Method for preparing hard carbon material from biomass waste physalis pubescens leaves, and sodium ion battery
A sodium-ion battery and waste mushroom technology, which is applied in non-aqueous electrolyte storage batteries, electrolyte storage battery manufacturing, secondary batteries, etc. The effect of saving resources and realizing commercialization prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A preparation method of a hard carbon material derived from biomass waste mushroom leaves, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) The leaves of Guniang fruit were washed several times with deionized water and then dried in an air-blast drying oven at 80 °C for 12 h;
[0028] (2) Soak the material in step (1) in a 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for 24 h;
[0029] (3) The material in step (2) is washed repeatedly with deionized water until neutral;
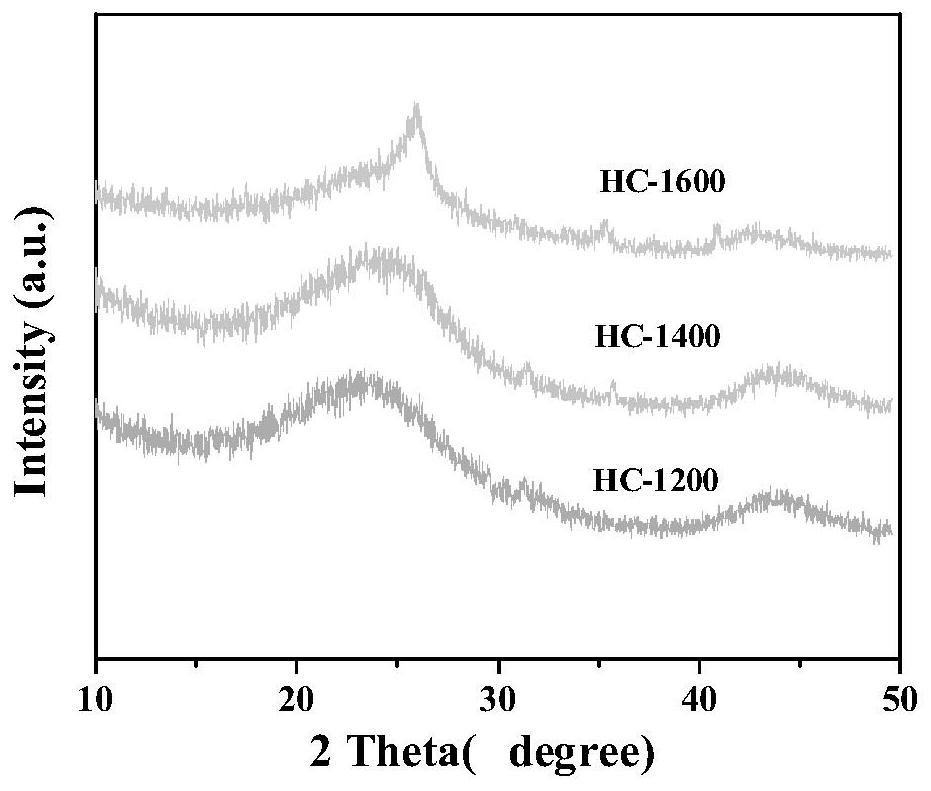
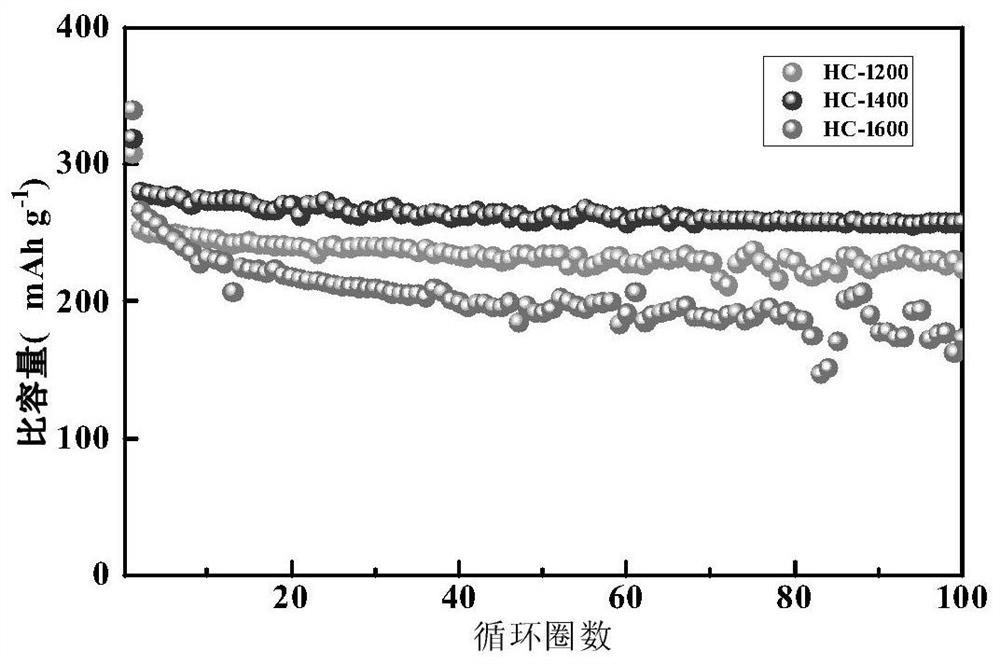
[0030] (4) Under an argon atmosphere, raise the material in step (3) to 1400 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C / min in a tube furnace, keep it warm for 2 hours, and then lower it to room temperature; take it out and grind it into powder, Obtain the sodium ion battery hard carbon negative electrode material, marked as HC-1400.
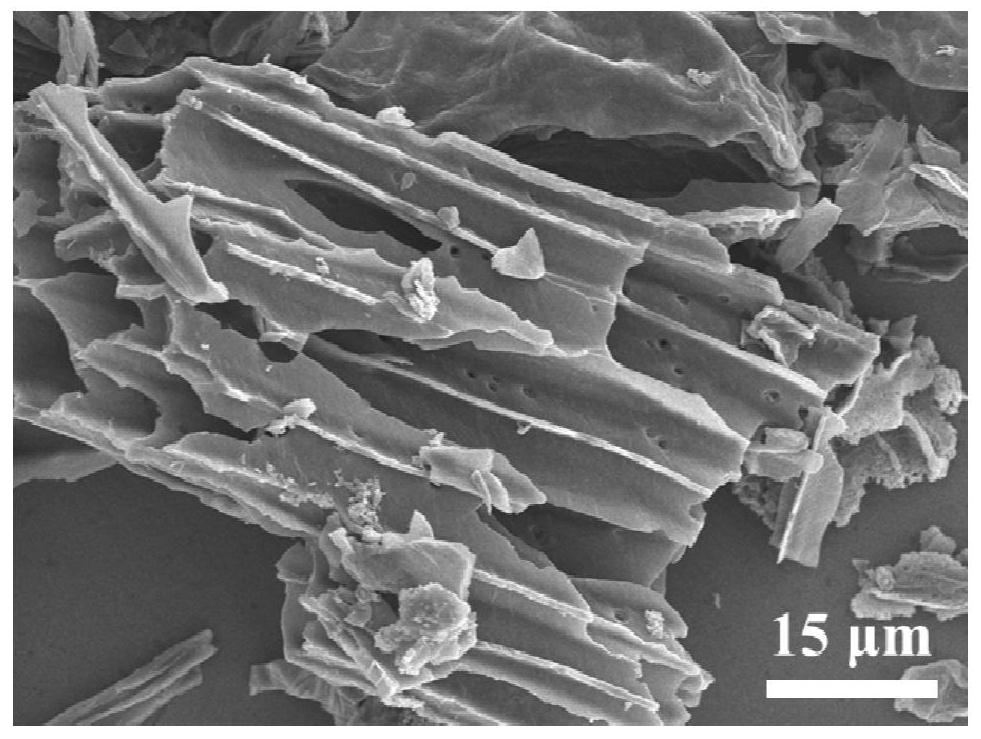
[0031] See attached figure 1 , is the SEM image of the biomass hard carbon material prepared in this example. It can be seen that the material shows the morphology of porous channels, which is c...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A preparation method of a hard carbon material derived from biomass waste mushroom leaves, comprising the following steps:
[0035] (1) The leaves of Guniang fruit were washed several times with deionized water and then dried in an air-blast drying oven at 80 °C for 12 h;
[0036] (2) Soak the material in step (1) in a 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for 24 h;
[0037] (3) The material in step (2) is washed repeatedly with deionized water until neutral;
[0038] (4) Under an argon atmosphere, raise the material in step (3) to 1200 °C in a tube furnace at a rate of 5 °C / min, keep it warm for 2 h, and then lower it to room temperature; take it out and grind it into powder , to obtain a hard carbon negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries, marked as HC-1200.
Embodiment 3
[0040] A preparation method of a hard carbon material derived from biomass waste mushroom leaves, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) The leaves of Guniang fruit were washed several times with deionized water and then dried in an air-blast drying oven at 80 °C for 12 h;
[0042] (2) Soak the material in step (1) in a 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for 24 h;
[0043] (3) The material in step (2) was washed with deionized water several times until neutral, and then dried in a blast drying oven at 80 °C for 12 h;
[0044] (4) Under an argon atmosphere, raise the material in step (3) to 1600 °C in a tube furnace at a rate of 5 °C / min, keep it warm for 2 h, and then lower it to room temperature; take it out and grind it into powder , to obtain a hard carbon negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries, marked as HC-1600.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reversible specific capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com