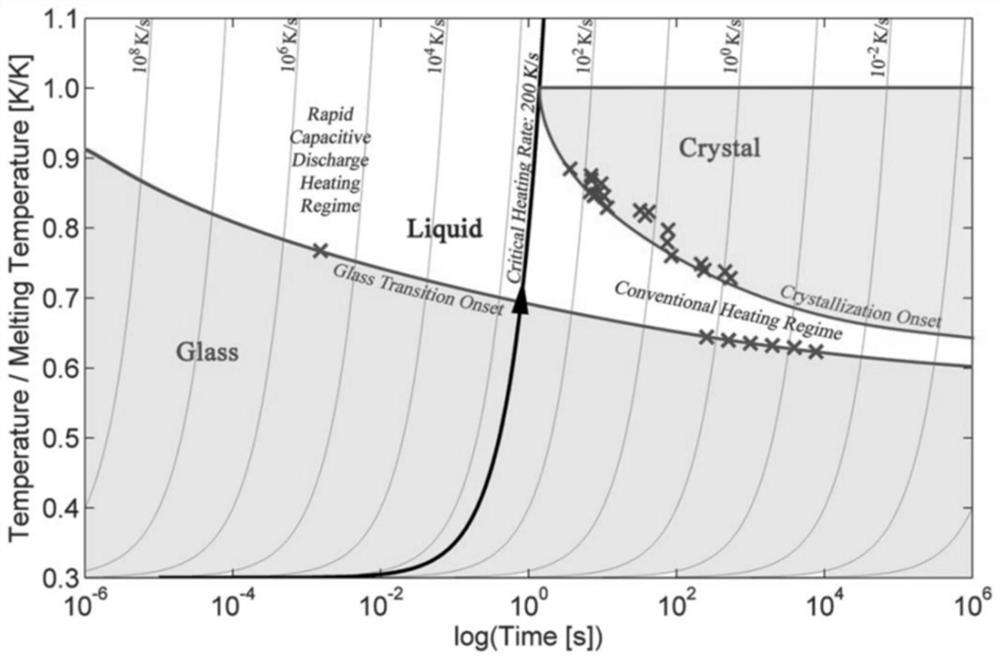
3D printing method and device based on pulse current
A pulse current and 3D printing technology, which is applied in 3D printing and space manufacturing, can solve the problems of easy crystallization of amorphous alloy materials, achieve the effect of increasing the transition temperature, small discharge area, and avoiding crystallization behavior
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] This embodiment realizes the welding between Fe base, La and Zr base amorphous alloy strips and keeps its amorphous characteristics by pulse current, see Figure 4 , showing fabrication drawings of welds between Fe-based, La and Zr-based amorphous alloy strips, see Figure 5 , shows the XRD results before and after welding between Fe-based, La and Zr-based amorphous alloy strips, proving that the welded product still maintains an amorphous structure; the specific steps are as follows:
[0049] 1. Selection of parameters
[0050] Fe-based amorphous alloy strip: choose 4700μF capacitor, discharge current 200A, current pulse width 0.5ms, welding point spacing 0.5mm, pressure value 3.5kg as the diffusion bonding control conditions of amorphous alloy strip.
[0051] La-based amorphous alloy strip: choose 4700μF capacitor, discharge current 400A, current pulse width 1ms, welding point spacing 0.5mm, pressure value 4kg as the diffusion bonding control conditions of amorphous ...
Embodiment 2
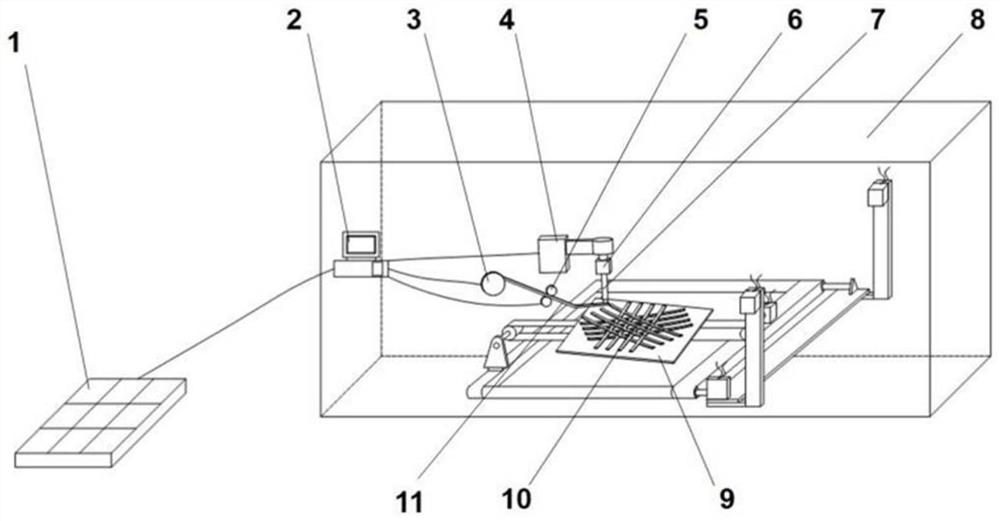
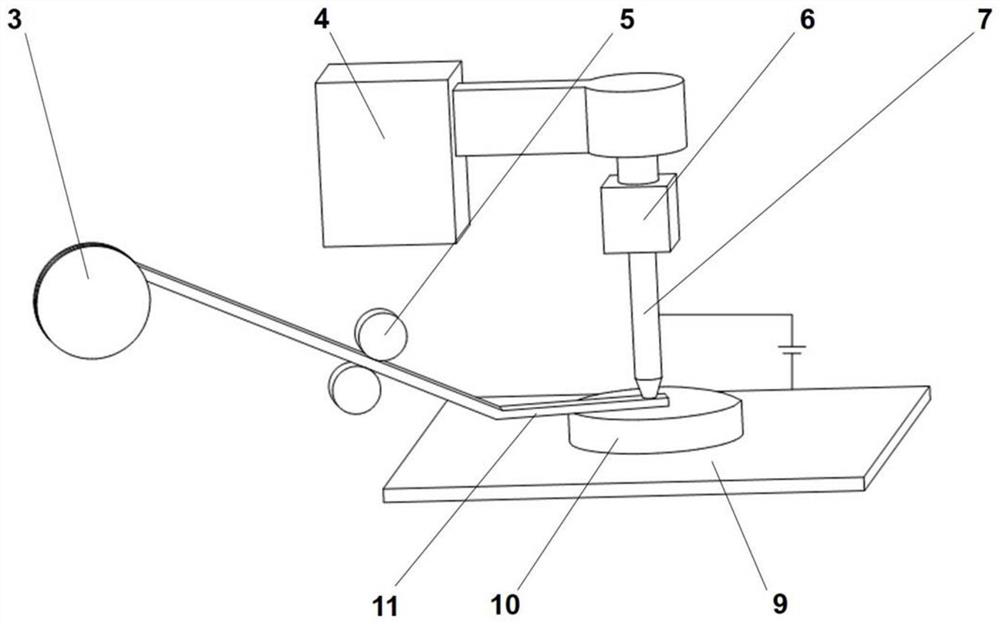
[0061] This embodiment is a 3D printing device based on pulse current, see figure 2 and image 3 As shown, it includes a frame 8, which is composed of aluminum alloy installation, and also includes a forming device and a control device 2 arranged in the frame 8. The control device 2 is connected to the forming device, and the control device is connected through a data line / wireless communication device. Send instructions to the forming device for real-time control. Among them, the forming device includes a transmission device 4, a metal electrode 7, a pulley 3, and a transmission wheel 5. The metal electrode 7 is connected to the transmission device 4 in transmission, and is driven by the transmission device 4 to perform linear reciprocating motion up and down; the pulley 3 is equipped with an amorphous Alloy material, transmission wheel 5 is arranged between belt pulley 3 and metal electrode 7, is used for the amorphous alloy material in belt pulley 3 is conveyed below meta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com