Application of ethanolamine in preparation of product for preventing, relieving and/or treating neuroinflammation-related diseases
A technology of neuroinflammation and ethanolamine, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems that the effect cannot meet the ideal expectation, and achieve the effect of reducing the level of retinal inflammation, activation and expression of inflammatory factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
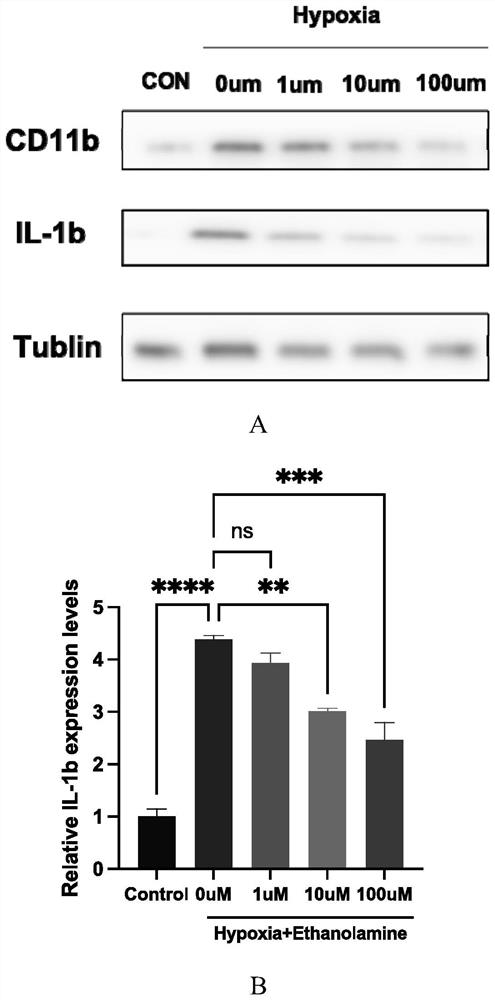
[0033] Example 1 Ethanolamine inhibits the inflammatory response of hypoxia-induced microglial cells
[0034] 1. Experimental method
[0035] In this experiment, hypoxia-induced BV2 cells were used as an in vitro model to verify the effect of ethanolamine on microglia by detecting the expression of inflammatory factors. The specific experimental process is:
[0036] Inoculate BV2 cells in a 6-well plate, add 10% FBS and penicillin / streptomycin double antibody high sugar (containing 4.5g / L glucose) DMEM medium (catalogue number 10-013-CV; Corning) for routine culture; When the cells grew to about 70%, different concentrations of ethanolamine ((catalogue number: S6210; SELLCK)) were added under hypoxic conditions to continue culturing, while a group of cells without ethanolamine but cultured under conventional conditions were kept as a control; cells were collected after 24 hours and RNA was extracted, and the expressions of related inflammatory factors were detected by qRT-PC...
Embodiment 2
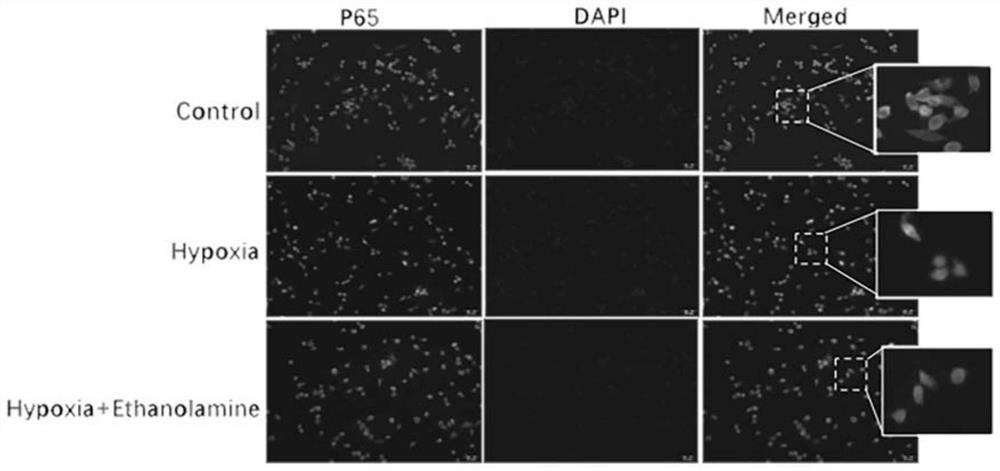
[0039] Example 2 Ethanolamine inhibits hypoxia-induced NF-κB nuclear translocation in microglial cells
[0040] 1. Experimental method
[0041]NF-κB plays a key role in DR inflammatory response. Hypoxic stimulation of BV2 cells promotes inflammatory response through activation of NF-κB pathway. In order to further characterize the molecular mechanism of Ethanolamine's inhibition of inflammatory response, we detected the translocation of NF-κBp65, which is a marker of NF-κB activation. The specific experimental process is:
[0042] Discard the culture medium after hypoxia induction of BV2 cells, add 4% paraformaldehyde to fix at room temperature for 15 minutes, and permeabilize with 0.1% Triton X-100 at room temperature for 10 minutes; cells are blocked with 5% goat serum for 1 hour at room temperature , and then incubated overnight at 4°C with rabbit anti-NF-κBp65 antibody; after washing 3 times with PBS, anti-rabbit secondary IgG (1:500; Thermo Fisher Scientific, A-11008) c...
Embodiment 3
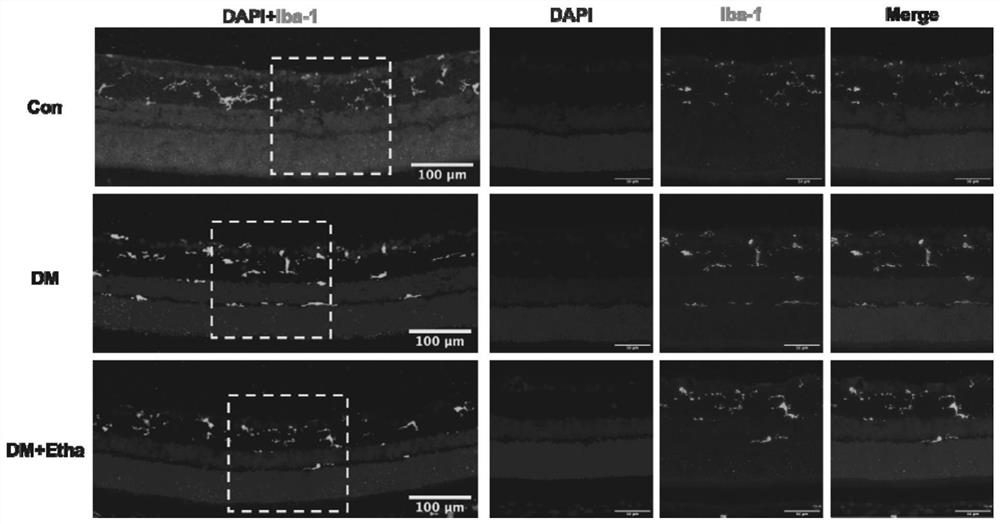
[0045] Example 3 Ethanolamine reduces the activation of retinal microglial cells in diabetic rats
[0046] 1. Experimental method
[0047] All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the ARVO Statement on the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research and in compliance with the guidelines required by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, China.
[0048] (1) Modeling treatment of diabetic rats
[0049] Male Sprague Dawley rats with a body weight of 120-160 g were randomly assigned to the diabetes group and the control group. Diabetic group rats: intraperitoneally inject streptozotocin (STZ, solvent is citrate buffer, 60 mg / kg body weight) after fasting for 24 hours; control group rats: inject the same volume of citrate buffer. Animals in the STZ model group were diagnosed as diabetic when their blood sugar exceeded 13.9mmol / L (250mg / dL) for 3 consecutive days.
[0050] (2) ethanolamine administr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com