Method for comprehensively utilizing waste liquid generated in process of preparing alkali by ammonia-alkali method
A technology of alkali-making waste liquor and ammonia-alkali method, applied in chemical instruments and methods, earthwork drilling, calcium/strontium/barium compounds, etc., can solve the problem of wasting resources, unable to be turned into products, and insufficient total utilization rate of sodium chloride 70% and other problems to achieve the effect of solving pipeline transportation and well injection and reducing calcium sulfate accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for comprehensive utilization of waste liquor from ammonia-soda production, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) Aeration process: Introduce air into the ammonia-soda process alkali-making waste liquid at a temperature of 83°C to aerate and remove ammonia, collect ammonia gas with water to obtain an ammonia solution, and return the ammonia solution to the soda-making section for use;
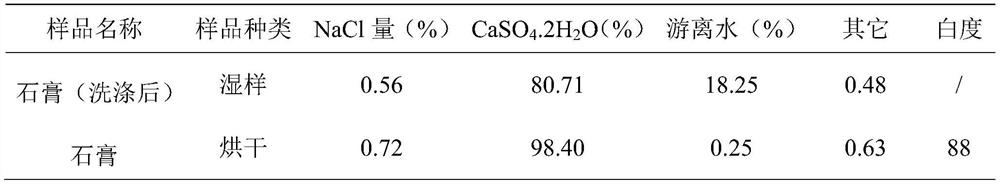
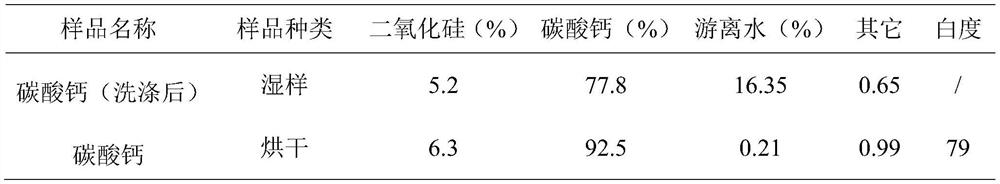
[0040] 2) Settling process: naturally settle the aeration-treated soda-making waste liquid to obtain supernatant and bottom thick slurry, and the supernatant flows out naturally by overflowing to obtain bottom thick slurry with a solid content of 35%. The thick slurry is wet-milled with a horizontal ball mill to obtain a grinding slurry. Zirconium silicate balls with a diameter of 6 mm are used as the grinding medium, and the material-to-ball ratio is 1:2.5. The D50 of the grinding slurry is 1 μm.
[0041] 3) pulping process: add 3% hydrogen peroxi...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment provides a method for comprehensive utilization of ammonia-soda alkali-making waste liquid uphole and downhole circulation, including the following steps:
[0048] 1) Aeration process: Introduce air into the ammonia-soda process alkali-making waste liquid at a temperature of 83°C to aerate and remove ammonia, collect ammonia gas with water to obtain an ammonia solution, and return the ammonia solution to the soda-making section for use;
[0049] 2) Settling process: naturally settle the aeration-treated soda-making waste liquid to obtain a supernatant and a bottom thick slurry, and the supernatant flows out naturally by overflowing to obtain a bottom thick slurry with a solid content of 30%. The thick slurry is wet-milled with a horizontal ball mill to obtain a grinding slurry. Zirconium silicate balls with a diameter of 8 mm are used as the grinding medium, and the material-to-ball ratio is 1:3. The D50 of the grinding slurry is 1.5 μm.
[0050] 3) pulp...
Embodiment 3
[0056] This embodiment provides a method for comprehensive utilization of ammonia-soda alkali-making waste liquid uphole and downhole circulation, including the following steps:
[0057] 1) Aeration process: Introduce air into the ammonia-soda process soda-making waste liquid at a temperature of 87°C to aerate and remove ammonia, collect ammonia gas with water to obtain an ammonia solution, and return the ammonia solution to the soda-making section for use;
[0058] 2) Grinding process: naturally settle the aerated soda-making waste liquid to obtain a supernatant and a bottom thick slurry, and the supernatant flows out naturally by overflowing to obtain a bottom thick slurry with a solid content of 40%. The thick slurry is wet-milled with a horizontal ball mill to obtain a grinding slurry. Zirconium silicate balls with a diameter of 8 mm are used as the milling medium. The material-to-ball ratio is 1:2.5, and the D50 of the grinding slurry is 1.2 μm.
[0059] 3) pulping proces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com