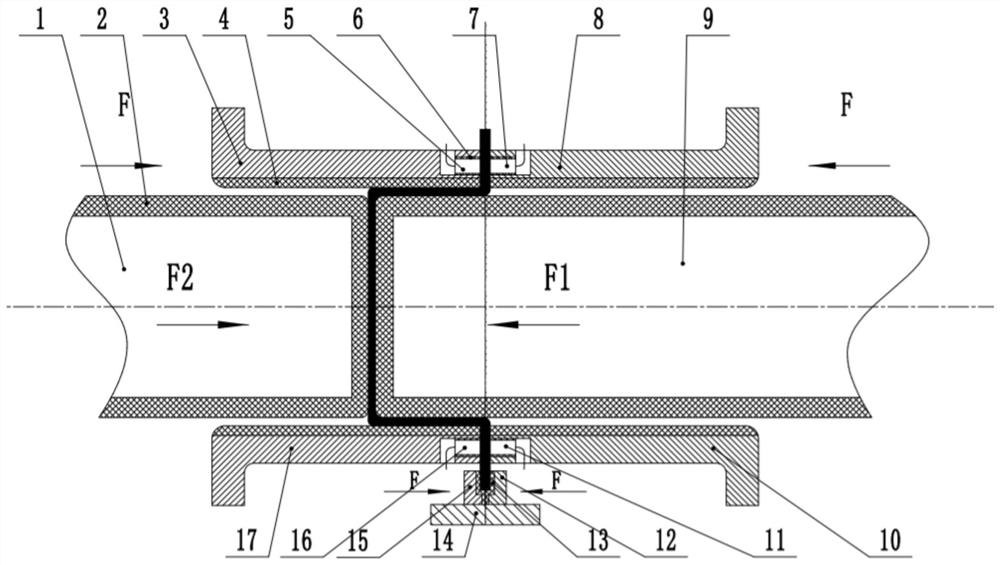
[0025] Specific embodiment: place the plate vertically in the groove formed by the first clamping part 12 and the second clamping part 15, the first electrode 5 and the second electrode 7 are externally connected to the power line, the third electrode 11 and the fourth electrode The electrode 16 is externally connected to the zero line of the power supply, and the pneumatic cylinder of the horizontal press applies the same and opposite pressure at the same time to clamp the sheet. At the same time, the first die 3 and the second die 8 press the upper end of the sheet, the third The die 10 and the fourth die 17 press the lower end of the sheet, and the piston rod applies the same and opposite pressure to the first die 3 and the second die 8 at the same time, and the piston rod simultaneously presses the third die 10 and the fourth die. The die 17 exerts the same and opposite pressure to prevent the sheet from wrinkling. The current flows through the sheet from the first electrod...
Embodiment 1
[0030] Comparison of the Vickers hardness of different positions of the workpiece under the traditional deep drawing and the electric assisted repeated deep drawing of the present invention when the aluminum alloy sheet is used for deep drawing:
[0031]The position a is at the center of the bottom of the workpiece. The average hardness of the traditional process is 64.8HV1 / 15. The hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawing is 67.2HV1 / 15, and the hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawing is 71.7HV1 / 15. , position b is the flat area at the bottom of the workpiece, the average hardness of the traditional process is 64.7 HV1 / 15, the hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawing once-drawn workpiece is 67.4HV1 / 15, and the hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep-drawn second-drawn workpiece is 71.8HV1 / 15 15. Position c is the transition fillet of the bottom surface of the workpiece. The average hardness of the traditional process is 68.4 ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Comparison of Vickers hardness at different positions of the workpiece under traditional deep drawing and electric assisted repeated deep drawing when low carbon steel is used for deep drawing:
[0034] The position a is the center of the bottom of the workpiece. The average hardness of the traditional process is 142.6HV1 / 15. The hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawing once drawn workpiece is 146.5HV1 / 15. , position b is the flat area at the bottom of the workpiece, the average hardness of the traditional process is 142.5 HV1 / 15, the hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawing once drawn workpiece is 146.8HV1 / 15, and the hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep drawn second drawn workpiece is 151.3HV1 / 15 15. Position c is the transition fillet on the bottom surface of the workpiece. The average hardness of the traditional process is 147.3HV1 / 15. The hardness of the electric-assisted repeated deep-drawing once-drawn workpiece is 151.2HV1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com