Halide nanocrystalline dispersion glass and application thereof
A technology of nanocrystals and halides, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for information processing, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in preparing photoelectric functional devices, reducing the overall efficiency of photoelectric devices, and difficult to achieve effective absorption of light sources. Achieve the effect of improving the overall optical efficiency, high practical value, and reducing weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Weigh raw materials according to the following mole percentage composition: SiO 2 :35%, B 2 o 3 : 35%, ZnO: 5%, CaO: 5%, PbO: 2%, Na 2 O: 3%, KBr: 15%. After mixing evenly, melt it at 1230°C for 20 minutes, then cool it rapidly and anneal it to obtain completely transparent glass. After cutting and polishing the original glass, CsNO at 480-510°C 3 Ion exchange in molten salt to obtain CsPbBr 3 Nanocrystalline dispersed transparent glass.
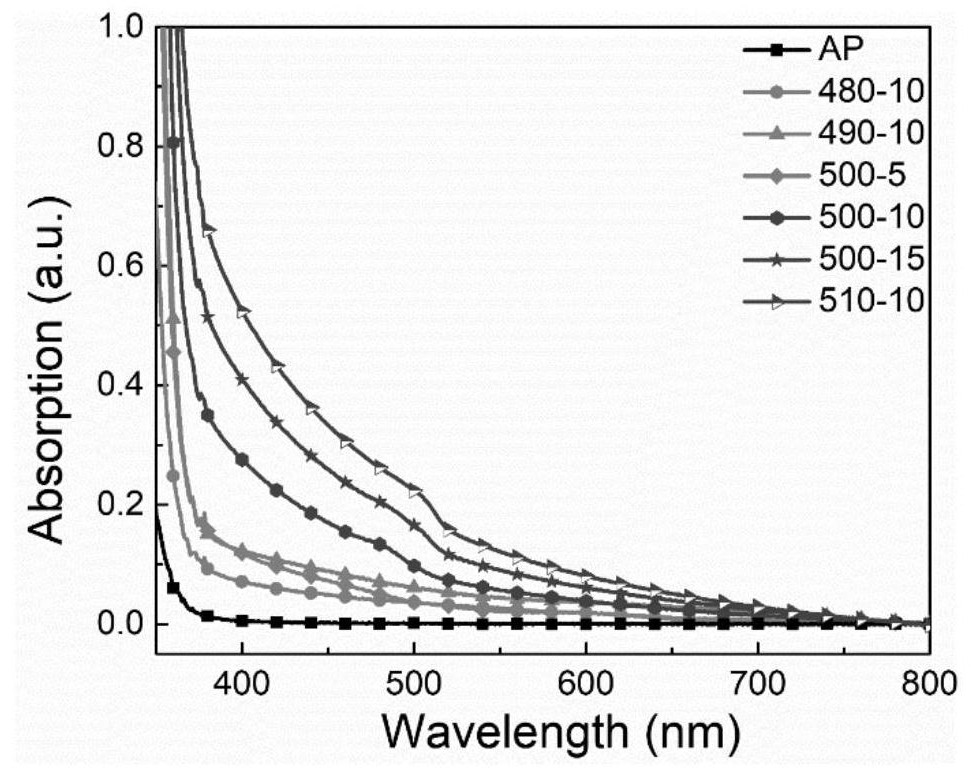
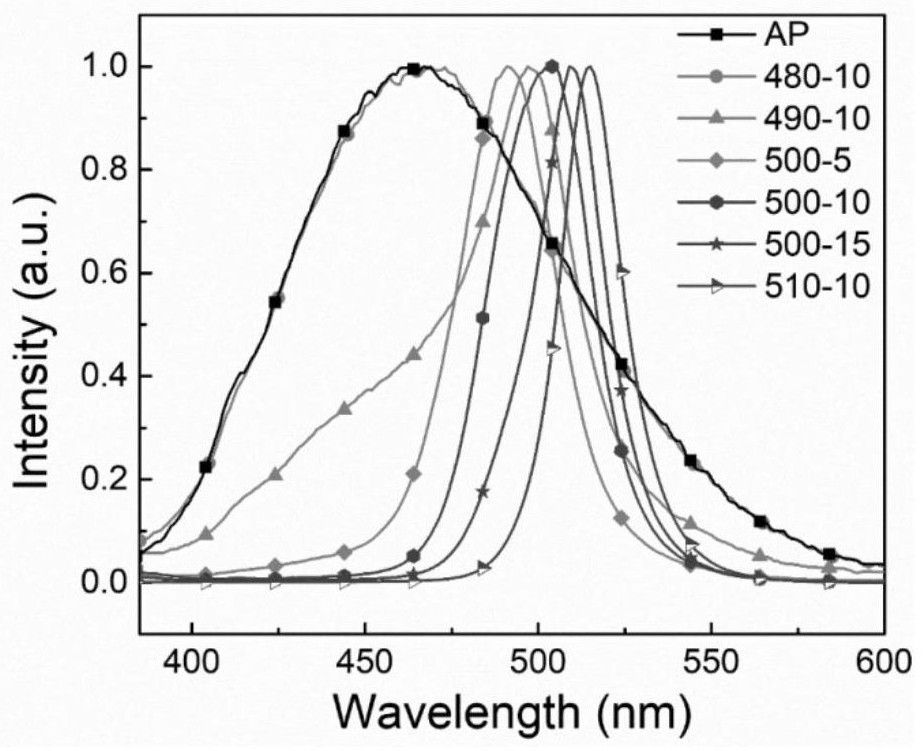
[0070] figure 1 are the absorption spectra of AP and ion-exchanged glass samples. From figure 1 It can be seen that as the ion exchange temperature increases or the time prolongs, the position of the absorption peak shoulder in the spectrum gradually moves from 481nm to 505nm; it shows that after ion exchange, CsPbBr is formed in the glass 3 nanocrystals, and the nanocrystals gradually become larger. figure 1 Under the excitation of 360nm light in the medium glass sample, visible light luminescence was observed in both the A...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The present embodiment glass composition (mol percentage) is SiO 2 :35%, B 2 o 3 : 35%, ZnO: 5%, CaO: 5%, PbO: 2%, Na 2 O: 3%, KCl: 3.75%, KBr: 11.25%. Glass preparation and ion exchange methods and conditions are the same as in Example 1. The difference between this example and Example 1 is that KCl is introduced into the glass composition, and the content ratio of KCl to KBr is 1:3. Figure 7 and Figure 8 For this embodiment sample in CsNO 3 Absorption spectra of glass samples obtained after ion exchange in molten salt. With the increase of ion-exchange temperature, the absorption shoulder of ion-exchange samples gradually red-shifted from 488nm to 501nm ( Figure 7 ), the luminescence peak red shifted from 488nm to 508nm ( Figure 8 ).
Embodiment 3
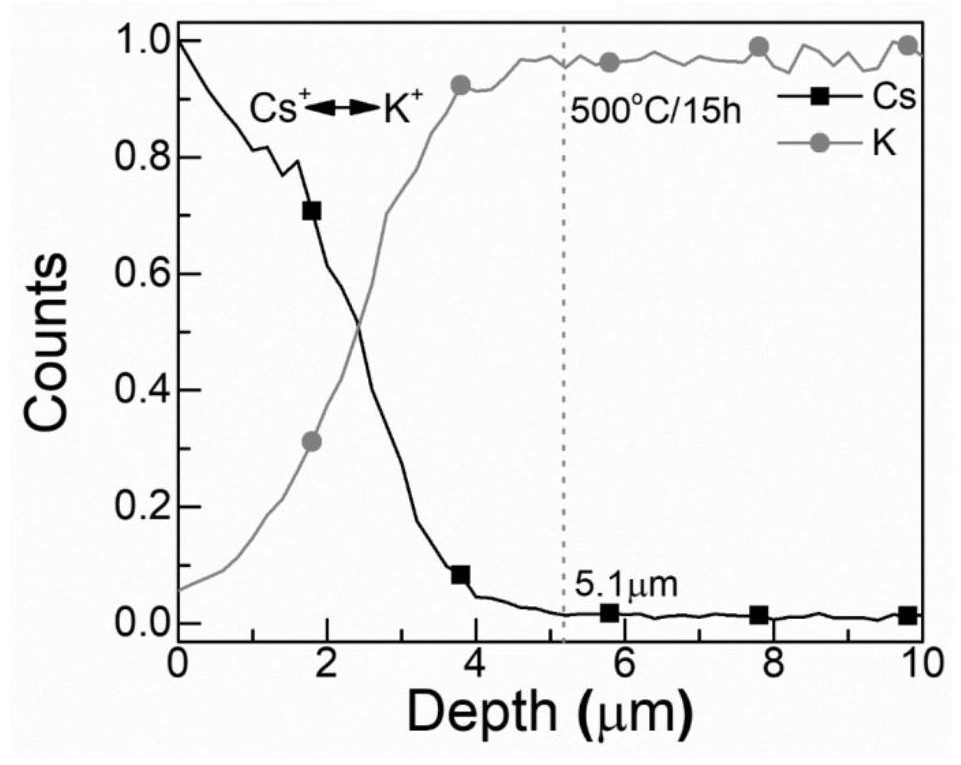
[0077] The present embodiment glass composition (mol percentage) is SiO 2 :35%, B 2 o 3 : 35%, ZnO: 5%, CaO: 5%, PbO: 2%, Na 2 O: 3%, KCl: 7.5%, KBr: 7.5%. The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 2 is that the content ratio of KCl and KBr is 1:1. The absorption shoulders of ion-exchanged glass samples are located at 467nm (480°C / 10h, the ion exchange temperature and time in brackets, the same below), 472nm (500°C / 5h), 474nm (500°C / 10h), 475nm (500°C / 15h), 480nm (510°C / 10h), the corresponding luminescence peaks of the samples are located at 481nm (480°C / 10h), 484nm (500°C / 5h), 486nm (500°C / 10h), 487nm (500°C / 15h) and 489nm (510°C / 10h).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com