Mutant polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase, gene and transformant thereof, and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoic acid
A technology of polyhydroxyalkanoate and enzyme synthesis, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, bacteria, etc., can solve the problem of low melt processability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0097] Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention in detail, this invention is not limited to these Examples.
[0098] The genetic manipulation described below can be carried out with reference to the description of Molecular Cloning (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (1989)). In addition, enzymes, cloning hosts, and the like used in genetic manipulation can be purchased from commercial suppliers and used according to their instructions. In addition, as said enzyme, if it can be used for gene manipulation, it will not specifically limit.
manufacture example 1
[0099] (Manufacturing Example 1) Preparation of H16ΔphaC1 Ptrc-phaJ4b dZ1,2,6 strains
[0100] First, a plasmid for disrupting the phaC1 gene was prepared. A DNA fragment (SEQ ID NO: 12) having the nucleotide sequences upstream and downstream of the phaC1 gene was obtained by PCR using synthetic oligo DNA. The resulting DNA fragment was digested with restriction enzyme SwaI. This DNA fragment was ligated with the vector pNS2X-sacB described in JP 2007-259708 A, which was also digested with SwaI, to prepare a plasmid vector pNS2X-sacB-phaC1UL for gene disruption having the nucleotide sequences upstream and downstream of phaC1. .
[0101] Next, ΔphaC1 Ptrc-phaJ4b dZ1,2,6 strains were prepared using pNS2X-sacB-phaC1UL. pNS2X-sacB-phaC1UL was introduced into Escherichia coli S17-1 strain (ATCC47055). The obtained transformants and KNK005 trc-phaJ4bΔphaZ1, 2, and 6 strains (see International Publication No. 2015 / 115619) were mixed on Nutrient Agar medium (manufactured by Difco)...
manufacture example 2
[0104] (Production Example 2) Preparation of pCUP2-Ptrp-NSDG
[0105] A DNA fragment having the base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13 was amplified by PCR using synthetic oligo DNA or the like. The obtained DNA fragment was ligated with a DNA fragment obtained by digesting the pCUP2 vector described in JP-A-2007-259708 with MunI and SpeI using the In-fusion HD Cloning Kit (TAKARA BIO), to obtain pCUP2-Ptrp -NSDG. pCUP2-Ptrp-NSDG is a plasmid expressing NSDG under the trp promoter.
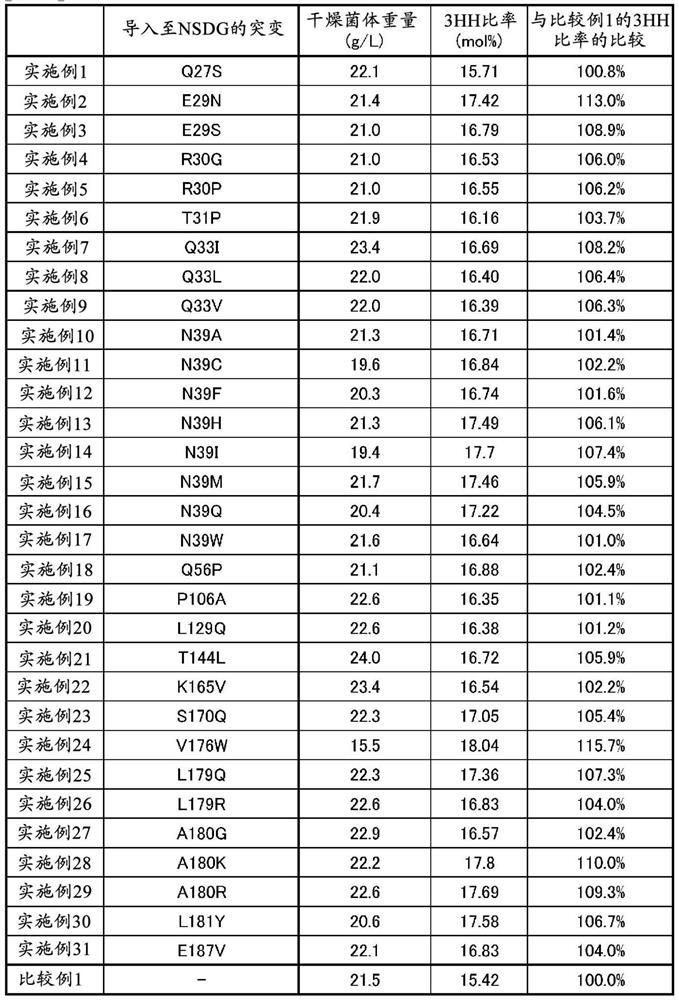
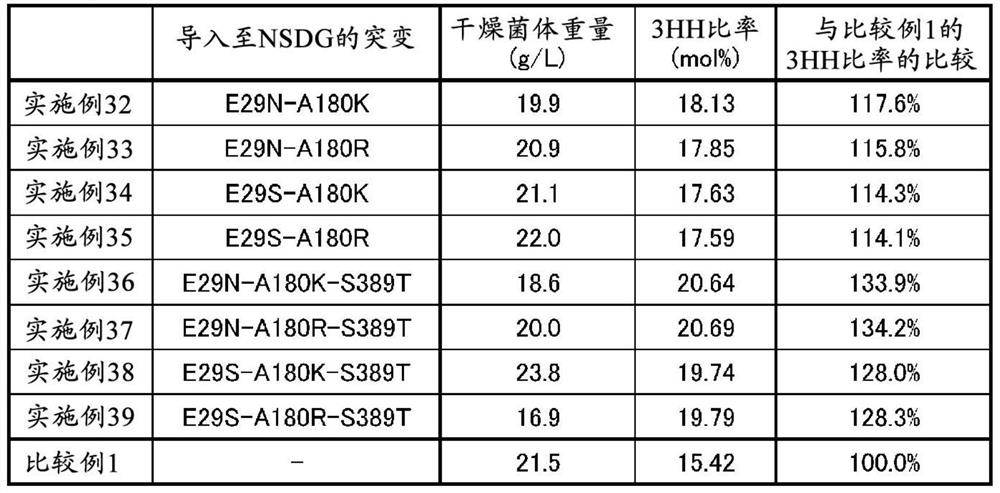
[0106] NSDG is a mutant PHA synthetase consisting of the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 14, in which asparagine at the 149th position from the N-terminus is replaced with serine and asparagine at the 171st position is introduced into the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 A mutant PHA synthetase obtained by replacing amino acid with glycine.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com