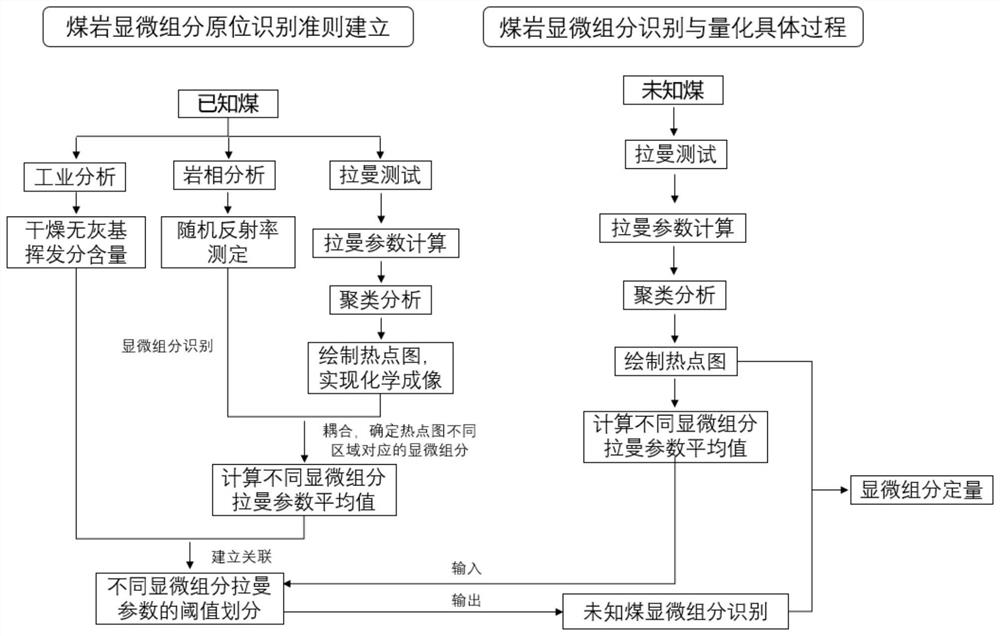
In-situ identification and rapid quantification method for coal rock macerals
A technology of microscopic composition and coal rock, applied in the field of clean and efficient utilization of coal, can solve the problems of structural error, poor repeatability, and inability to industrial application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] In this embodiment, the dry ash-free base volatile content is used as the coal quality parameter, and the drift coefficient α is used as the Raman characteristic parameter for illustration.
[0056] 1) Select 8 kinds of standard coal for industrial analysis, and the specific data are shown in the following table:
[0057]
[0058] 2) According to the national standard GB / T 16773-2008, coal light slices were prepared for subsequent petrographic analysis and Raman spectrum testing;
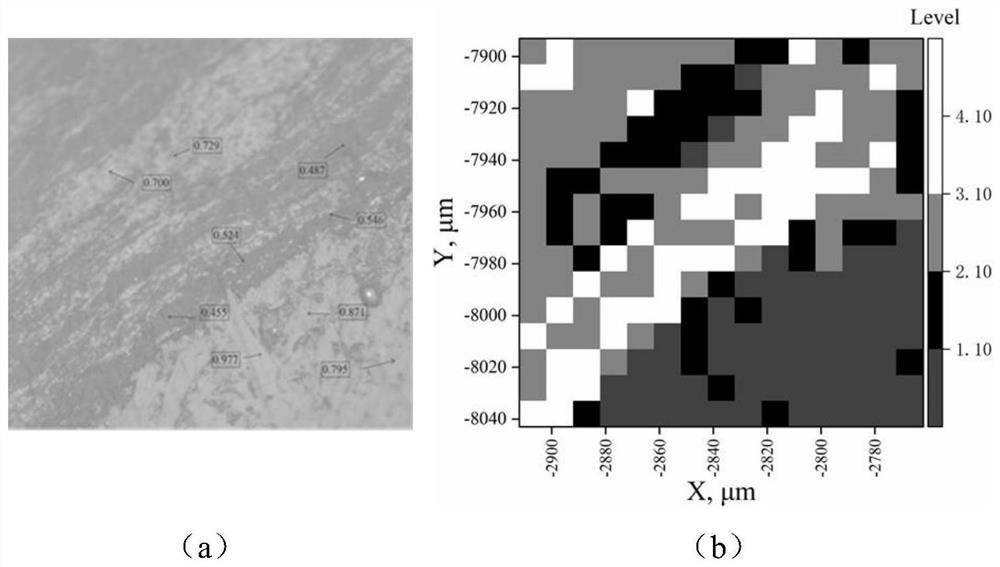
[0059] 3) Carry out petrographic analysis on the above 8 kinds of standard coal, use 10X objective lens to find a two-dimensional plane that contains as many different microscopic components as possible, take and save its microscopic pictures under the oil immersion microscope, and then in the whole Randomly measure the reflectivity of several points in the plane and mark them. Discriminate the types of microscopic components according to the color, shape, fluorescence characteristics and...
Embodiment 2
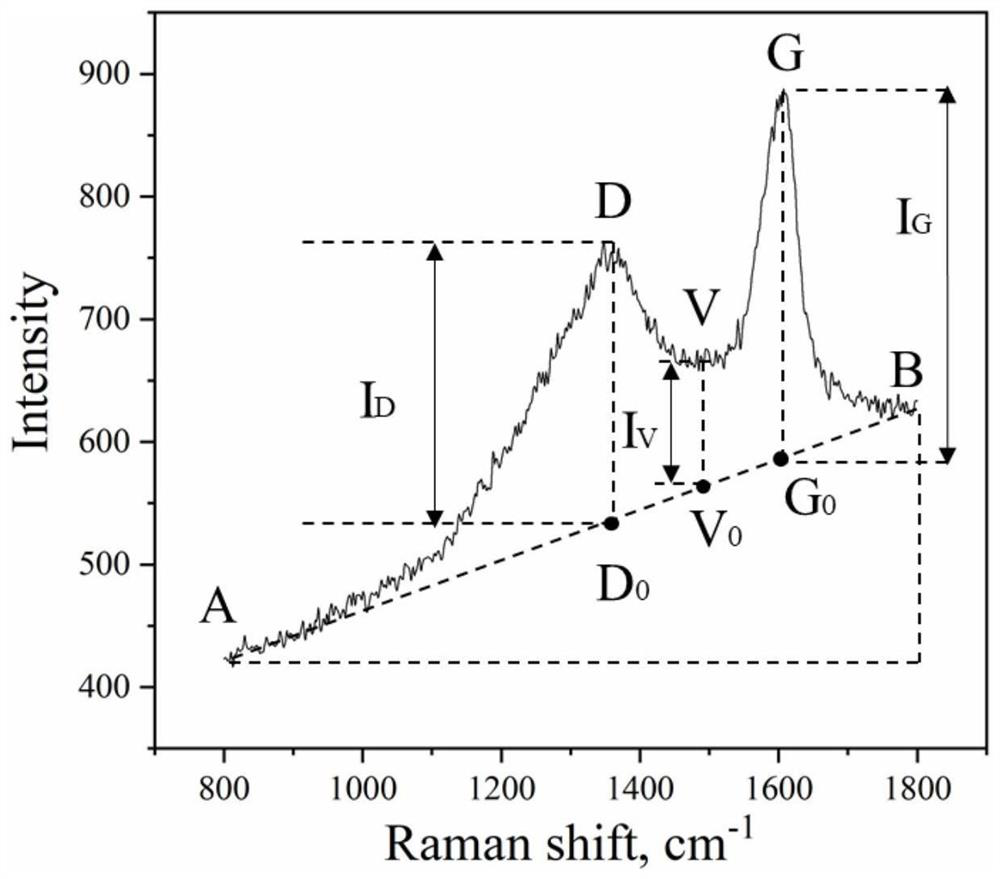
[0067] The experiment and data processing method that embodiment 2 adopts are identical with embodiment 1, difference is to adopt comprehensive index, K=k 1 α+k 2 (I V / I D )+k 3 (I V / I G ), where k 1 、k 2 and k 3 is the component score coefficient of the corresponding Raman characteristic parameter, which is determined by principal component analysis of the above three Raman characteristic parameters, and k is obtained according to the above-mentioned collected data 1 =0.970,k 2 =0.972,k 3 =0.978, namely K=0.970α+0.972I V / I D +0.978I V / I G .
[0068] like Figure 7 As shown, take the comprehensive index K as the ordinate, and take the dry ash-free base volatile content V daf is the abscissa, the average values of Raman characteristic parameters and coal quality parameters of 8 kinds of standard coal samples are plotted in the two-dimensional plane coordinate system, and the curve is fitted by the same method as in Example 1, as the analysis of different m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com