High-throughput screening method based on biosensor and application of high-throughput screening method in multi-gene metabolic pathway optimization
A screening method and sensor technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve problems such as the lack of high-throughput screening methods for glycolic acid production strains, and achieve the effects of avoiding fluorescence quenching, avoiding difficult identification, and expanding screening throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Design and Construction of Glycolic Acid Sensor
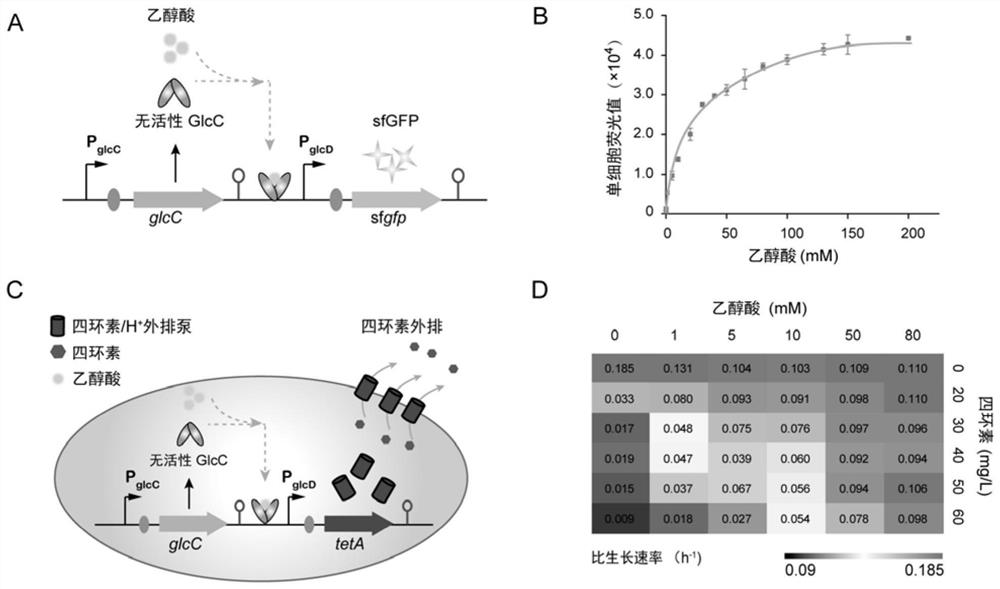
[0048] Such as figure 1 As shown in A, pGBS-P ffS - sfGFP sensor includes promoter P glcD , sfGFP protein, promoter P ffS , glcC gene; The promoter P glcD To initiate expression of sfGFP, P glcD There is a cis-response element enhancing factor UAS on it; the P glcD contains the binding site of GlcC-glycolate allosteric protein; the downstream of glcC is the kanamycin resistance gene and the thermosensitive replicon Ori101; the P glcD Located downstream of the replicon Ori101, the glcC upstream sets the promoter P ffS . (the content is the patent of CN110684792A with publication number).
[0049] Biosensor pGBS-P ffS -tetA builds like figure 1 C, pGBS-P ffS -tetA sensor will pGBS-P ffS - The reporter gene sfGFP protein in sfGFP was replaced by the tetracycline resistance gene tetA, and the other structures were unchanged. in pGBS-P ffS Amplified linearized vector P with primers GBS-F / GBS-R on the b...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Response of glycolic acid sensor to glycolic acid
[0053] In order to detect the response performance of the glycolic acid sensor, the expression of the reporter gene was induced by exogenous addition of different concentrations of glycolic acid.
[0054] After pGBS-PffS-sfgfp was introduced into the host strain MG1655ΔglcC, a single colony was picked and inoculated into a kanamycin-resistant liquid LB medium, and cultivated overnight at 30°C at 250 rpm to prepare a seed solution. The seed solution was divided into initial OD 600 =0.05 of the inoculum was inoculated into the M9 medium, which contained a glucose concentration of 4g / L. After culturing for 7-8h, wait for OD 600 The expression of green fluorescent protein was induced by adding different concentrations of glycolic acid to about 0.6. Continue to culture under the same conditions for 6 hours, take a sample of 50 μL and dilute it 3 times with PBS buffer solution, then measure the fluorescence valu...
Embodiment 3
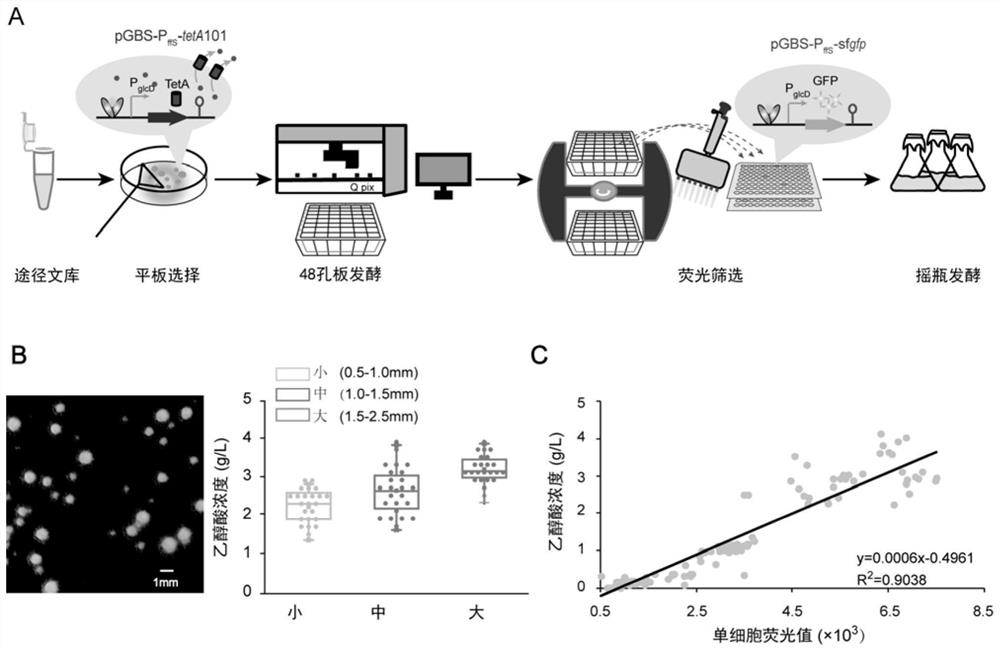
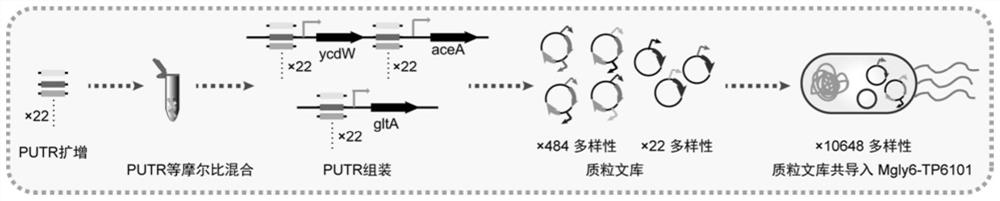
[0056] Construction of embodiment 3 pathway library
[0057] In glycolic acid production, there are three key pathway genes, ycdW, aceA and gltA, which are controlled by inducible promoters ptrc and T7 promoters. Replace the Trc and T7 promoters with a series of promoters with gradient strengths to fine-tune metabolic pathways and avoid the use of IPTG. 22 PUTRs with gradient strength (promoter and 5'UTR complex) were amplified and randomly connected to the upstream of the three pathway genes respectively, and the constructed plasmid library was co-transformed into the glycolic acid engineering strain Mgly6(pGBS -P ffS -tetA), the strain was named Mgly6-TP6101, generating a final library with a theoretical diversity of 10648. The specific construction steps are as follows image 3 Shown:
[0058]Using the plasmid pJUN-YA containing the gene ycdW as a template, the linearized vector ptrc-ycdWaceA was amplified with primers PycdW-F / PycdW-R, and the plasmid pJUN-5 containing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com