Anti-corrosive alloy steel for heating radiator, and preparation method thereof
A technology of alloy steel and radiator, applied in the field of anti-corrosion alloy steel for heating radiators and its preparation, can solve the problems of insufficient anti-corrosion and heat conduction modification, to ensure anti-corrosion and thermal conductivity, reduce grain boundary segregation, and improve thermal conductivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
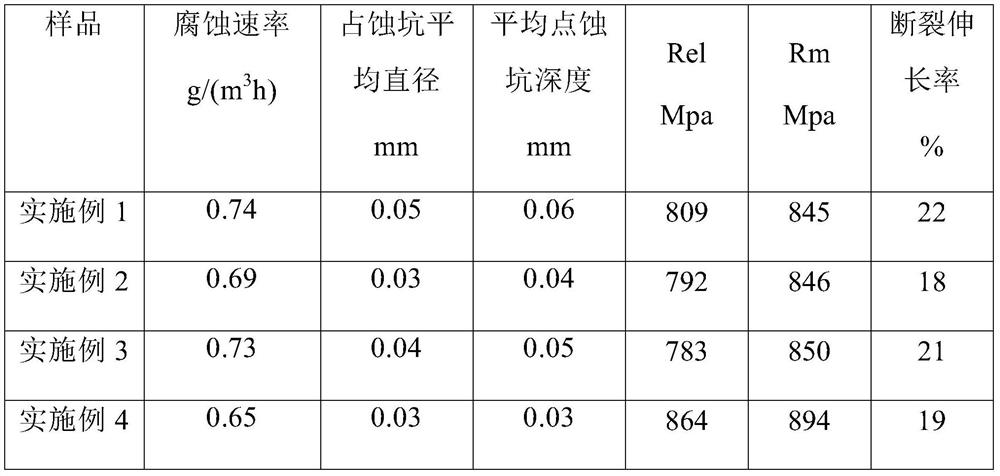
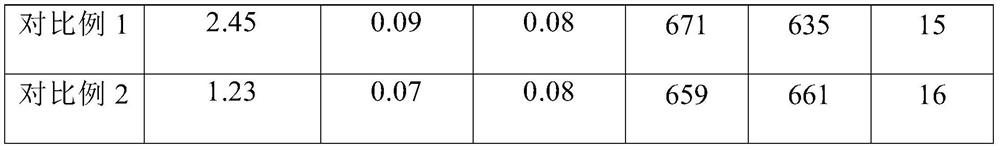
Embodiment 1
[0033] A preparation method of anti-corrosion alloy steel for heating radiators: comprising the following steps:
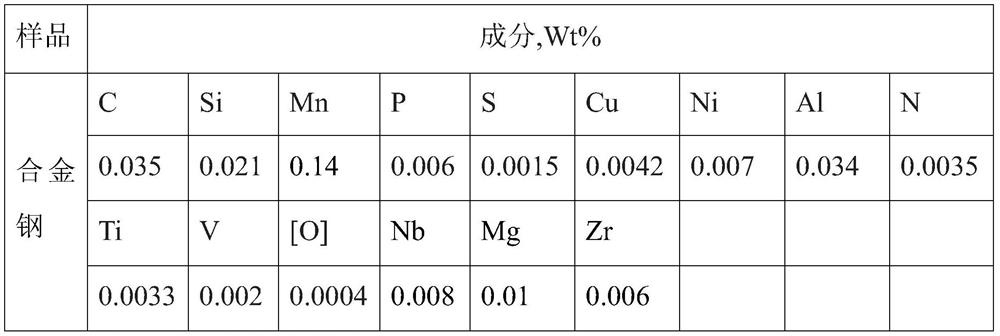
[0034]Feeding: Provide molten steel raw materials with optimized composition. When feeding Fe-graphene cored wire into the molten steel tank in a near-vacuum environment, control graphene to account for 35% of the final C mass in the alloy steel, and at the same time control the Fe-graphene cored wire in the molten steel The free oxygen content is lower than 5ppm, keep argon blowing and stirring, when blowing argon, blow argon gas into the molten steel through the argon hole at the bottom of the tank and stir, control the flow of argon blowing to make the surface of the molten steel weakly roll, the diameter of the exposed surface of the molten steel is 30mm, and the stirring time 3~10min;
[0035] Pouring: pouring on the upper machine after the stirring is completed, the superheat of the molten steel in the tundish needs to be controlled at 10°C for continuous ca...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A preparation method of anti-corrosion alloy steel for heating radiators: comprising the following steps:
[0040] Feeding: Provide molten steel raw materials with optimized composition. When feeding Fe-graphene cored wire into the molten steel tank in a near-vacuum environment, control the graphene to account for 45% of the final C mass in the alloy steel, and control the free carbon in the molten steel. When the oxygen content is lower than 5ppm, keep argon blowing and stirring. When blowing argon, blow argon into the molten steel through the argon hole at the bottom of the tank and stir. Control the flow of argon blowing to make the surface of the molten steel weakly roll. ~10min;
[0041] Pouring: pouring on the upper machine after the stirring is completed, the superheat of the molten steel in the tundish needs to be controlled at 10°C for continuous casting, and the cast slab is obtained through continuous casting;
[0042] Rolling: casting the slab produced by c...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A preparation method of anti-corrosion alloy steel for heating radiators: comprising the following steps:
[0046] Feeding: Provide molten steel raw materials with optimized composition. When feeding Fe-graphene cored wire into the molten steel tank in a near-vacuum environment, control the graphene to account for 40% of the final C mass in the alloy steel, and control the free carbon in the molten steel. When the oxygen content is lower than 5ppm, keep argon blowing and stirring. When blowing argon, blow argon into the molten steel through the argon hole at the bottom of the tank and stir. Control the flow of argon blowing to make the surface of the molten steel weakly roll. The diameter of the exposed surface of the molten steel is 20mm, and the stirring time is 3 ~10min;
[0047] Pouring: pouring on the upper machine after the stirring is completed, the superheat of the molten steel in the tundish needs to be controlled at 15°C for continuous casting, and the cast sl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com