Lateral flow analysis strip and molecular diagnostic method using same
A technology for stripping and capturing molecules, applied in chemical instruments and methods, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0103] Preparation Example 1: Preparation of Streptavidin-AuNP Conjugation Solution
[0104] 1 mL of 40nm AuNP (Cat.EM.GC40, BBI Solutions) solution, 100 μL borate buffer (pH8.5, 0.1M, Cat.BB001, Bio-solution) and streptavidin (Cat.434302, Thermo) was mixed to a final concentration of 10 μg / mL to prepare a mixed solution. The mixed solution was vortexed and spun down, followed by incubation at ambient temperature for 1 hour. 10 μL of PBS (10 mM, pH 7.4) containing 100 mg / mL BSA was added to the mixture solution to a final concentration of 0.1% to block the AuNP surface. The mixture was vortexed and spun down, then incubated at ambient temperature for 2 hours. The mixture was centrifuged at 9,000 rpm and 10° C. for 15 minutes using a centrifuge. The supernatant was discarded, and 1 mL of borate buffer (10 mM, pH 8.5) was added and suspended. After repeating the centrifugation and suspension process 3 times, the supernatant was removed, and 100 µL of borate buffer (10 mM) ...
Embodiment 1
[0105] Example 1: Preparation of Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) Strips
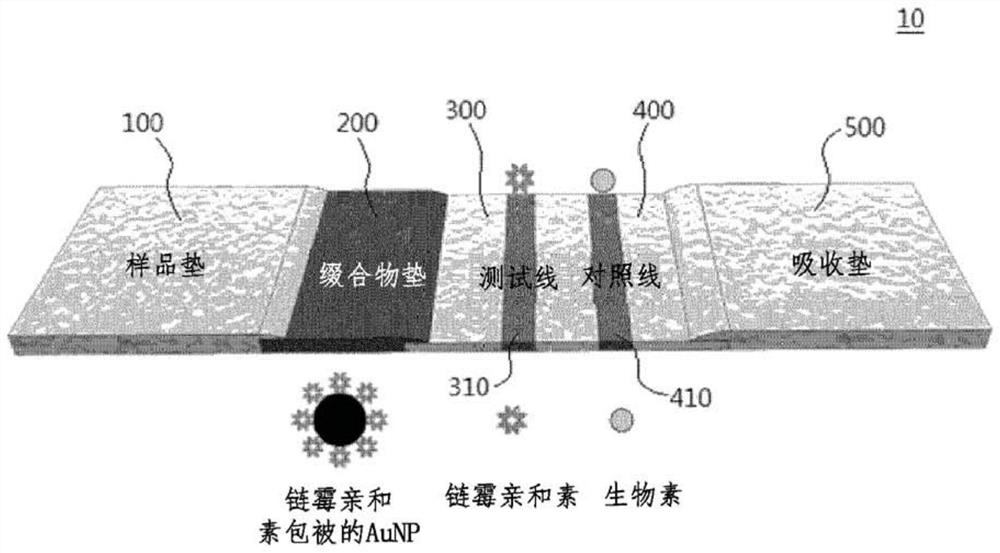
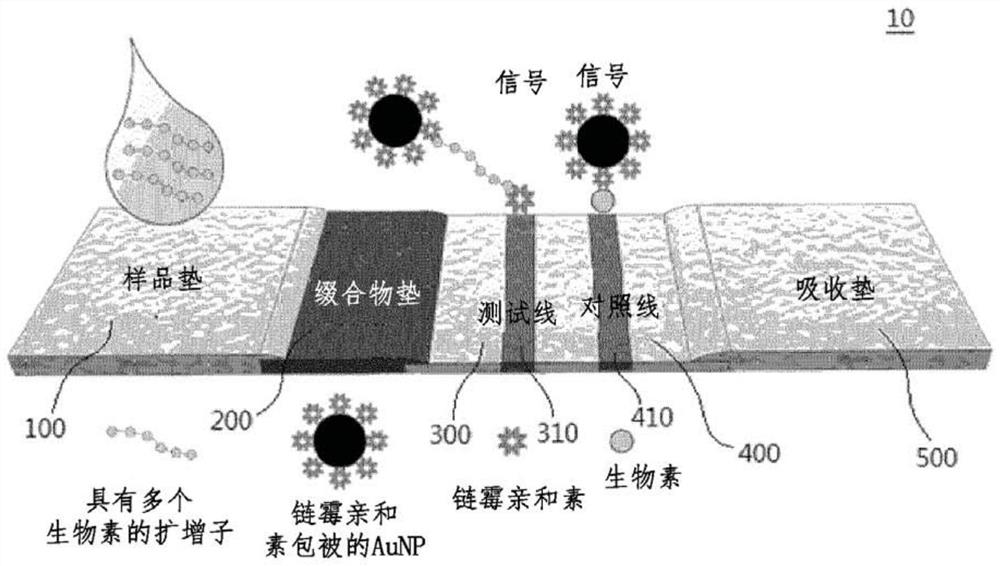
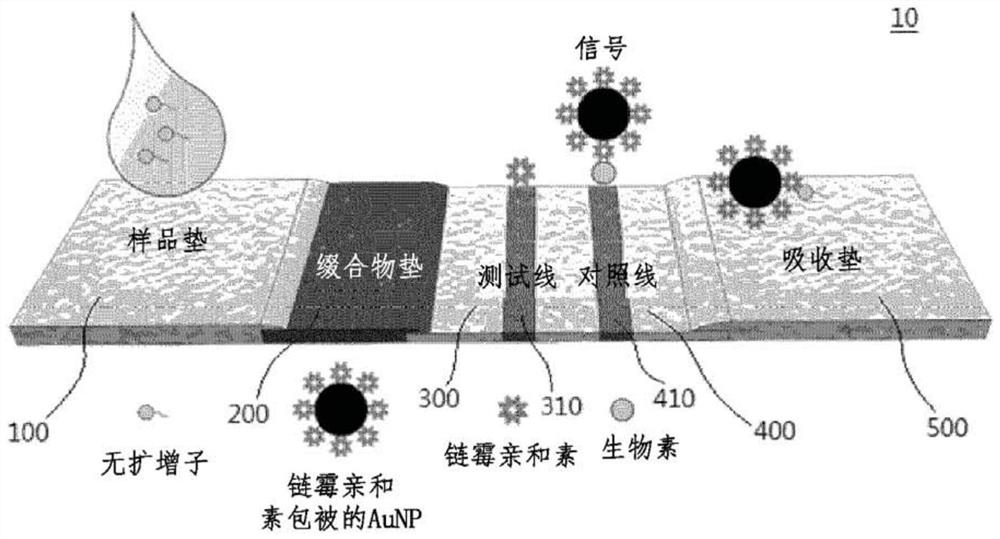
[0106] The LFA strip consists of four components: sample pad, conjugate pad, nitrocellulose membrane, and absorbent pad. Secure the components to the polyester backing card. Cut the backing card to 4 mm width using a cutting tool to prepare LFA strips. Avidin (1 mg / mL) was loaded onto the test line on the nitrocellulose membrane and biotin-BSA (1 mg / mL) was loaded onto the control line on the nitrocellulose membrane using a 1 μL pipette. The distance between these two lines is 3mm. After loading, the nitrocellulose membrane was dried at 37 °C for 1 h. 2×Avidin-AuNP conjugates were loaded onto a conjugate pad (4 mm×8 mm) and stored after drying at a temperature of 37° C. and a humidity of 25%. Thereafter, the sample pad, conjugate pad, nitrocellulose membrane, and absorbent pad were assembled in this order on an adhesive-backed card. Each section overlaps each other by 1.5mm to facilitate solution movemen...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Example 2: RT-LAMP in the presence of influenza virus RNA
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com