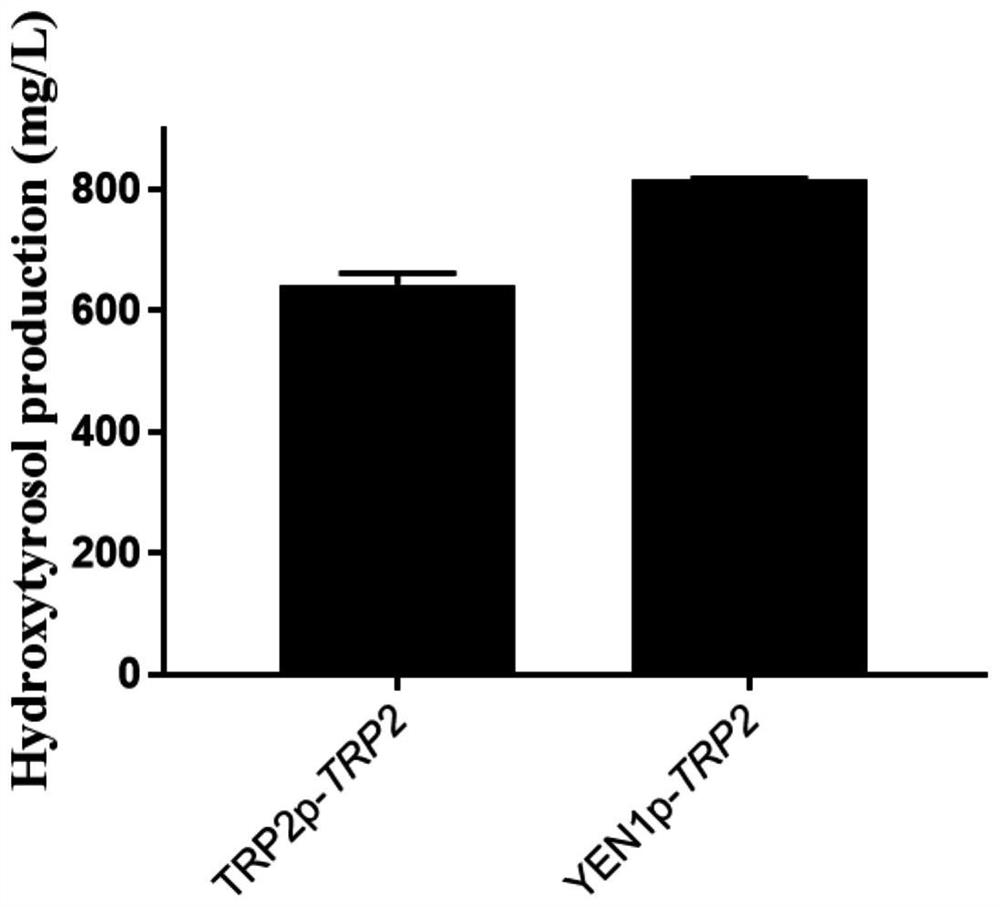
Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of hydroxytyrosol and construction method thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and hydroxytyrosol, which is applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its construction with high production of hydroxytyrosol, can solve the problems of low efficiency and achieve the effect of increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: the construction of the chassis bacterial strain of producing tyrosol
[0045] 1) Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C genome as a template, using PCR to amplify the ARO2, ARO10, TKL1, RKI1 gene fragments and ARO4, ARO7, ARO3 fragments; using the Escherichia coli BL21 genome as a template, using PCR to amplify the TyrA fragment;
[0046] 2) Obtain ARO4 by point mutation method K229L , ARO7 G141S , ARO3 D154N mutant;
[0047] 3) Expressing the above-mentioned genes using a constitutive promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and constructing PRS406 and PRS404 integration plasmids;
[0048] 4) using CRISPR-Cas9 method to knock out PDC1 and PHA2 genes in the above Saccharomyces cerevisiae;
[0049] PDC1-spacer: ATTGGATCTGACTCCTCACG;
[0050] PDC1 homology arm:
[0051] ACAGCAGCAAAATGACGATAGTTCCATAAATATGTATCCCGTGTATGCGTATTTGCCATCCATATCTAAAATTGGCACAATTGAACAACCCTGATAGAAAGGAATCATTTCTGTTGGAAA;
[0052] PHA2-spacer: GGGGGATAGAGGCTGCTGGG;
[0053] PHA...
Embodiment 2
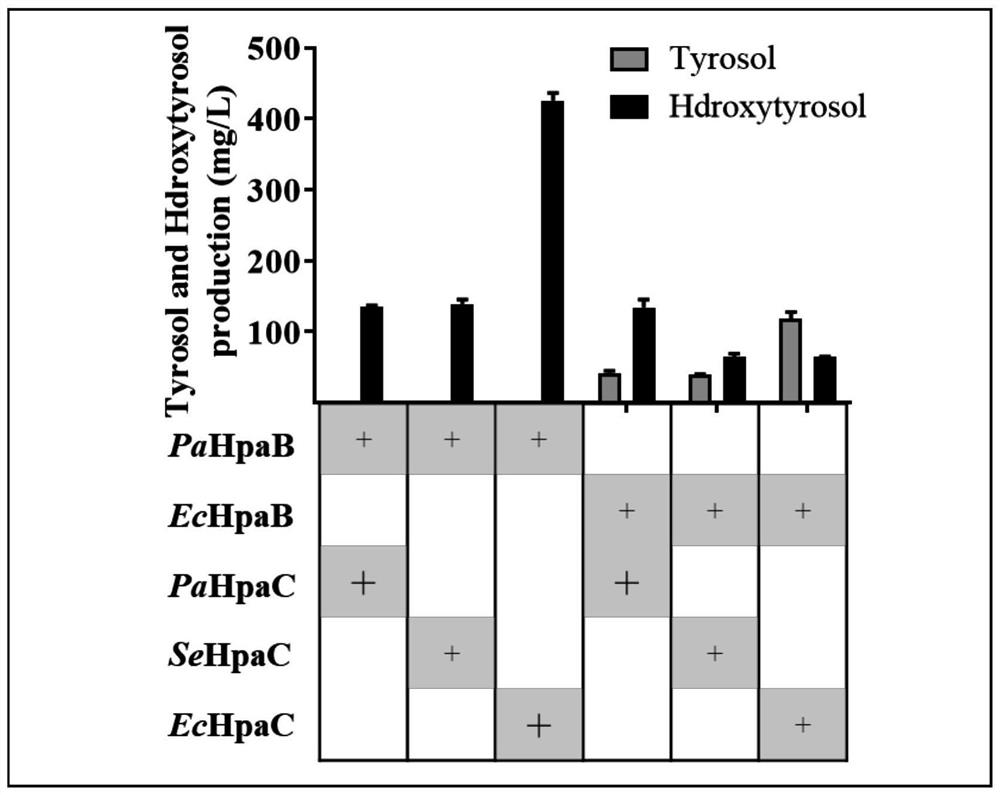
[0057] Example 2: Construction of HpaB and HpaC combination
[0058] 1) Synthesize the coding genes of HpaB and HpaC from different sources by the reagent company, and use this as a template to design upstream and downstream primers (add the sequences of the PDC1p promoter homology arm and the GPM1t terminator homology arm at both ends of the amplification primer, and add TEF1p promoter homology arm and PGK1t terminator homology arm sequence) for PCR amplification. The PCR amplification conditions are as follows:
[0059] Pre-denaturation at 95°C for 10 minutes, followed by 25 cycles at 98°C for 30s, 58°C for 30s, and 72°C for 1min and 30s; finally, extension at 72°C for 5 minutes.
[0060] The above PCR products were recovered by gel, and HpaB-encoding gene fragments from different sources with PDC1p promoter homology arms and GPM1t terminator homology arms were obtained, as well as HpaC encoding with TEF1p promoter homology arms and PGK1t terminator homology arms. Gene fra...
Embodiment 3
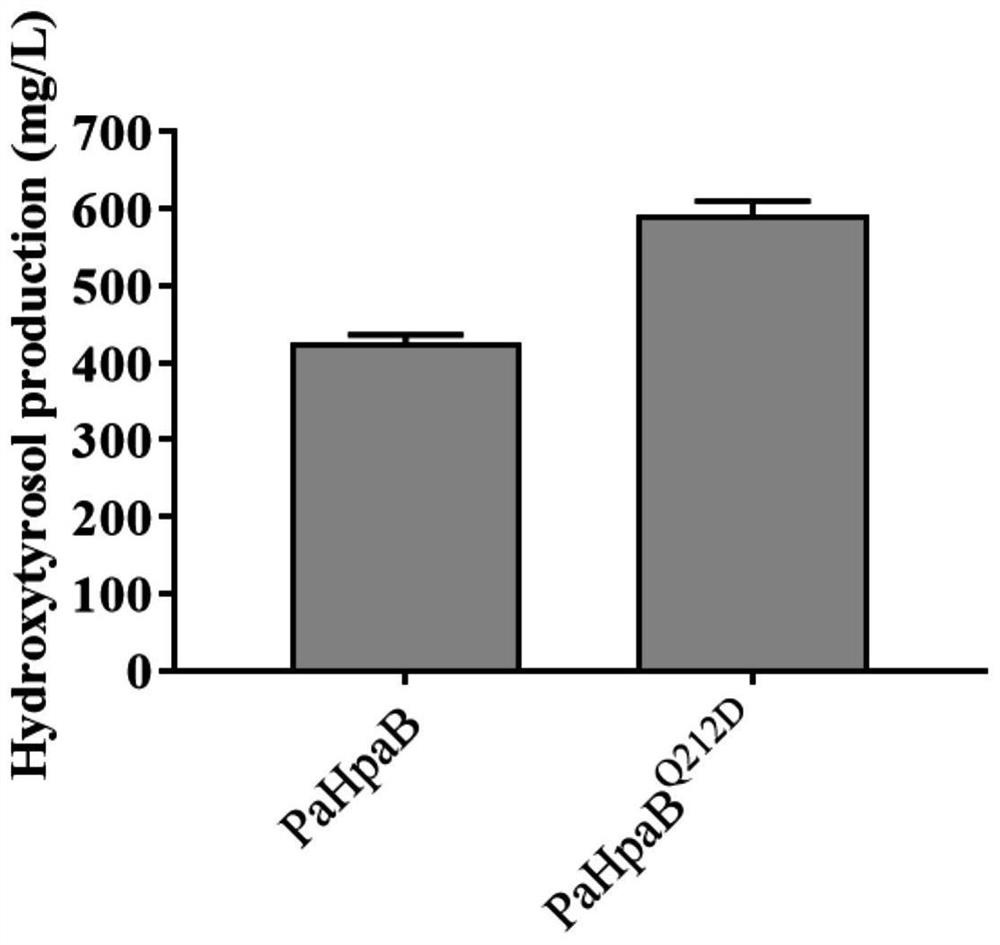
[0064] Example 3: Constructing and expressing PaHpaB Q212D mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0065] 1) Utilize CRISPR-Cas9 to mutate PaHpaB into PaHpaB for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain constructed in Example 2 Q212D . The spacer is designed as 5'-TCAAGGTTCTGCTCAATTGT-3', and the homology arm sequence is:
[0066] TTGTTTCTGGTGCTAAGGTTGTTGCTACTAACTCTGCTTTGACTCACTACAACTTCGTTGGTCAAGGTTCTGCTGACCTACTTGGTGACAACACTGACTTCGCTTTGATGTTCATCGCTCCAATGAACACTCCAGGTAT;
[0067] 2) Transfer the Cas9 plasmid and homology arm with the corresponding spacer into a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain expressing the PaHpaB-HpaC combination, and after colony PCR and genome PCR amplify the PaHpaB sequence, sequence verification that PaHpaB was successfully mutated into PaHpaB Q212D .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com