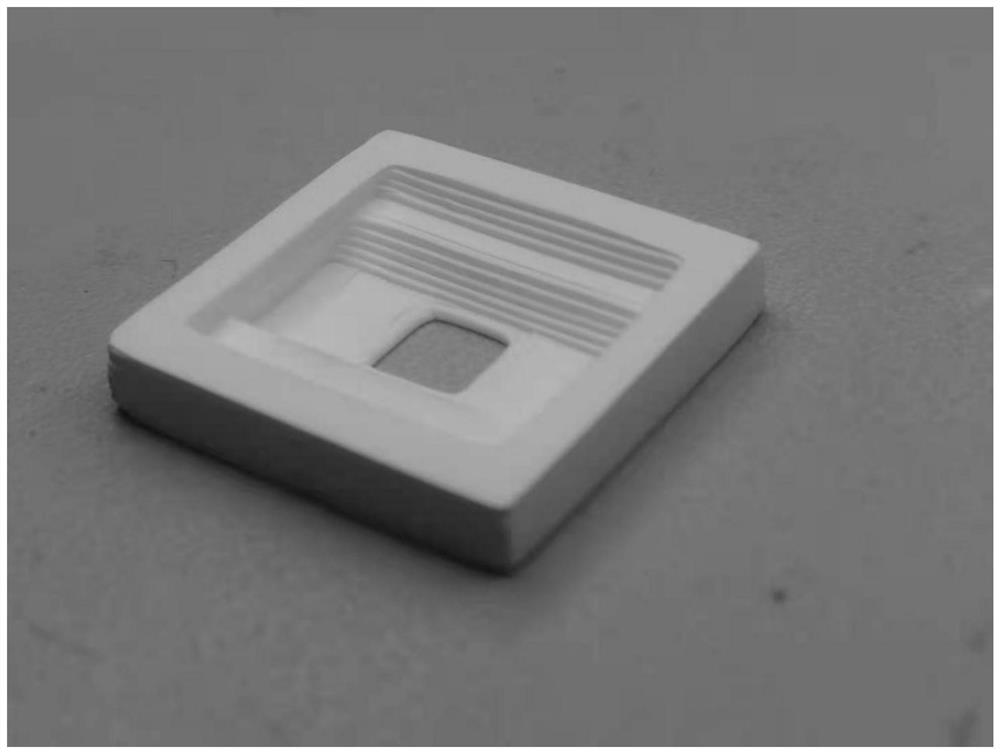
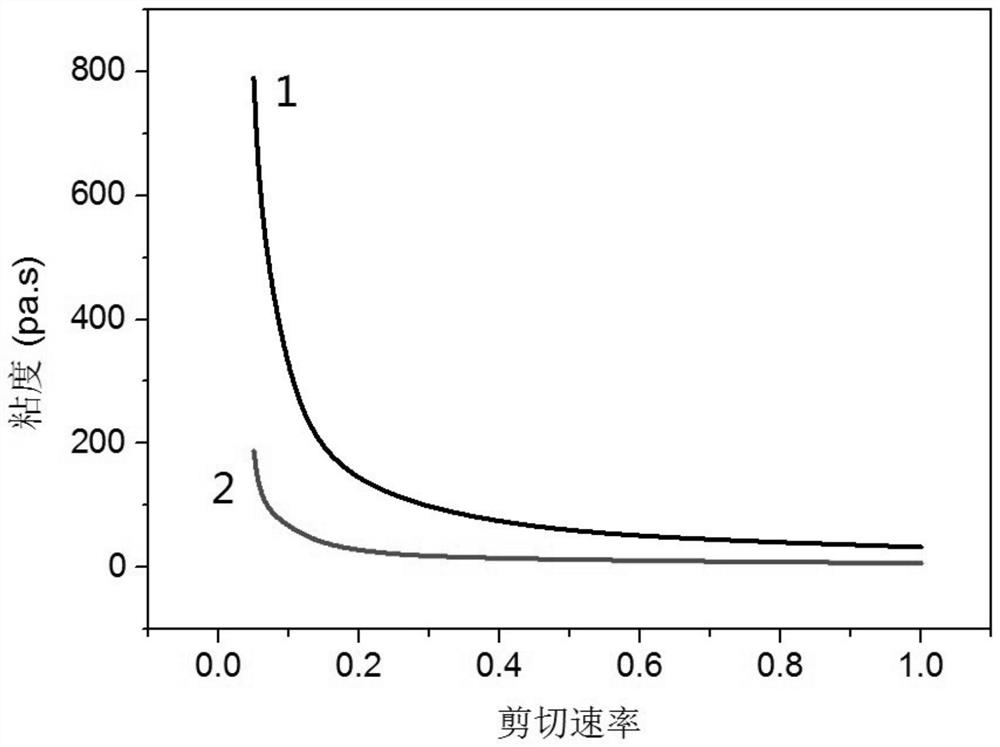
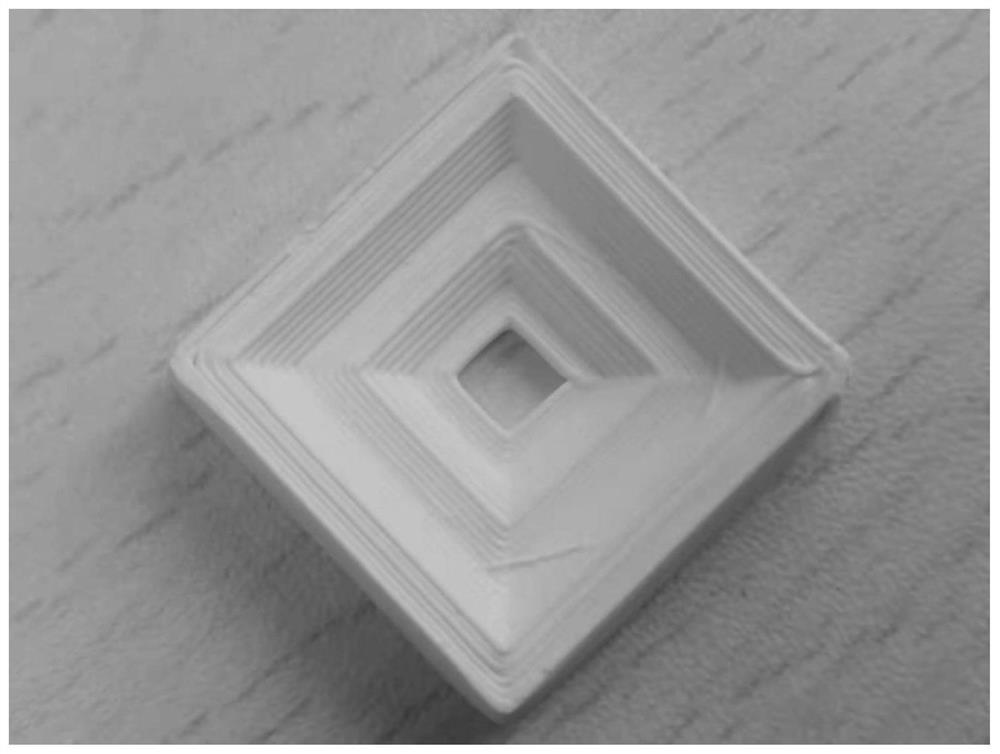
Method for 3D printing of high-solid-content low-temperature co-fired alumina ceramic complex structure
A kind of alumina ceramics, 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of high-speed, high-precision direct-write 3D printing, difficult long-term storage, poor slurry stability, etc., and achieve low sintering shrinkage , uniform shrinkage and reduced shrinkage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode is a method for 3D printing a complex structure of low-temperature co-fired alumina ceramics with high solid phase content, which is carried out according to the following steps:
[0030] 1. Weighing:
[0031] Weigh 4 to 8 parts of solvent, 0.5 to 1 part of dispersant, 0.5 to 1 part of surfactant, 0.5 to 1 part of binder, 0.5 to 5 parts of diluent, 2 parts to 4 parts of thixotropic agent, 60-88 parts of alumina powder, 1-20 parts of glass powder and 300-500 parts of absolute ethanol;
[0032] 2. Preparation of organic colloids:
[0033] Mix 4 to 8 parts of solvent, 0.5 to 1 part of dispersant and 0.5 to 1 part of surfactant and stir evenly, then add 0.5 to 1 part of binder, and in a temperature range of 50°C to 90°C Under certain conditions, heat and stir for 2h to 4.5h, then use vacuum defoaming to stir and mix evenly, then add 0.5 to 5 parts of diluent and 2 to 4 parts of thixotropic agent, use vacuum to defoa...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the solvent described in step one is one or more mixtures in terpineol, ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; Described dispersant is Efka 110; The tensio-active agent described in step one is triton; The binding agent described in step one is ethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose or Polyvinyl butyral; The thinner described in step one is N-ethylpyrrolidone, thinner BYK164 or thinner 4300; The thixotropic agent described in step one is castor oil; The oxidation described in step one The aluminum powder is a spherical particle with a particle diameter of 200nm-10μm; the glass powder described in step 1 is a spherical particle with a particle diameter of 500nm-10μm. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0050] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the vacuum degassing, stirring and mixing described in step 2 are uniform, specifically, when the vacuum degassing and stirring speed is 500r / min~2000r / min and Under the condition of vacuum degree of 30kPa~50kPa, vacuum degassing and stirring for 5min~20min. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com