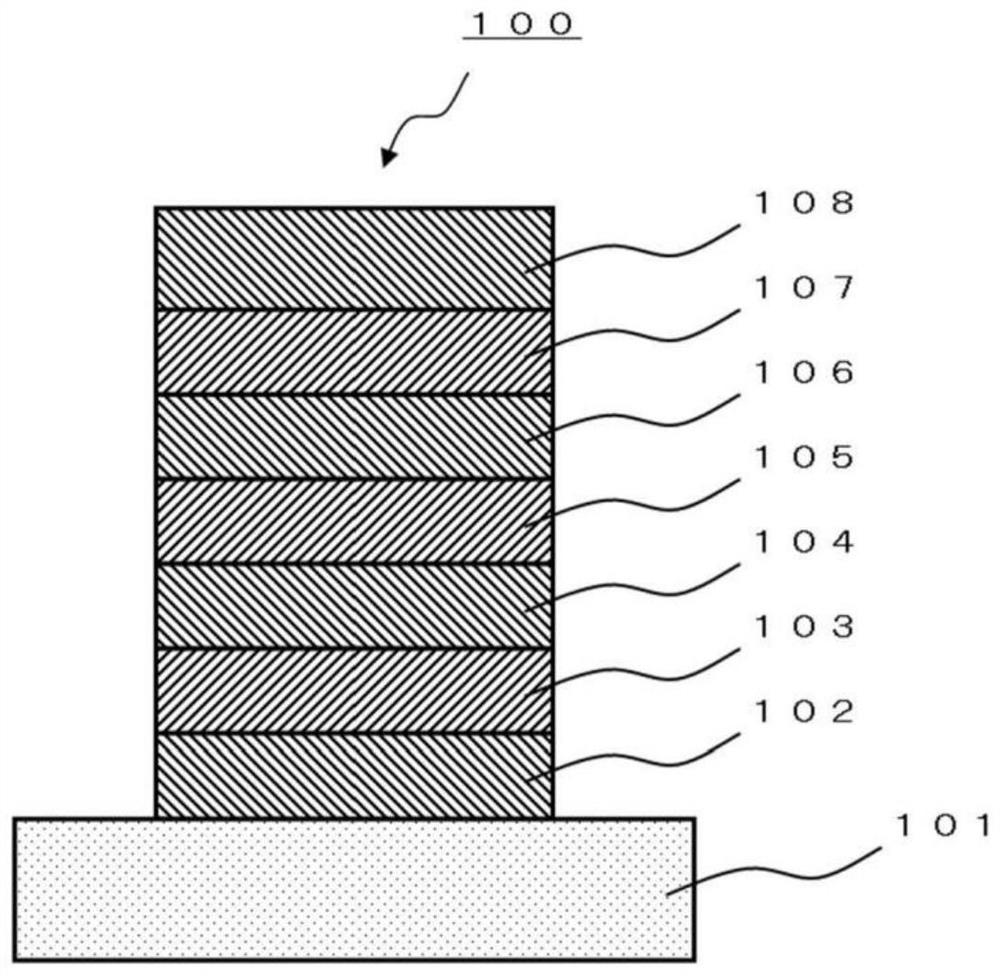
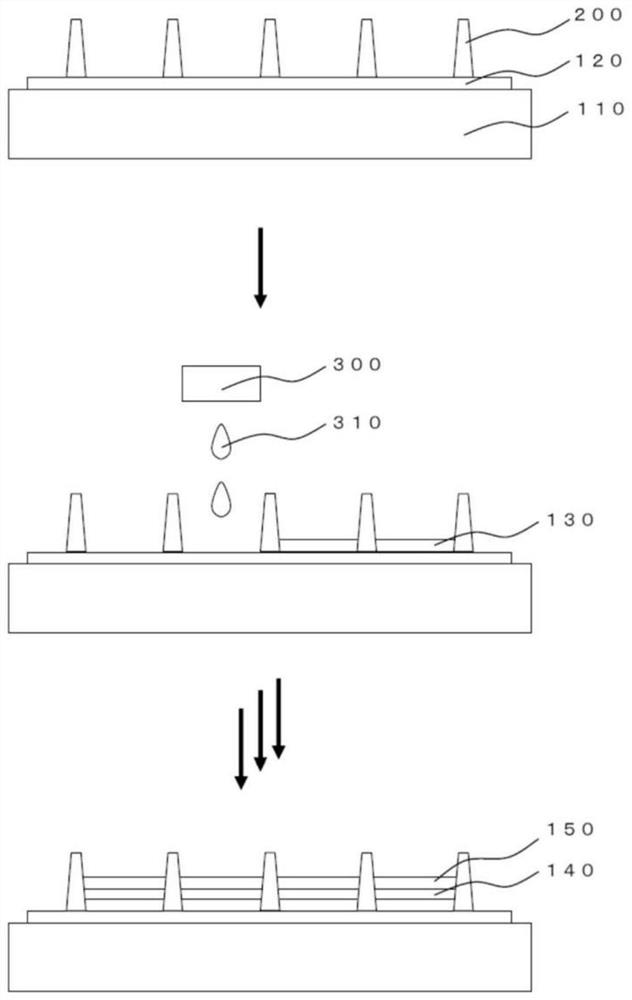
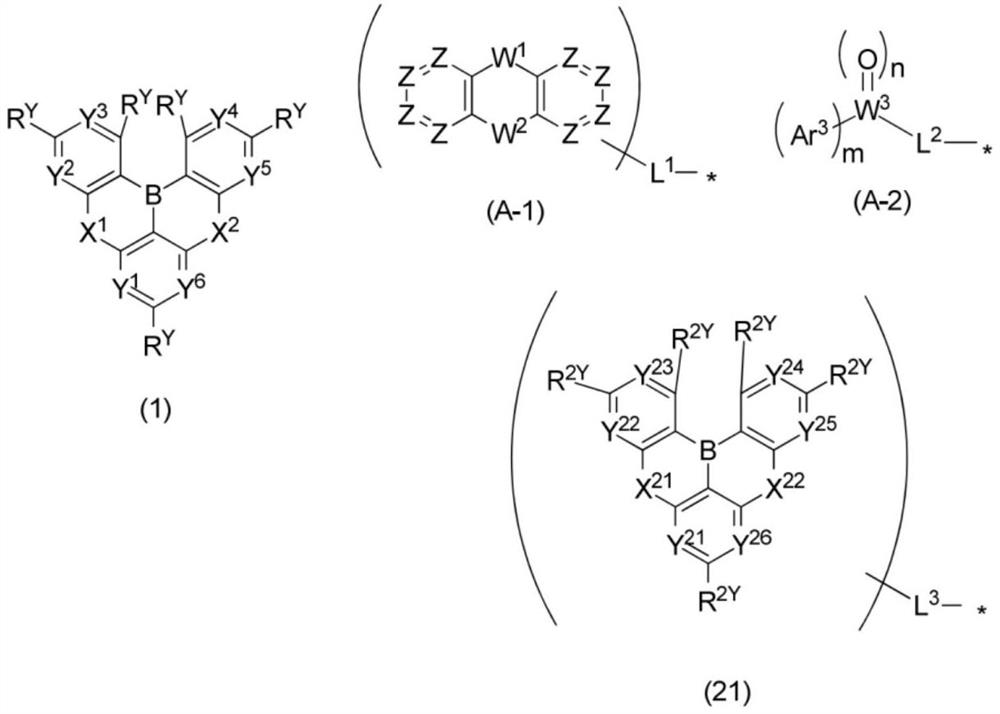
Polycyclic aromatic compound and application thereof
A polycyclic aromatic compound technology, which is applied in the field of display devices and lighting devices, can solve the problems of insufficient life, insufficient stability of aromatic epoxidation and reduction, and unsuitable main materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[1295] Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described by examples, but the present invention is not limited by these examples.
[1296]
[1297] First, a synthetic example of the compound of the present invention will be described below.
Synthetic example (1
[1298] Synthesis Example (1): Synthesis of Compound (1-11)
[1299] [化 228]
[1300]
[1301] In a nitrogen, compound (I-1) (91.7 mg, 0.30 mmol), compound (I-2) (110 mg, 0.33 mmol), bis (di-tert-butyl (3-methylpine) 2-olene-1-yl) phosphine) chloride (II) (5.5 mg, 0.009 mmol), tert-butoxide (31.7 mg, 0.33 mmol), and average toluene (1.5 mL) flask heated to 140 ° C And stirred for 6 hours. After the reaction solution was placed to room temperature, it was injected into water, and the aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane. The obtained organic layer was cleaned with saturated brine, and dried was carried out using anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, and after the residue was washed with acetonitrile, purified by silica gel shortation (unfolding the media: dichloromethane: ethyl acetate = 1: 1). Further, the chloride heating washing was purified by ethyl acetate, and dichloroethane was purified, thereby obtaining a compound (...
Synthetic example (2
[1306] Synthesis Example (2): Synthesis of Compound (1-13)
[1307] [化 230]
[1308]
[1309] In a nitrogen, compound (I-1) (61.1 mg, 0.20 mmol), compound (I-3) (256 mg, 0.48 mmol), bis (di-tert-butyl (4-dimethylamino) Phenyl) phosphine) chloride (II) ((AMPHOS) 2 PDCL 2 (8.5 mg, 0.012 mmol), tripotassium phosphate (204 mg, 0.96 mmol), and 1,4-dioxane (2.0 mL) were stirred under heating and reflux for 4 hours. After cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, the water layer was extracted with dichloromethane. The obtained organic layer was cleaned with saturated brine, and dried was carried out using anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, purified by silica gel shortation (unfolding the media: dichloromethane: ethyl acetate = 1: 1). Further, purification is purified by acetonitrile heating, thereby obtaining a compound (1-13) (114 mg; 75%) in the form of a white solid.
[1310] [化 231]
[1311]
[1312] The structure of the ob...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com