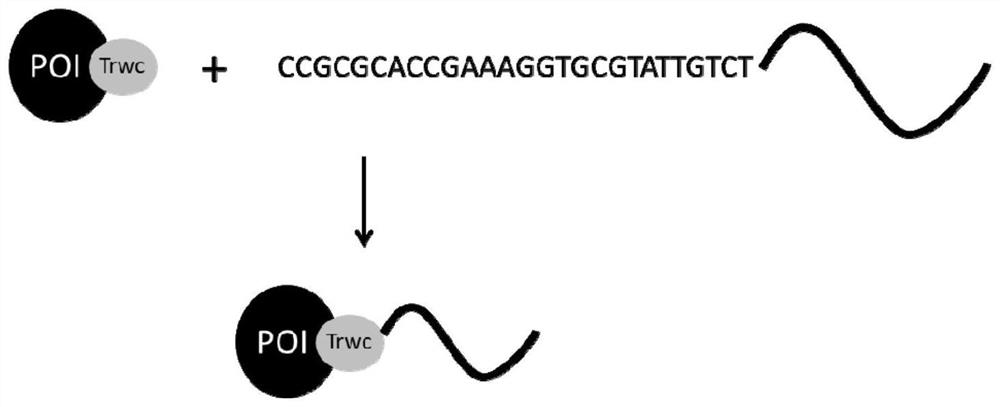
Method for covalently linking protein or peptide to nucleic acid
A technology of covalent connection and nucleic acid, applied in the field of covalent connection of protein and nucleic acid, which can solve the problems of vulnerable protein or nucleic acid, high randomness and cumbersome operation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Fusion and expression of embodiment 1SPG and Trwc enzyme
[0072] In this example, SPG, (Streptococcus Protein G) was used as the target protein, which was fused and expressed with Trwc enzyme.
[0073] (1) Cloning of fusion protein
[0074] The nucleotide sequences of SPG and Trwc enzyme are artificially synthesized, the nucleotide sequence of SPG is shown in SEQ ID NO:6, and the nucleotide sequence of Trwc enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
[0075] In this example, SPG and Trwc enzyme are connected through a flexible linker peptide GGGGS to form a fusion protein, referred to as SPG-Trwc for short, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the fusion protein SPG-Trwc is shown in SEQ ID NO:7.
[0076] (2) Expression and purification of fusion protein
[0077] The gene of the fusion protein SPG-Trwc was cloned into the expression vector PET32a (the protein can be well expressed in various expression vectors and expression hosts, only the expression in Escherichia coli is descri...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The preparation of the complex that embodiment 2SPG forms with nucleic acid
[0079] The fusion protein SPG-Trwc purified in Example 1 and the recognition nucleotide sequence A: ATTGACTTACGCGCACCGAAAGG TGCGTATTGTCT ATAGCCCAGTTTA (SEQ ID NO: 4) was mixed, and magnesium ions with a final concentration of 1 mM were added, and reacted at 37° C. for 30 minutes to obtain the protein-nucleic acid complex SPG-Trwc-nucleic acid.
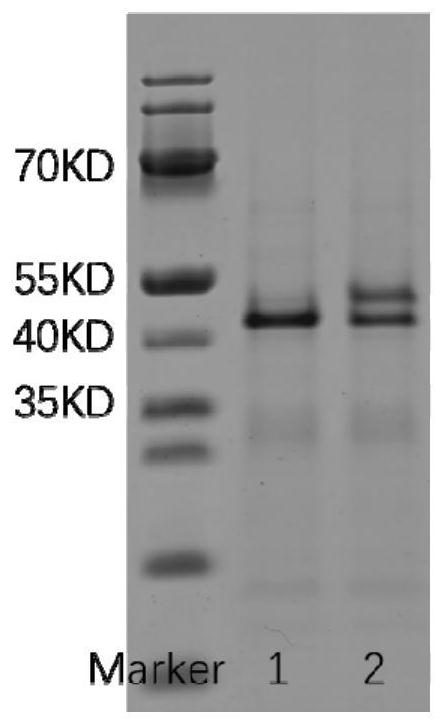
[0080] The resulting protein-nucleic acid complex SPG-Trwc-nucleic acid is confirmed by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and the results are as follows figure 2 shown. figure 2 The channels from left to right in the figure represent respectively: lane 1 is fusion protein control; lane 2 is SPG-Trwc-nucleic acid complex. From figure 2 It can be seen that there is an obvious hysteresis band in channel 2 compared with the control, indicating that the target protein and target nucleic acid in this example have been covalently linked to form a protein-nucleic ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Fusion and expression of embodiment 3ECFP and Trwc enzyme
[0082] In this example, the fluorescent protein ECFP was used as the target protein, which was fused and expressed with the Trwc protein.
[0083] (1) Cloning of fusion protein: the nucleotide sequence of artificially synthesized ECFP and Trwc protein, the nucleotide sequence of ECFP is shown in SEQ ID NO: 9, and the nucleotide sequence of Trwc enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 .
[0084] In this example, ECFP and Trwc enzyme are connected through a flexible linker peptide GGGGS to form a fusion protein, which is referred to as ECFP-Trwc, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the fusion protein ECFP-Trwc is shown in SEQ ID NO:10.
[0085] (2) Expression and purification of the fusion protein: the gene of the fusion protein ECFP-Trwc was cloned into the expression vector PET32a. The constructed expression vector was transformed into Escherichia coli expression strain BL21(DE3), and positive clones were selected. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com