Non-toxin-producing aspergillus flavus SX0104 and application thereof
A technology of SX0104, Aspergillus flavus, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of mycotoxins pollution and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1. Separation and purification
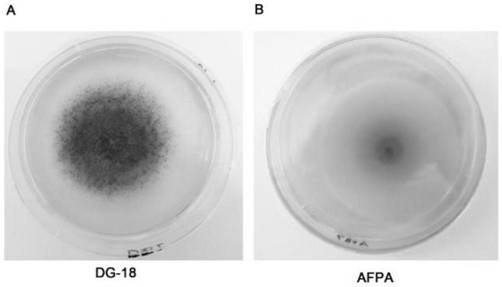
[0041] DG-18 medium (article number: HB0296, Qingdao Hi-Tech Industrial Park Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was selected as the medium for the isolation of Aspergillus flavus. The soil samples collected from the peanut planting field in Nanchai Village, Xiangfen, Shanxi were treated by removing plant residues and large particle stones, soil grinding, and mixing.
[0042] Weigh 10.0g of the ground soil sample and add it into 90mL of sterilized water, put it into a shaker and shake for 2h to make 100mL of sample suspension. Take 50 μl of the suspension, add it to the DG-18 medium plate, and spread it evenly with a coating rod. Then put the coated plate into a constant temperature incubator and culture it at 28±1° C., 90% relative humidity and dark conditions.
[0043] After 5 days, the colonies with yellow-green spores were picked and transferred to a new DG-18 medium plate for secondary streaking and purification until a single colony w...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1. Strain toxin-producing culture
[0066] The Aspergillus flavus strain SX0104 to be tested was inoculated on DG-18 solid medium for activation. After culturing at 28±1° C. for 5 days in the dark, the aspergillus flavus conidia on the plate were washed with sterilized 0.1% Tween 80 to obtain a conidia suspension.
[0067] Determine the conidia suspension concentration using a hemocytometer.
[0068] Take a certain amount of conidia suspension and inject it into the Erlenmeyer flask filled with sterilized 30ml liquid Sabouraud medium, so that the final concentration is 4×10 5 pieces / ml. Place the Erlenmeyer flask on a shaker at 28±1°C, 200rpm in the dark.
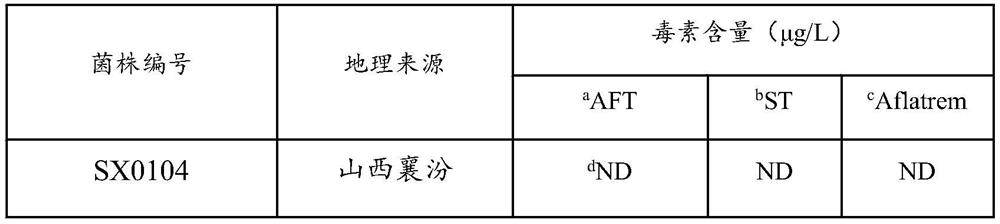
[0069] 2. Determination of strain toxin content
[0070] After 5 days, use sterilized gauze to filter the mycelial culture solution, discard the mycelium ball, collect the toxin-producing culture solution and store it in a centrifuge tube, let it stand for 1 hour, pipette 500μl of the toxin-producing culture soluti...
Embodiment 3
[0078] 1. Preparation of conidia suspension
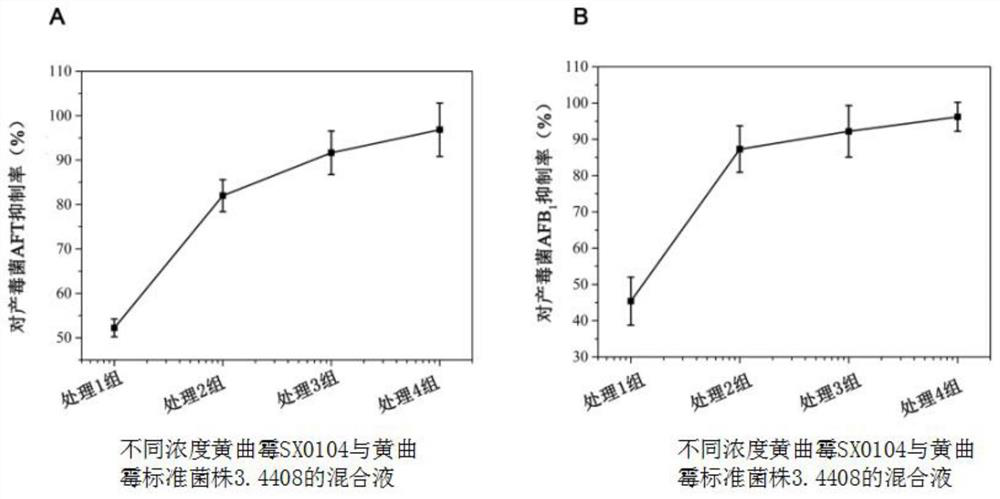
[0079] The non-toxigenic Aspergillus flavus strain SX0104 to be tested and the toxigenic Aspergillus flavus standard strain 3.4408 and the toxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolated from different regions are numbered (SCPA-32-12 (Peng'an, Sichuan) , XZCY-24-6 (Zayu, Tibet), LNFX-25-1 (Fuxin, Liaoning), HBHA-129-1 (Hong’an, Hubei), HBYL-12-7 (Yangluo, Hubei), HBTS-94-2 ( Hebei Tangshan), JXZS-118-9 (Jiangxi camphor tree) and JXZS-69-3 (Jiangxi camphor tree) were respectively inoculated in DG-18 solid medium for activation. After culturing for 5 days at 28±1°C in the dark, use sterilized The conidia of Aspergillus flavus on the plate were washed with 0.1% Tween 80 and placed in a 10 ml centrifuge tube to obtain conidia suspension.
[0080] Determine the concentration of the conidia suspension with a hemocytometer under a microscope, and dilute the concentration of conidia to 1×10 with sterile water. 6 pcs / ml for use.
[0081] 2. Compe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com