Method for degrading glyphosate pesticide by using lactobacillus alkaline phosphatase
A phosphatase and glyphosate technology, applied in the field of pesticide degradation, can solve problems such as pollution, endangering human health, increasing the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease and infertility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
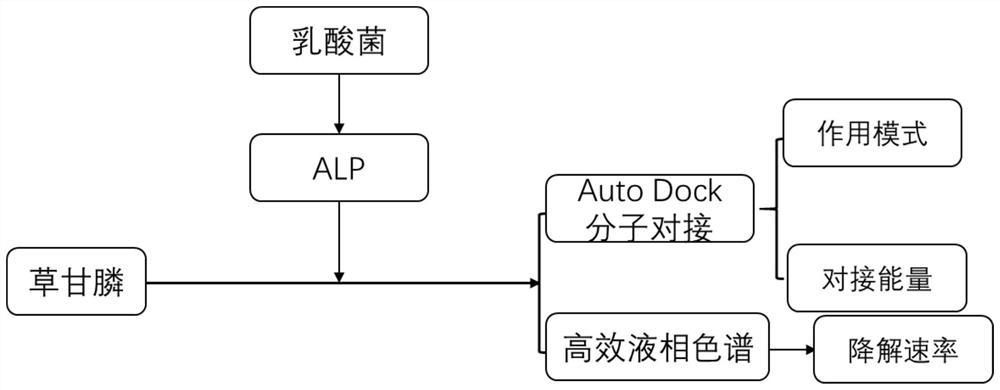
[0020] (1) culturing lactic acid bacteria and adopting ultrasonic pulverization method to obtain alkaline phosphatase;
[0021] (2) Detect the residue of glyphosate pesticide by high performance liquid chromatography;
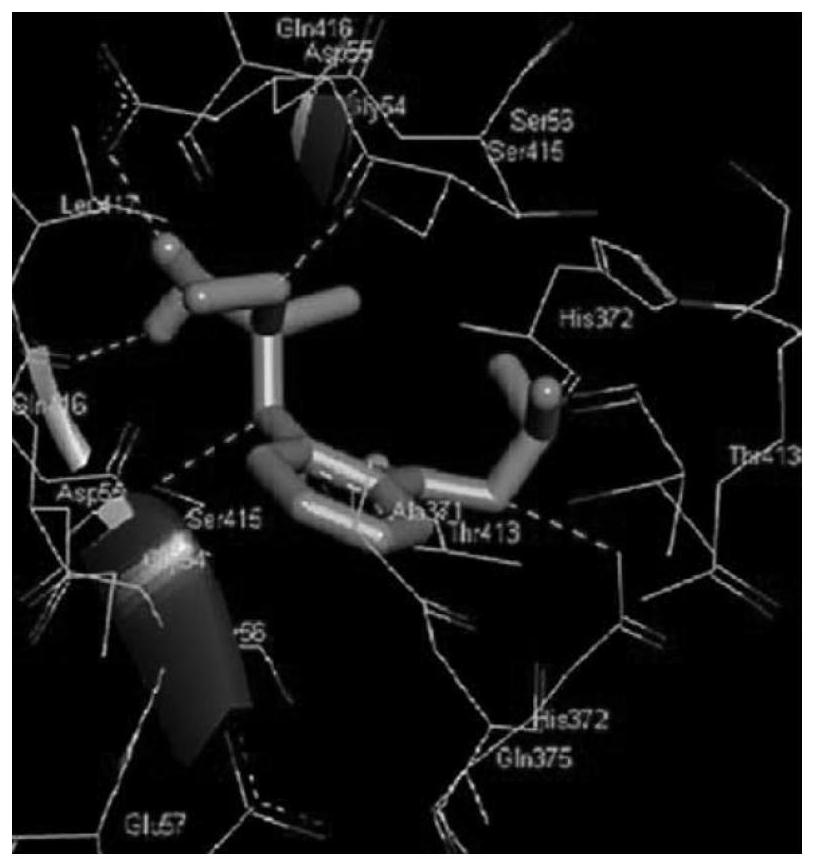
[0022] (3) Discover the mode of action of glyphosate and ALP by molecular docking Auto Dock technology, and visualize the information such as the action site and binding force;
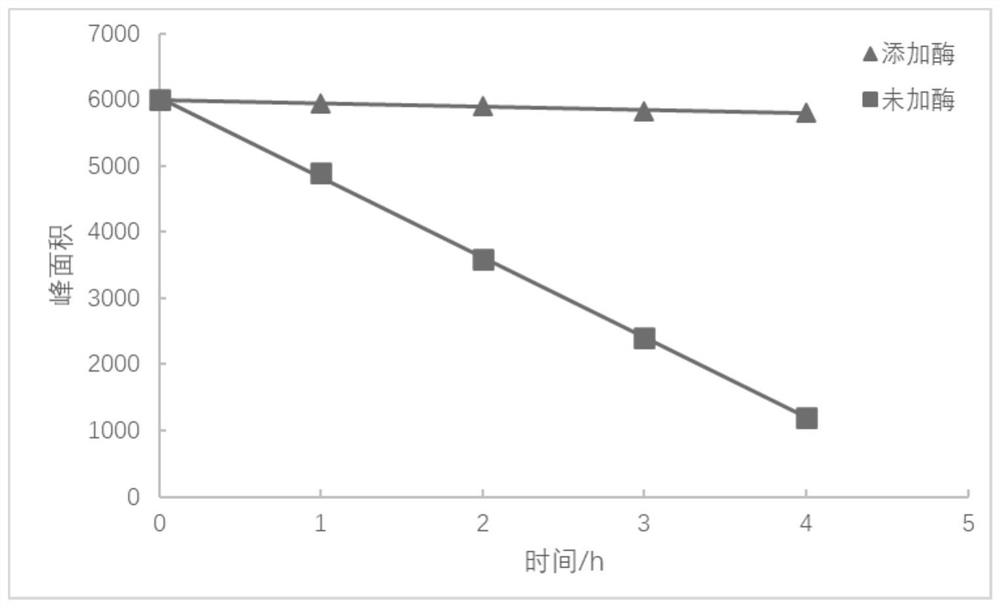
[0023] (4) ALP was used to degrade glyphosate pesticides at a concentration of 0.5 mg / L, respectively, and the degradation rate was analyzed in combination with the liquid phase peak area after 4 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0025] (1) culturing lactic acid bacteria and adopting ultrasonic pulverization method to obtain alkaline phosphatase;
[0026] (2) Detect the residue of glyphosate pesticide by high performance liquid chromatography;
[0027] (3) Discover the mode of action of glyphosate and ALP by molecular docking Auto Dock technology, and visualize the information such as the action site and binding force;
[0028] (4) Glyphosate pesticides with a concentration of 1 mg / L were degraded by ALP respectively, and the degradation rate was analyzed in combination with the peak area of the liquid phase after 4 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0030] (1) culturing lactic acid bacteria and adopting ultrasonic pulverization method to obtain alkaline phosphatase;
[0031] (2) Detect the residue of glyphosate pesticide by high performance liquid chromatography;
[0032] (3) Discover the mode of action of glyphosate and ALP by molecular docking Auto Dock technology, and visualize the information such as the action site and binding force;
[0033] (4) Glyphosate pesticides with a concentration of 2 mg / L were degraded by ALP respectively, and the degradation rate was analyzed in combination with the liquid phase peak area after 4 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com