Method for improving bacterial blight resistance of rice
A technology for resisting bacterial blight and rice, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as unclear molecular mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 OsRLK1 gene editing and vector transformation of wild-type rice Z H11
[0033] 1. Experimental method
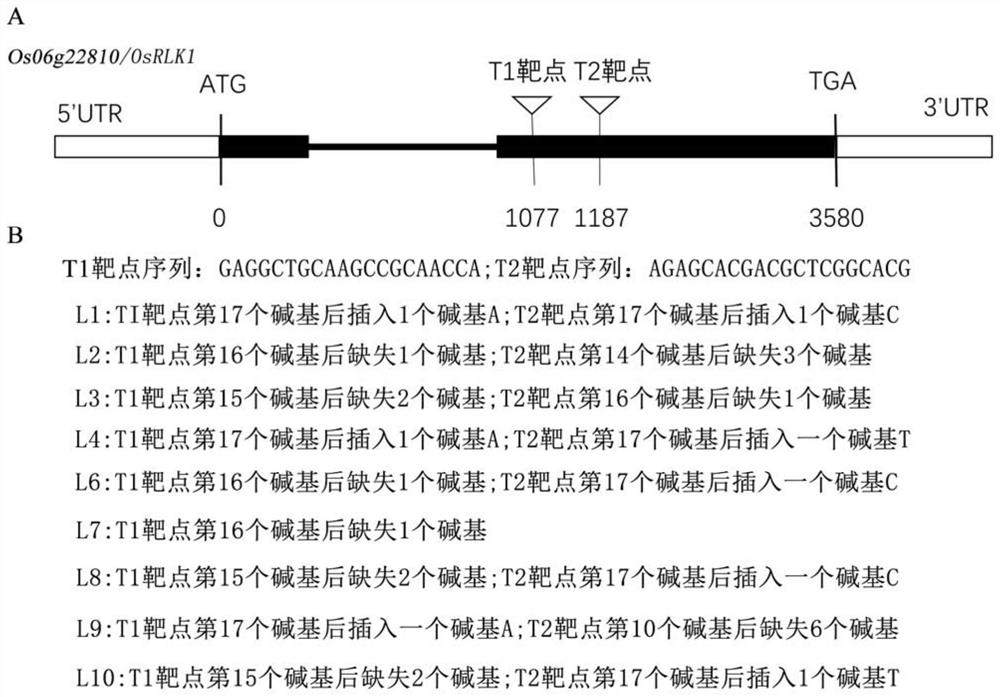
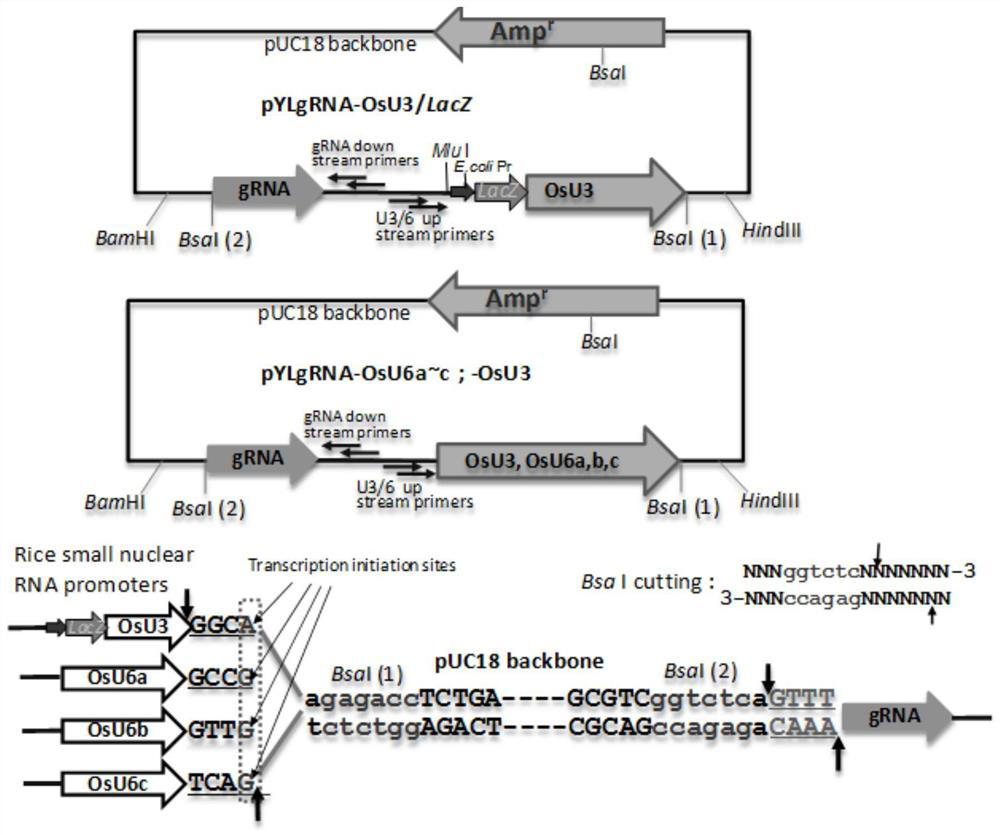
[0034] According to the Nipponbare reference sequence design gene editing target sequence 1: GAGGCTGCAAGCCGCAACCA (SEQ ID NO: 3), and target sequence 2: AGAGCACGACGCTCGGCACG (SEQ ID NO: 4); its position is as follows figure 1 As shown in A. First, find the genome sequence of OsRLK1 on the NCBI website (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), then select the above two targets in the genome sequence of OsRLK1, and connect the DNA sequences of the two targets together into the DNA sequence initiated by U6a. sub-promoted Cas9 vector ( figure 2 ) to obtain a dual-target targeting vector.
[0035] Then, the above-mentioned targeting vector was introduced into wild-type rice ZH11 plants through genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium EHA105, the transgenic plants were screened by hygromycin, and the transgenic plants were sequenced and identified using primers OsRLK1-F...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Detection of ROS and cell death
[0041] 1. Experimental method
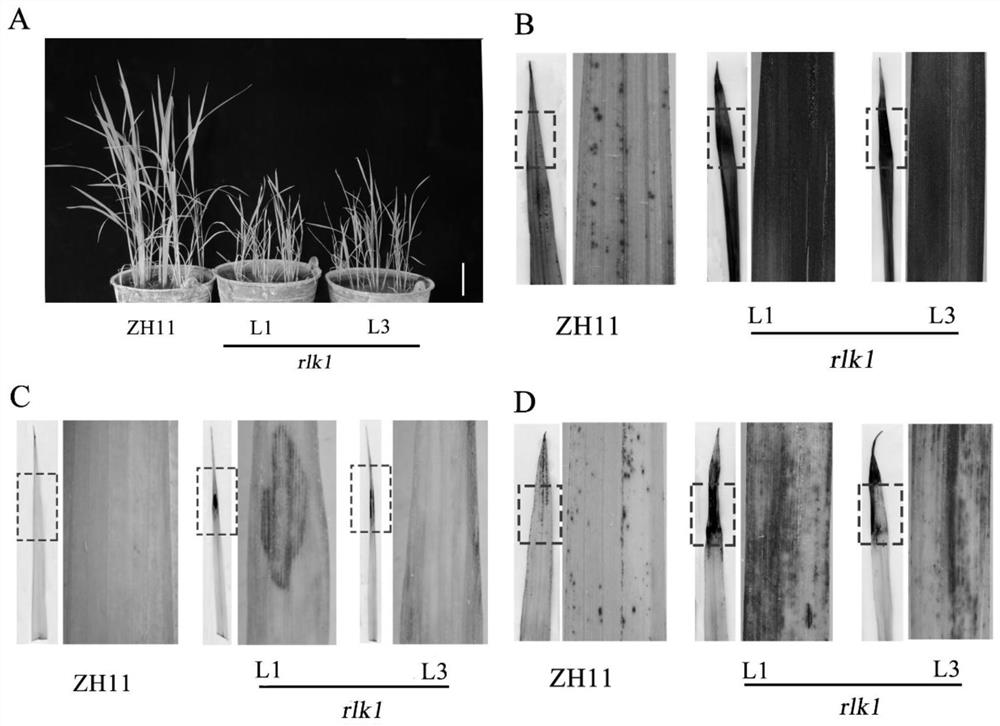
[0042] (1) DAB staining: two leaves were taken from the eight-week-old mutant Osrlk1 (L1 and L3) and wild-type ZH11 plants, and quickly inserted into the DAB (pH=3.8) solution with a concentration of 1 mg / mL, and vacuumed for 30 After 5 minutes in the dark at room temperature, the floating color was removed in 95% ethanol after staining. Each genotype used 6 leaves for measurement.
[0043] (2) NBT staining: Take two leaves from mutant Osrlk1 (L1 and L3) and wild-type ZH11 plants of eight weeks seedling age, insert them into 0.1% NBT solution quickly, vacuumize for 30 minutes, and then place them in a dark place at room temperature Let it stand for 3 hours, remove the floating color in 95% ethanol after staining, and use 6 leaves for each genotype for measurement.
[0044] (3) Trypan blue staining: take the inverted two leaves from the eight-week-old mutant Osrlk1 (L1 and L3) and wild-type ZH1...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3 Bacterial blight inoculation experiment
[0048] 1. Experimental method
[0049] Leaf-cut method was used for inoculation, and two strains Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae guangdong 4( image 3 A) and Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae guangdong 5( image 3 B), the cells were cultured in a 28°C incubator for 2 days to become bright yellow, then diluted with PBS solution, and the concentration was diluted to about 9×10 by turbidimetric method. 9 bacteria / mL. (The strains are from the Institute of Plant Protection, Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences), and the mutant Osrlk1 (L1 and L3) and wild-type ZH11 plants were inoculated at the rice booting stage. When inoculating, use scissors to dip in the bacterial solution, cut off the about 2 cm long part of the leaves, and measure the length of the lesion 21 days after inoculation.
[0050] 2. Experimental results
[0051] Such as Figure 4 As shown, Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae guangdong 4( Figure 4 A) The l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com