Method for separating liquid-phase organic mixture by utilizing phase change of hydrate
An organic mixture and separation method technology, applied in the field of separation science, can solve the problems of large energy input, high reflux ratio, and complicated process, and achieve the effect of high separation efficiency, extremely low energy consumption, and simple and easy operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
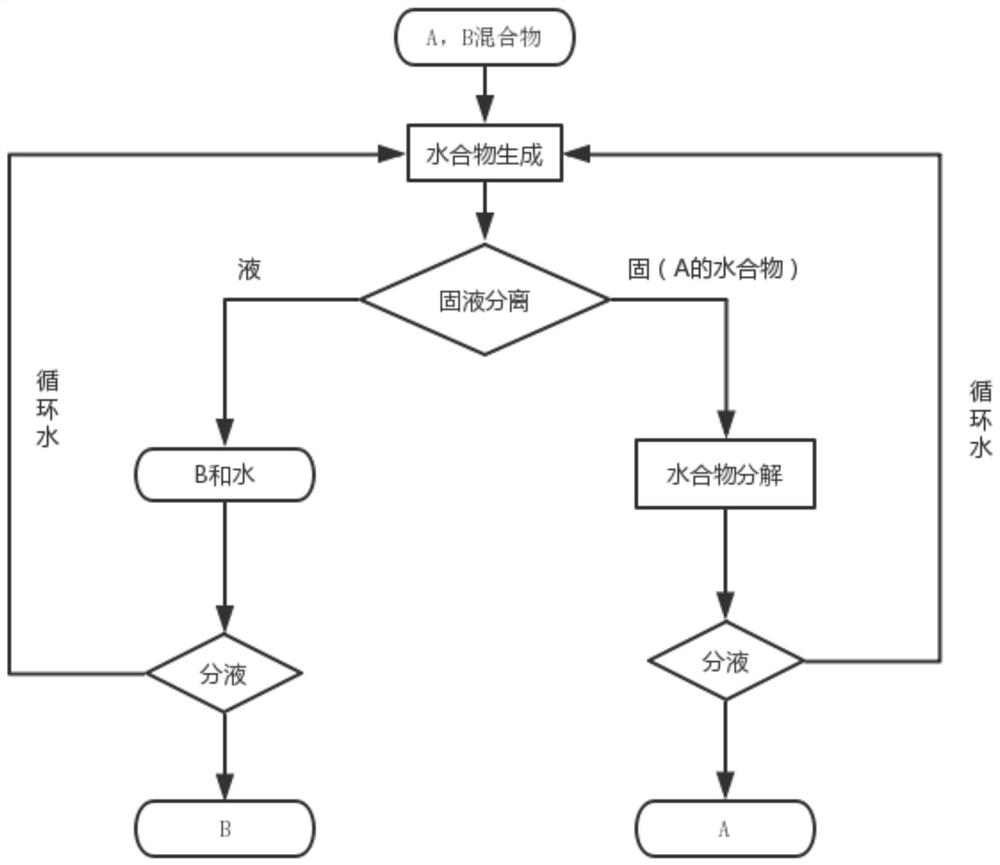
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: Taking the liquid-phase organic mixture of cyclopentane and benzene as an example
[0020] (1) Utilize gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to analyze cyclopentane and benzene liquid-phase organic mixture, determine the type and ratio of organic matter contained therein, obtain this liquid-phase organic mixture by massfraction 40% cyclopentane and 60% Composed of benzene, the component cyclopentane can form hydrate with water;
[0021] (2) The liquid-phase organic mixture of cyclopentane and benzene of 100g is charged in the reactor, so the cyclopentane added to the reactor is 40g (0.57 moles), and 1 mole of cyclopentane can generate cyclopentane with 17 moles of water Alkane hydrate, so the theoretical water requirement is 174.42g (9.69 mole), add the water of 261.63g in the reactor, make the cyclopentane in the liquid phase organic mixture can generate solid hydrate completely;
[0022] (3) The phase equilibrium temperature of cyclopentane hydrate under...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: Take the liquid phase organic mixture of cyclopentane and neohexane as an example
[0028] (1) Utilize gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to analyze cyclopentane and neohexane liquid-phase organic mixture, determine the organic species and ratio contained therein, obtain this liquid-phase organic mixture by massfraction 85% cyclopentane and 15% % neohexane, wherein the component cyclopentane can form hydrates with water; the component neohexane cannot form hydrates under normal pressure;
[0029] (2) The liquid-phase organic mixture of cyclopentane and neohexane is charged into the reactor, so the cyclopentane added to the reactor is 7.5 g (0.17 moles), and 1 mole of cyclopentane can generate cyclopentane with 17 moles of water Pentane hydrate, so the theoretical water requirement is 32.7g (1.82 moles), and 49.05g of water is added to the reactor, so that the cyclopentane in the liquid-phase organic mixture can completely generate solid hydrate;
[0030...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com