Method for recognizing maize rough dwarf virus resistance by virus transmission inoculation of laodelphax striatellus
A technology for corn rough dwarf and BPH, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe measurement/inspection, grain cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of large identification groups, high cost of virus detection, and large site occupation, and achieve The result is highly effective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Evaluation of corn rough dwarf resistance:
[0045] Corn rough dwarf disease causes shortening of plant internodes, and severe cases lead to poor powder loosening of tassels and deformed ears. Corn rough dwarf disease can show typical symptoms at the earliest 3-leaf stage and slow growth. After the onset of 17-leaf stage at the latest, only the upper leaves Show wax tear-like protrusions, tassels become shorter.
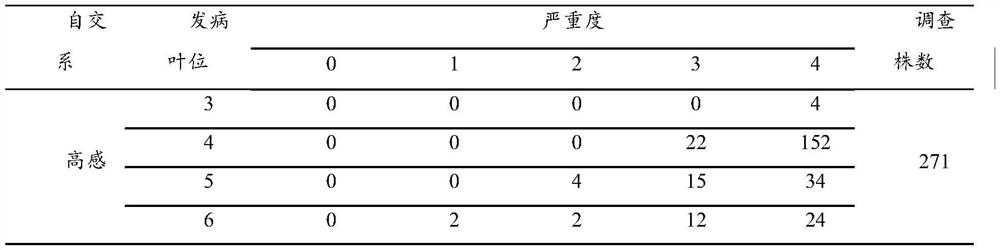
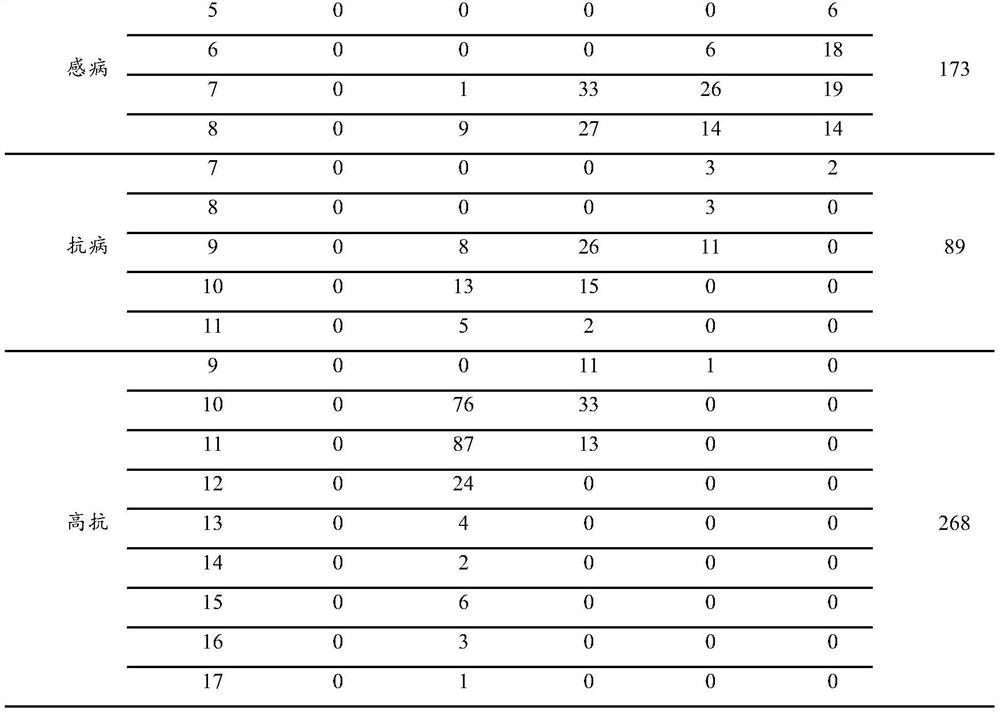
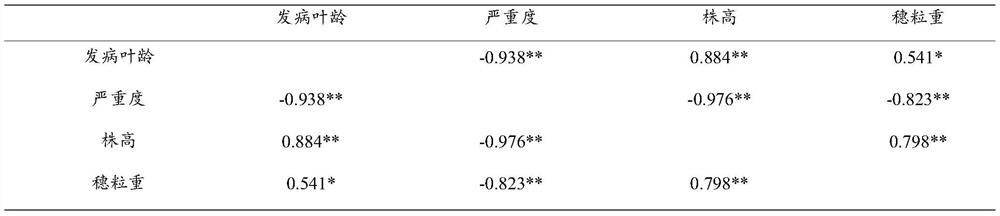
[0046]From 2015 to 2017, 3 highly susceptible inbred lines (5003, Ye 478, Ye 107), 2 susceptible inbred lines (Huangzao 4, Dan 360), 1 The resistance of the disease-resistant inbred line (Ji 35) and three high-resistant inbred lines (90110, Shen 137, DB544) (Table 1). The survey showed that the highly susceptible inbred lines had the disease at the 3-leaf stage, the most at the 4-leaf stage, all at the 6-leaf stage, and the most diseased plants were at the 4th stage, accounting for 78.97% of the total number of investigated plants; the susceptible inbred line...
Embodiment 2
[0055] experiment one:
[0056] 1. Feeding of SBPH:
[0057] On April 15, 2018, 10 wheat plants were sown in flower pots with a diameter of 10 cm. When the wheat grew to 4 cm, a glass tube with a diameter of 8 cm and a glass tube made of 60-mesh gauze was inserted into the flower pot to cover it. For wheat, healthy adults of SBPH collected in the field were inoculated on the wheat seedlings at a ratio of 1:1 male to female, and the upper opening of the glass yarn tube was covered with fine gauze and tied tightly with a rubber band, and the breeding was carried out at a room temperature of 20°C, and the wheat was regularly checked. Whether the stems, sheaths and leaves of SBPH have "spawning marks" of SBPH. After SBPH lay eggs, transfer SBPH to a pot of new wheat seedlings to continue to lay eggs and reproduce, and replace the wheat seedlings with glass yarn tubes Cover and continue the cultivation of wheat seedlings until the nymphs of SBPH hatch, and each pot can obtain 2000...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com