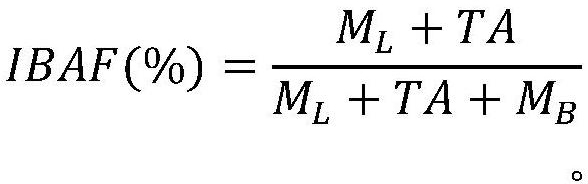Method for evaluating particulate chemicals released in consumer goods by simulating lung tissue liquid in-vitro substitution technology
A technology for consumer goods and particulate matter, applied in the field of exposure simulation, can solve problems such as overestimation of biological accessibility, difficulty in separation, and impact on the accuracy of results, to avoid overestimation of biological accessibility, low experimental cost, and convenient sample collection Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for assessing particulate chemicals released from consumer products using an extrafluid replacement technique simulating lung tissue, comprising the following steps:
[0047] Preparation:
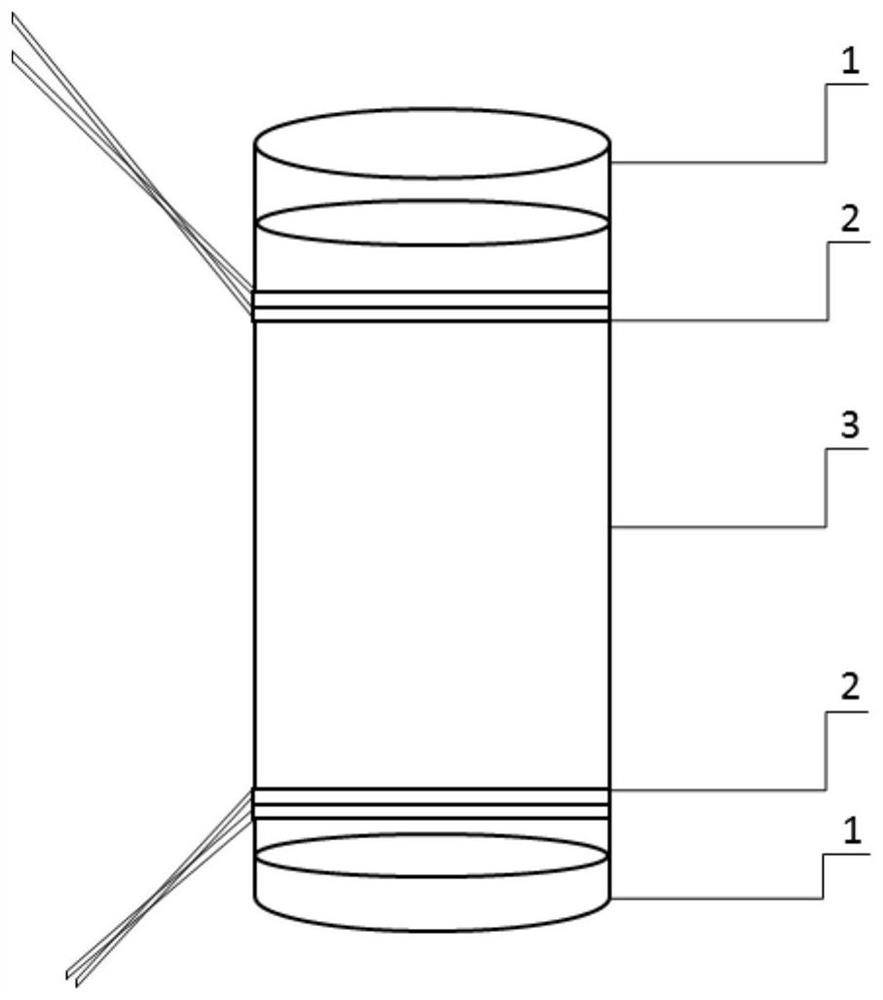
[0048] 1) Preparation of silica gel column: the chromatographic column is filled with glass fiber or empty SPE column and sieve plate, 1 g of acid silica gel (44% concentrated sulfuric acid), and 3 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate from bottom to top. The filled silica gel column was pre-cleaned with 6 mL of a mixture of n-hexane and dichloromethane (1:1 volume ratio of n-hexane and dichloromethane was 1:1).
[0049] The preparation method of acidic silica gel is as follows: dry and activate 100g of silica gel in an oven at 450°C for 6 hours, then take it out and put it in a drying oven to cool to room temperature; add 43mL of concentrated sulfuric acid to the silica gel drop by drop, and stir with a glass rod at the same time to prevent the silica gel from forming. block; afte...
Embodiment 2
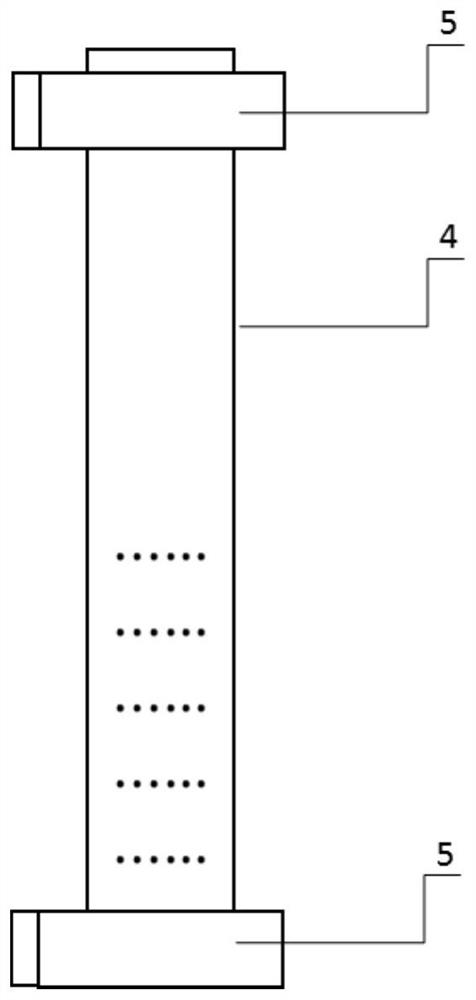
[0075] A method of simulating the lung tissue liquid replacement technology to evaluate the release of particulate chemicals in consumer products. In this example, it is verified that the removal of the dialysis bag leads to the increase of the bioavailability of particulate matter into the Tenax structure, which is the same as that of Example 1. The difference is that instead of using a dialysis bag, the schoolbag particles and the Tenax device are directly placed in the simulated lung fluid, and the other steps are the same as those in Example 1.
[0076] In this example, the bioavailability fraction of SCCPs in schoolbag particulate matter was 15.85-35.65%. Among them, the bioavailability fraction of SCCPs in ALF solution was 15.85-26.48%; the bioavailability fraction of SCCPs in MGS solution was 17.36-35.65%. Compared to Example 1, SCCPs had an increased fraction of bioaccessibility due to the incorporation of particulate matter into the Tenax structure. Due to the need t...
Embodiment 3
[0078] A method for evaluating particulate chemicals released in consumer products by simulating lung tissue liquid replacement technology. In this example, the difference from Example 1 is that the particulate material is changed to an eraser, and the target pollutant is PAEs. Carry out solid-phase extraction with C18 glass column, the process internal standard is changed to D 4 -PAEs, other steps are similar to the method and steps of Example 1.
[0079] Three kinds of PAEs were detected in the lung fluid samples, namely DBP, DIBP, and DEHP, among which the bioaccessible fraction of DBP was 8.20-86.07%, the bioaccessible fraction of DIBP was 15.35-85.91%, and the bioaccessible fraction of DEHP 0.023-0.64%
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com