Image splicing method and splicing system based on grid optimization and readable storage medium
An image mosaic and grid technology, which is applied to the details of image mosaic, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problem of inconsistent horizontal overlap rate, achieve the effect of low cost, strong versatility, and pixel alignment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
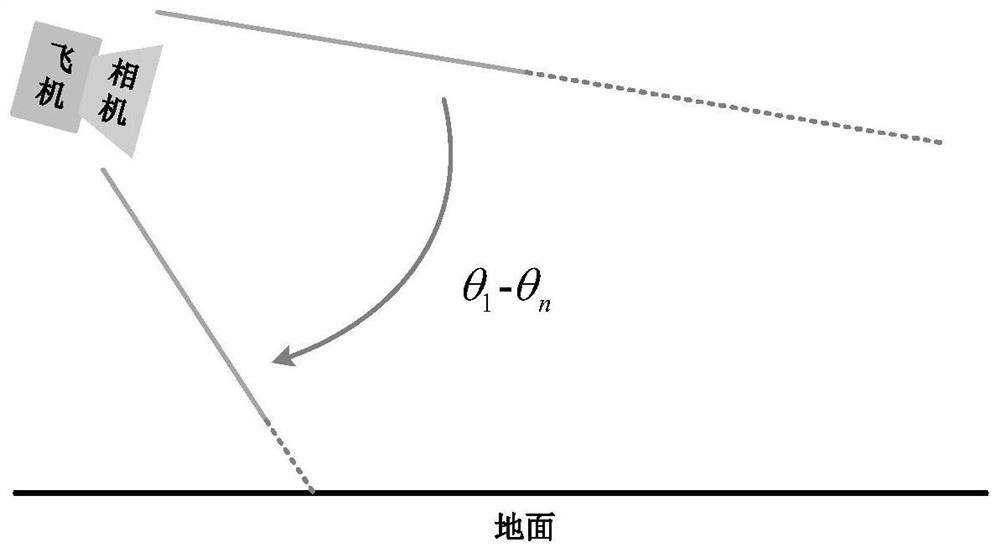
[0086] This embodiment is aimed at an island (20*15 images) between the aerial photography at a height of 10,000 meters and the horizontal line at an angle of 45 degrees to 60 degrees. The schematic diagram is as follows figure 2 As shown, the image refinement stitching process is carried out as follows:
[0087] Step A: In the single-column image stitching stage, suppress the density of local feature points to obtain the homography matrix, and derive the transfer relationship to obtain the coordinate relationship between the current images to stitch the single-column far-infrared images.
[0088] Wherein, in this embodiment, aiming at the aerial images, stitching is first performed in a single row of images, and the process is as follows:
[0089] 1) Image preprocessing: Bilateral filter noise reduction
[0090] Among them, there are many noises in the far-infrared image, which will seriously interfere with the detection and matching of feature points. Bilateral filter (Bi...
Embodiment 2
[0149] This embodiment is aimed at the continent (33*32 images) between the 10,000-meter-high aerial photography and the horizontal line at an angle of 30 degrees to 60 degrees. The schematic diagram of image acquisition is as follows figure 2 shown. The first step is to detect, match and screen out suitable feature points using SIFT and RANSAC.
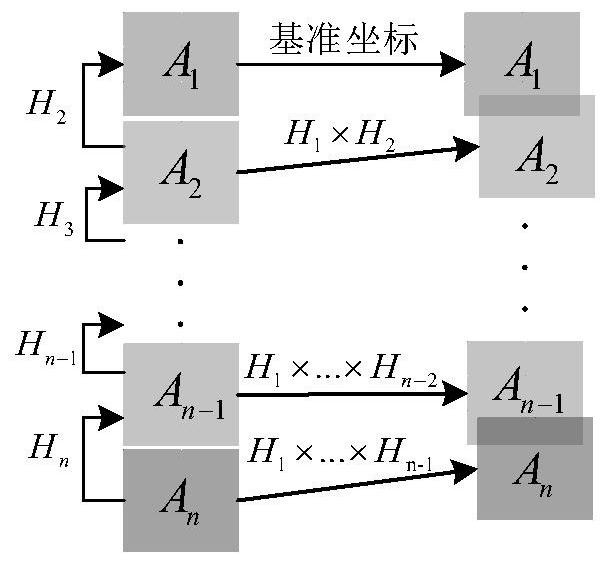
[0150] The second step is to use the feature points extracted in the previous step to calculate the homography transformation matrix, and then recursively deduce the homography transformation matrix through the image position relationship to realize all the splicing of single-column images.
[0151] The third step is to perform column-to-column splicing for each column that has been spliced. First, use SIFT and RANSAC to obtain all the appropriate feature points, and then subdivide the single-column long image into 40*200 grids, and assign the grids to different The area (including overlapping area and non-overlapping area), accord...
Embodiment 3
[0156] This embodiment is aimed at 360-degree panorama stitching (9-18 images), and the images collected by the wide-angle lens are severely distorted and have high resolution. The first step is to detect, match and screen out suitable feature points using SIFT and RANSAC.
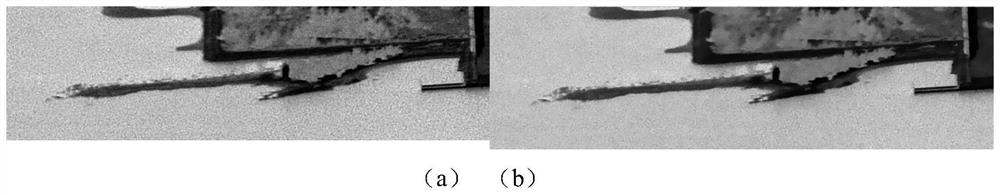
[0157] The second step is to use the feature points extracted in the previous step to calculate the homography transformation matrix, subdivide the image into 80*80 grids, and attribute the grids to different areas (including overlapping areas and non-overlapping areas), according to the Belonging to different positions, the judgment is the proportion of its regional similarity transformation and local homography transformation. The final transformation equations of different grids are slightly different, which can realize the smooth mapping of one column of images to another column of images, and at the same time help reduce Distortion, better fusion of images.
[0158] The fourth step is to use the form...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com