Method for carbon sequestration by using organic ore bed subjected to in-situ pyrolysis
An in-situ pyrolysis and organic mineral technology, which is applied in the fields of earth drilling, mining fluids, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve problems such as excessive carbon dioxide emissions, achieve efficient energy recovery, and reduce carbon dioxide content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
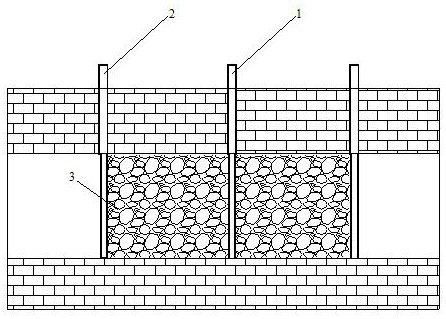
[0028] When the thickness of the oil shale deposit is 5m, the buried depth is 300m. A method for carbon sequestration using in-situ pyrolyzed organic mineral layers, the specific steps of which are as follows:
[0029] (1) After the in-situ pyrolysis of the organic mineral layer is completed, normal temperature water is injected into the middle well 1, and the remaining peripheral wells 2 are drained. 2, the discharge and production port monitors the temperature change of the water vapor.
[0030] (2) During the heat exchange process of water at normal temperature, a large amount of stagnant water will be formed inside the ore seam, which can fully dissolve calcium and magnesium ions. When the water vapor temperature monitored after drainage reaches 150°C, the peripheral well 2 will be closed, and the middle well 1 will be closed. Inject 0.5MPa of carbon dioxide and monitor the pressure change at the bottom of the peripheral well 2; when the pressure at the bottom of the peri...
Embodiment 2
[0036] When the thickness of the oil shale deposit is 10m, the buried depth is 600m. A method for carbon sequestration using in-situ pyrolyzed organic mineral layers, the specific steps of which are as follows:
[0037] (1) After the in-situ pyrolysis of the organic mineral layer is completed, normal-temperature water is injected into the peripheral well 2, and the middle well 1 is drained. After the normal-temperature water passes through the high-temperature mineral layer, the temperature rises rapidly to form water vapor, which is monitored at the drainage outlet The temperature change of water vapor.
[0038] (2) During the heat exchange process of water at normal temperature, a large amount of stagnant water will be formed inside the ore seam, which can fully dissolve calcium and magnesium ions. When the water vapor temperature monitored after drainage reaches 150°C, the peripheral well 2 will be closed, and the middle well 1 will be closed. Inject 1.0 MPa of carbon diox...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com