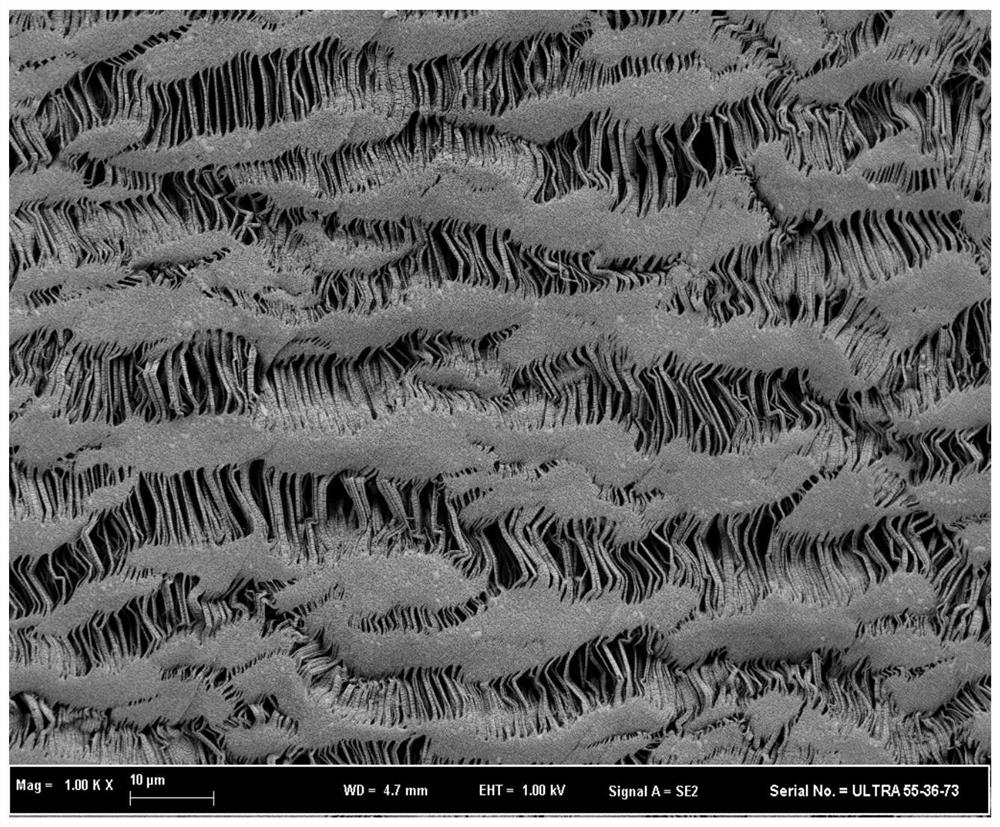
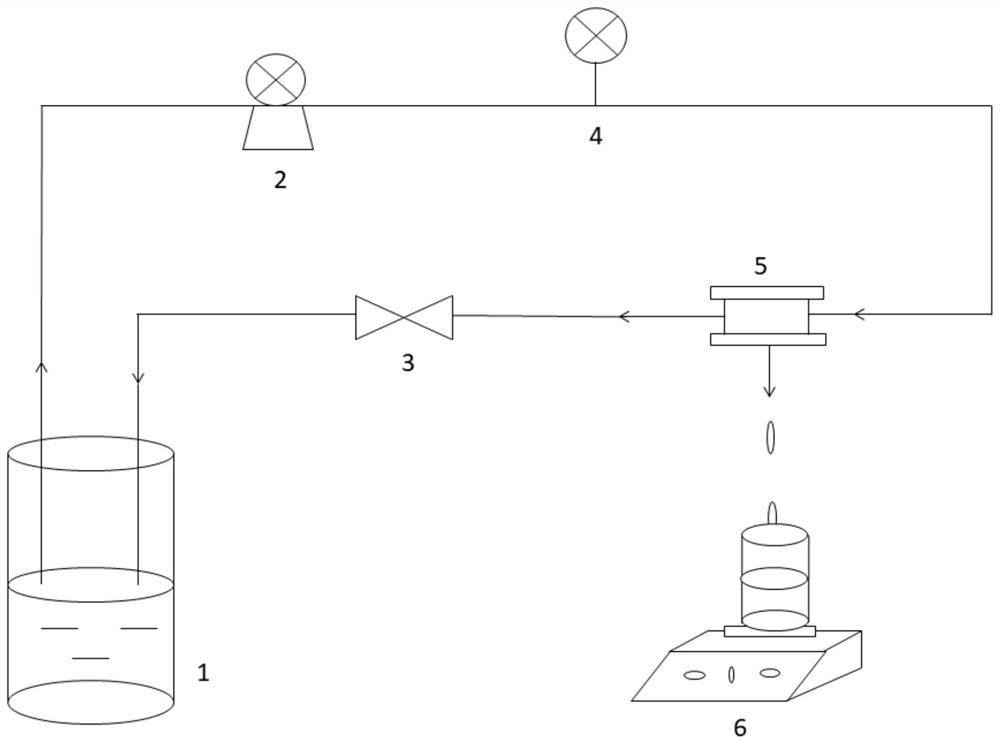
Preparation method of chlorine-resistant composite nanofiltration membrane
A composite nanofiltration membrane and chlorine-resistant technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membranes, membrane technology, etc., can solve problems such as depletion, lack of chlorine resistance evaluation methods, and membrane performance decline, and achieve the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Activation: immerse the polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane in 50% ethanol aqueous solution for 1 min. After draining, the active base film was obtained.
[0029] (2) Water phase immersion: immerse the active base film described in step (1) in an aqueous solution of 0.1% mass concentration of amine monomers, stay for 5 minutes, take it out and dry it in the air to obtain the first intermediate film;
[0030] (3) Oil phase impregnation: immerse the first intermediate film described in step (2) in the organic solvent solution of acid chloride monomers with a mass concentration of 0.1%, stay for 5 minutes, and then place it in the air to dry to obtain the second intermediate film. Two intermediate membranes;
[0031] (4) Post-treatment: rinse the second interlayer with deionized water, then place it in a drying oven at 70° C., stay for 60 minutes, and take it out to obtain the third interlayer.
[0032] (5) Cross-linking agent impregnation: immerse the third...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Activation: immerse the polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane in 50% ethanol aqueous solution for 5 minutes. After draining, the active base film was obtained.
[0038] (2) Water phase immersion: immerse the active base film described in step (1) in an aqueous solution of amine monomers with a mass concentration of 1.5%, stay for 1 min, take it out and place it in the air to dry to obtain the first intermediate film;
[0039] (3) Immersion in oil phase: immerse the first intermediate film described in step (2) in the organic solvent solution of acid chloride monomers with a mass concentration of 3.0%, stay for 60s, and then place it in the air to dry to obtain the second intermediate film. Two intermediate membranes;
[0040] (4) Post-treatment: rinse the second interlayer with deionized water, then place it in a drying oven at 70° C., stay for 10 minutes, and take it out to obtain the third interlayer.
[0041] (5) Cross-linking agent impregnation: immerse...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Activation: immerse the polytetrafluoroethylene microporous membrane in 50% ethanol aqueous solution for 3 minutes. After draining, the active base film was obtained.
[0047] (2) Water phase immersion: immerse the active base film described in step (1) in an aqueous solution of amine monomers with a mass concentration of 1.0%, stay for 3 minutes, take it out and place it in the air to dry to obtain the first intermediate film;
[0048] (3) Oil phase impregnation: immerse the first intermediate film described in step (2) in an organic solvent solution of acyl chloride monomers with a mass concentration of 2.0%, stay for 3 minutes, and then place it in the air to dry to obtain the second intermediate film. Two intermediate membranes;
[0049] (4) Post-treatment: rinse the second interlayer with deionized water, then place it in a drying oven at 70° C., stay for 50 minutes, and take it out to obtain the third interlayer.
[0050] (5) Crosslinking agent impregnation:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com