Fungal amylase preparation and storage method
A technology of fungal amylase and amylase, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of low acquisition rate, achieve the effects of improving production efficiency, increasing acquisition rate, and saving production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
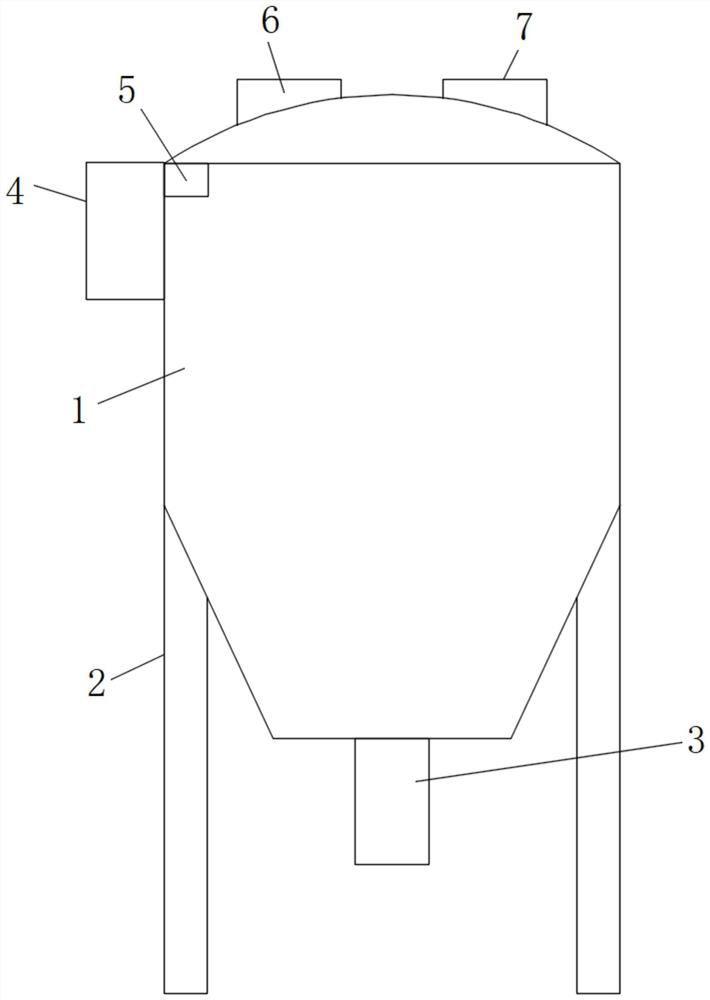
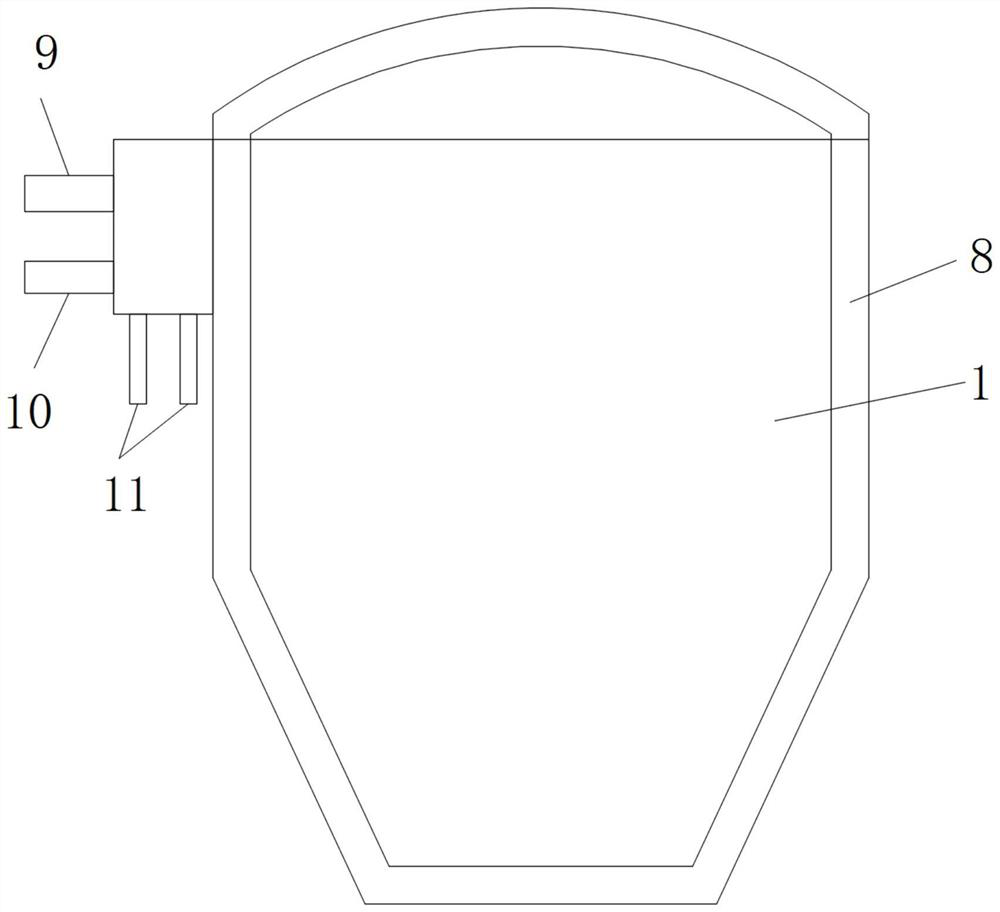
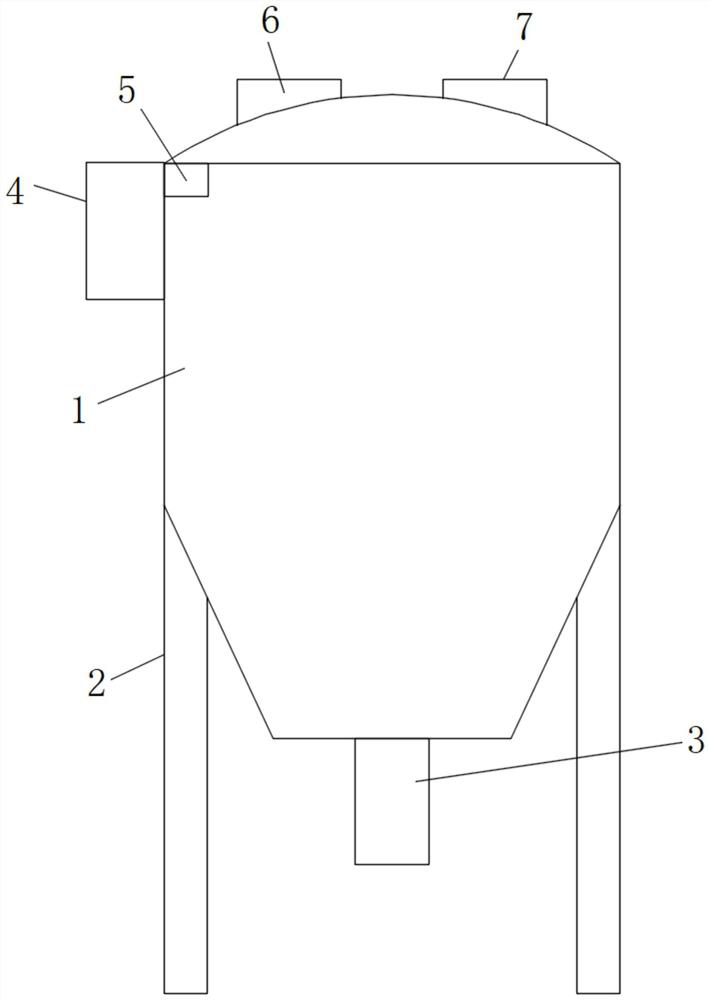
[0039] according to Figure 1-2 Shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides that the present invention provides a kind of fungal amylase preparation method, comprising:
[0040] Use Bacillus subtilis to react with the raw material starch to obtain α-amylase liquid; further, inoculate the strain on the culture medium, and cultivate it for 60-80 hours at a culture temperature of 25-40 degrees Celsius; then culture it on the culture medium The strains in the seed tank are transferred to the seed tank for cultivation; cultivation time: 10-18 hours, cultivation temperature: 25-40 degrees Celsius; Fermentation is terminated after secondary cultivation until the enzyme activity does not increase; the fermented product in the fermenter is destroyed by protease, and cooled and filtered to obtain a filtrate.
[0041] purifying the α-amylase to obtain a purified α-amylase solution; washing the filtrate with water, concentrating in vacuo, adding a salt out product, adding dia...
experiment example 1
[0049] Utilize Bacillus subtilis to react with the raw material starch to obtain α-amylase liquid; further, inoculate the strain on the culture medium, and cultivate it for 65 hours, and the culture temperature is 40 degrees Celsius; then transfer the strain cultured on the culture medium to Inoculate into the seed tank for cultivation; cultivation time: 10 hours, cultivation temperature: 40 degrees Celsius; after the cultivation of the strain in the seed tank is completed, transfer the cultured strain into the fermenter for stirring and secondary cultivation until the enzyme activity does not increase Finally, the fermentation is terminated; the fermented product in the fermenter is destroyed by protease, and cooled and filtered to obtain a filtrate.
[0050] Purifying the α-amylase liquid to obtain a purified α-amylase liquid; washing the filtrate with water, concentrating in vacuo, adding a salt out product, adding diatomaceous earth to the salt out product, and performing p...
experiment example 2
[0058] Use Bacillus subtilis to react with raw material starch to obtain α-amylase liquid; further, inoculate strains on the culture medium, and cultivate it for 76 hours, and the culture temperature is 36 degrees Celsius; transfer the strains cultured on the culture medium to Inoculate into the seed tank for cultivation; cultivation time: 12 hours, cultivation temperature: 36 degrees Celsius; after the cultivation of the strain in the seed tank is completed, transfer the cultured strain into the fermenter for stirring and secondary cultivation until the enzyme activity does not increase Finally, the fermentation is terminated; the fermented product in the fermenter is destroyed by protease, and cooled and filtered to obtain a filtrate.
[0059] Purifying the α-amylase liquid to obtain a purified α-amylase liquid; washing the filtrate with water, concentrating in vacuo, adding a salt out product, adding diatomaceous earth to the salt out product, and performing pressure filtrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com