Cadmium-free quantum dots and preparation method thereof
A technology of quantum dots and indium quantum dots is applied in the field of cadmium-free quantum dots and their preparation, which can solve the problems of dimensional uniformity, influence on luminous efficiency and stability, and unfavorable large-scale preparation of indium phosphide quantum dots. Defects, improved thermal stability, simple and safe experimental process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
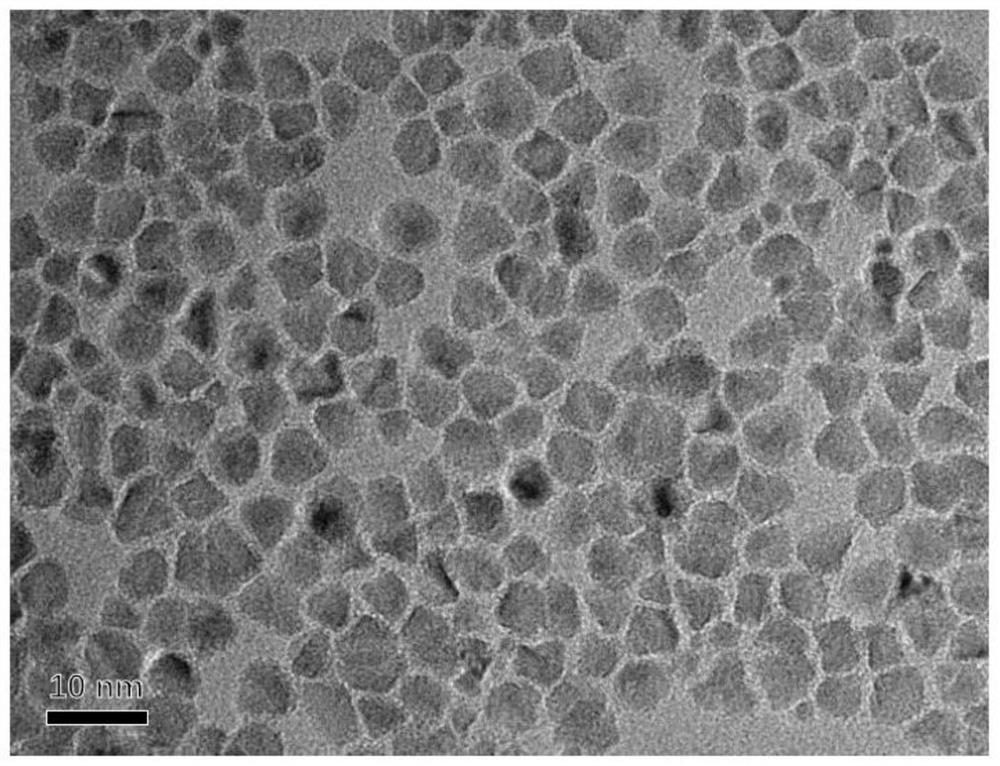
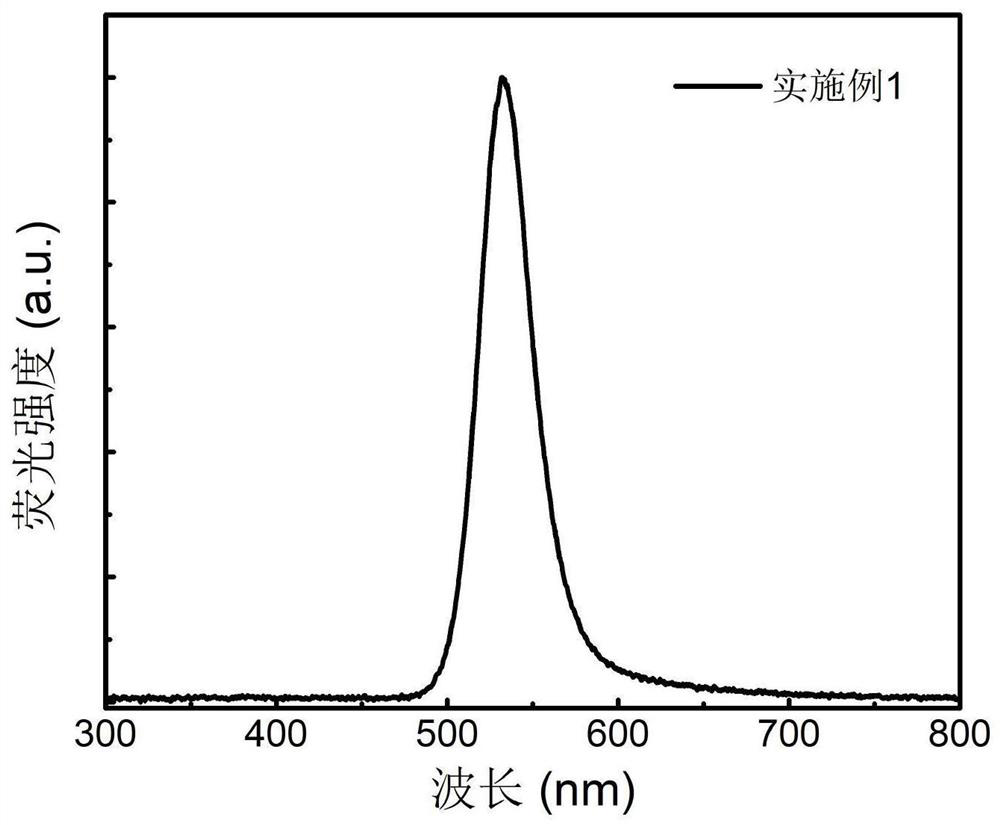
[0026] The invention provides a method for preparing cadmium-free quantum dots: comprising the following steps: S1, mixing phosphorus precursors, fatty acid indium precursors and non-coordinating solvents at a first temperature, and raising them to a second temperature to obtain phosphating Indium quantum dot core; S2, a reaction system in which the indium halide precursor is added dropwise to the indium phosphide quantum dot core to perform surface treatment on the indium phosphide core to obtain cadmium-free quantum dots. By selecting the fatty acid indium precursor as the indium source in the first step, it is beneficial to the nucleation of indium phosphide quantum dots, and the small-sized indium phosphide quantum dot core with few surface defects is generated. When the second step continues to use fatty acid When the indium precursor is used as the indium source, the surface defects of the grown indium phosphide quantum dots will increase instead, which is not conducive t...
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1) Preparation of indium phosphide core:
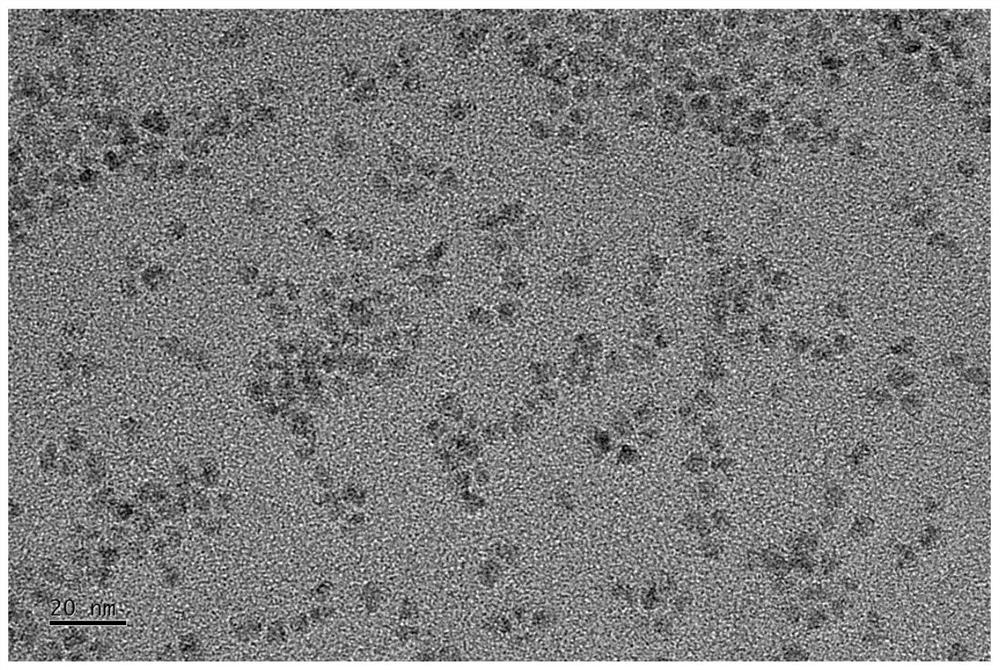
[0040] Add 0.2mmol indium myristate, 10mL 1-octadecene, 0.1mmol zinc stearate to a three-neck flask, vacuumize at 120°C for 2 hours to remove water and oxygen, add 0.1mmol tris(trimethylsilyl) Phosphine, and heated to a second temperature of 280° C., and maintained for 5 minutes, then added indium chloride glycerol solution (20 mg / mL) dropwise to complete the preparation of indium phosphide quantum dot cores.
[0041] 2) Preparation of InP / ZnSe:
[0042] Add 0.8 mmol of zinc stearate into a three-neck flask, then slowly add 1 mmol of TOP-Se, and keep warm for 1 h to form InP / ZnSe quantum dots.
[0043] 3) Preparation of InP / ZnSe / ZnS:
[0044] On the basis of the quantum dots prepared in step 2), continue to add 2mmol of Zn-OA and 2mmol of 1-dodecanethiol, keep warm for 30min, then heat up to 280°C, continue to add 2mmol of Zn-OA and 2mmol of 1 -Dodecanethiol, after 30 minutes of heat preservation, the temperature was raised to...
Embodiment 2
[0052] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0053] In this comparative example, the indium chloride glycerol solution in step 1) was replaced by an indium bromide glycerol solution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| full width at half maximum | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com