Polypeptides and methods for improving skin conditions
A technology for skin and pathological conditions, applied in the field of peptides and methods for improving skin pathological conditions, which can solve problems such as reducing the quality of life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
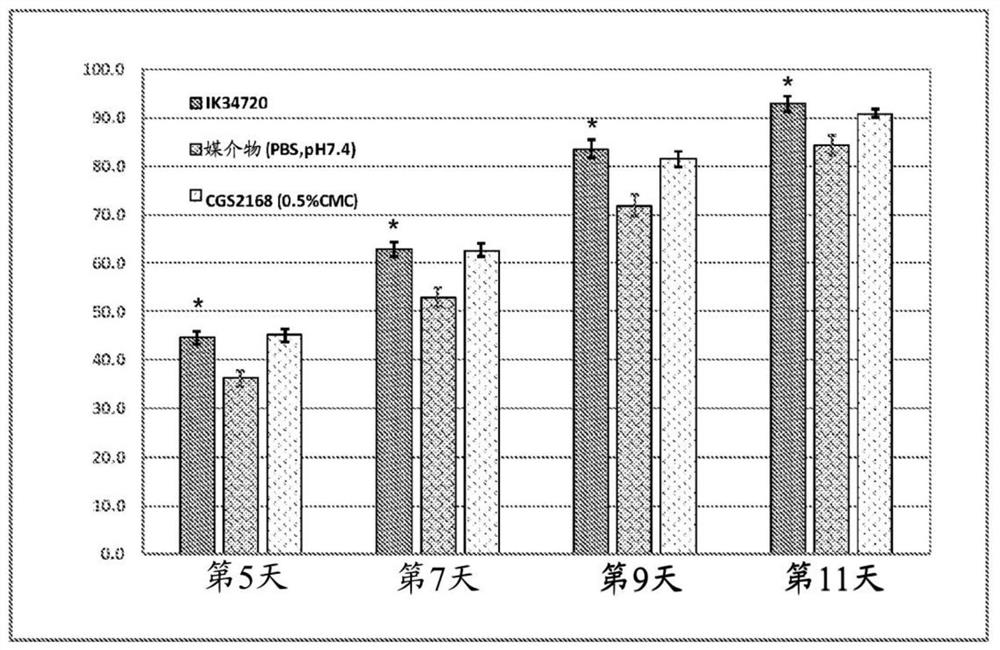
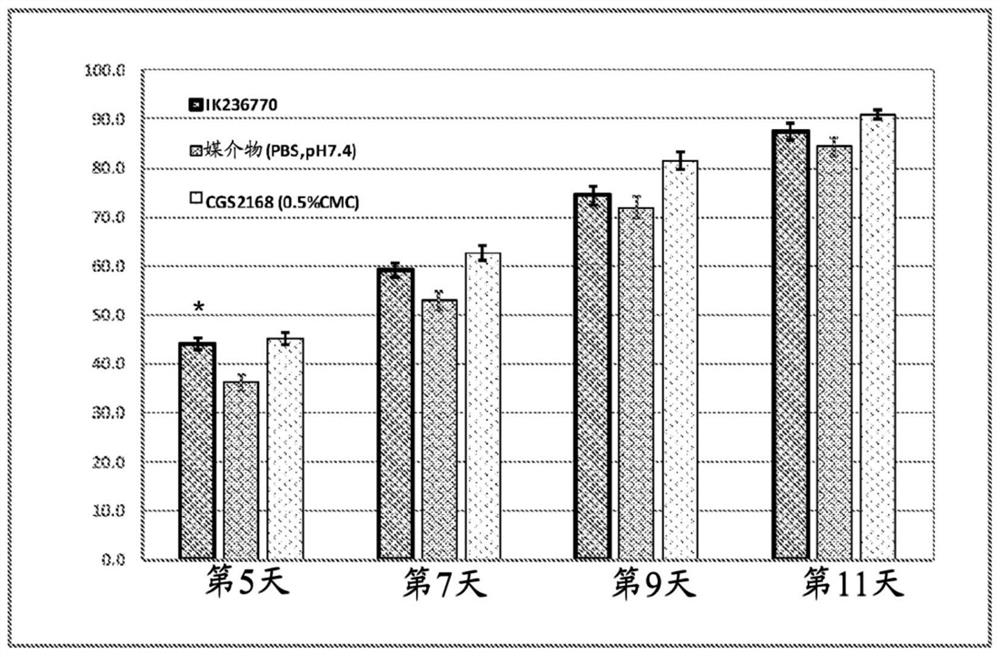
[0197] Example 1: Polypeptides RSKAKNPLYRRRRRRRR and rrrrrrrrylpnkaksr promote wound healing.
[0198] figure 1 and figure 2 The polypeptide IK34720 (SEQ ID NO:3-RSKAKNPLYRRRRRRRR) ( figure 1 ) and dextro-reversal sequence IK236770 (SEQ ID NO:4–rrrrrrrrrylpnkaksr) ( figure 2 ) on wound healing over 10 days in a murine wound model according to the following protocol.
[0199] In this study, three groups of 8 male ICR mice with an average weight of 22 g (± 2 g) were used. Animals were housed in individual cages during the study. Under isoflurane gas anesthesia, the shoulders and back of each animal were shaved and induced on day 1 by removing the skin, including panniculus carnosus and adhesions, using a sharp punch (12 mm inner diameter). Wound.
[0200] After wound induction, polypeptides IK34720 and IK236770 were topically applied to the wound site at a dose of 10 μg per animal. Additionally, the positive control group was administered 10 μg per animal of an α2A agon...
Embodiment 2
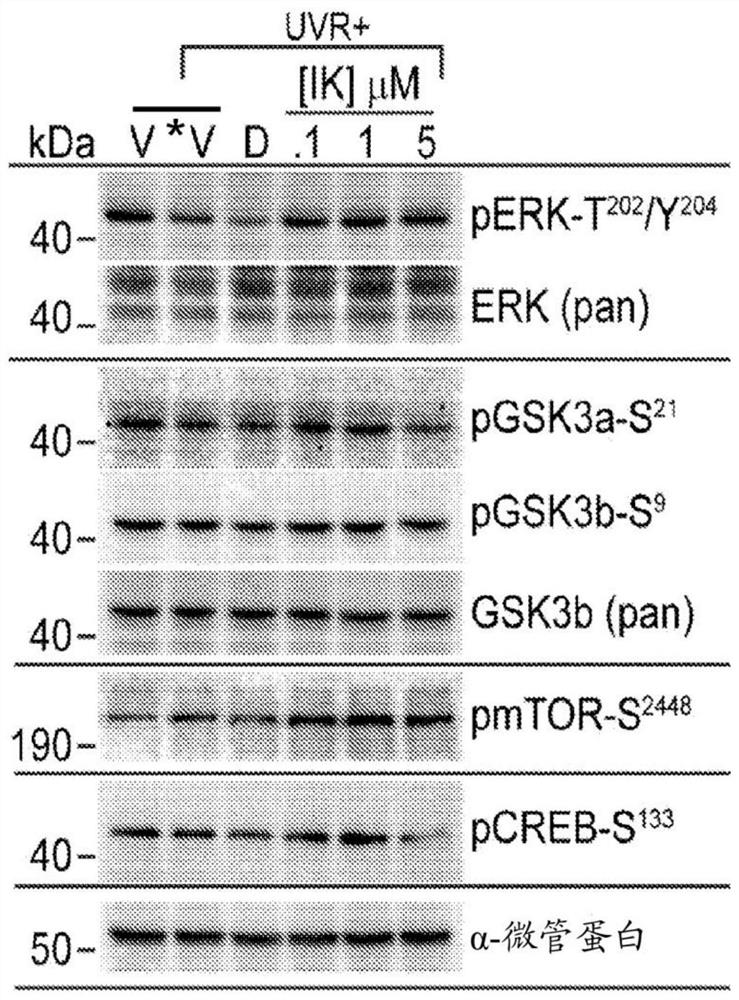
[0206] Example 2: The polypeptide RSKAKNPLYRRRRRRRR inhibits pCREB formation in primary keratinocytes and restores UV-induced inhibition of the TGFβ receptor (TGFβRII) when applied after exposure of keratinocytes to sun-mimicking UV radiation.
[0207] CREB is phosphorylated at serine at position 133 (Ser-133) in response to exposure of cells to UV irradiation. Increased phosphorylation of CREB is associated with a range of functions including cell proliferation, cell cycle, metabolism, DNA repair, differentiation, inflammation, angiogenesis, immune response and cell survival. Thus, aberrant CREB phosphorylation is associated with tumor development, malignancy and survival (Steven. A and Seliger B., Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):35454–35465).
[0208] The effect of polypeptide IK34720 (SEQ ID NO:3) on CREB phosphorylation was assessed using the following protocol.
[0209] Keratinocytes were harvested and cultured as previously described (Gupta et al., J Invest Dermatol, 2007,...
Embodiment 3
[0220] Example 3: The polypeptide RSKAKNPLYRRRRRRRR increases ATP levels in primary keratinocytes exposed to solar simulated UV irradiation.
[0221] Figure 4 The effect of polypeptide IK34720 (SEQ ID NO:3) on ATP levels in primary keratinocytes exposed to solar simulated UV irradiation is illustrated. Inadequately repaired DNA damage after UV exposure has been shown to be a causative factor in the development of skin cancer. DNA repair requires energy, but after UV exposure, skin cells have a limited ability to produce ATP, the main source of energy.
[0222] The following protocol was used to assess the effect of polypeptide IK34720 (SEQ ID NO:3) on intracellular ATP after UV exposure.
[0223] Primary keratinocytes were harvested as described above in Example 2 and were treated in the presence or absence of calcitriol (positive control) or polypeptide IK34720 (SEQ ID NO:3; RSKAKNPLYRRRRRRRR) at concentrations described in Example 2 They were exposed to ssUV irradiation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com