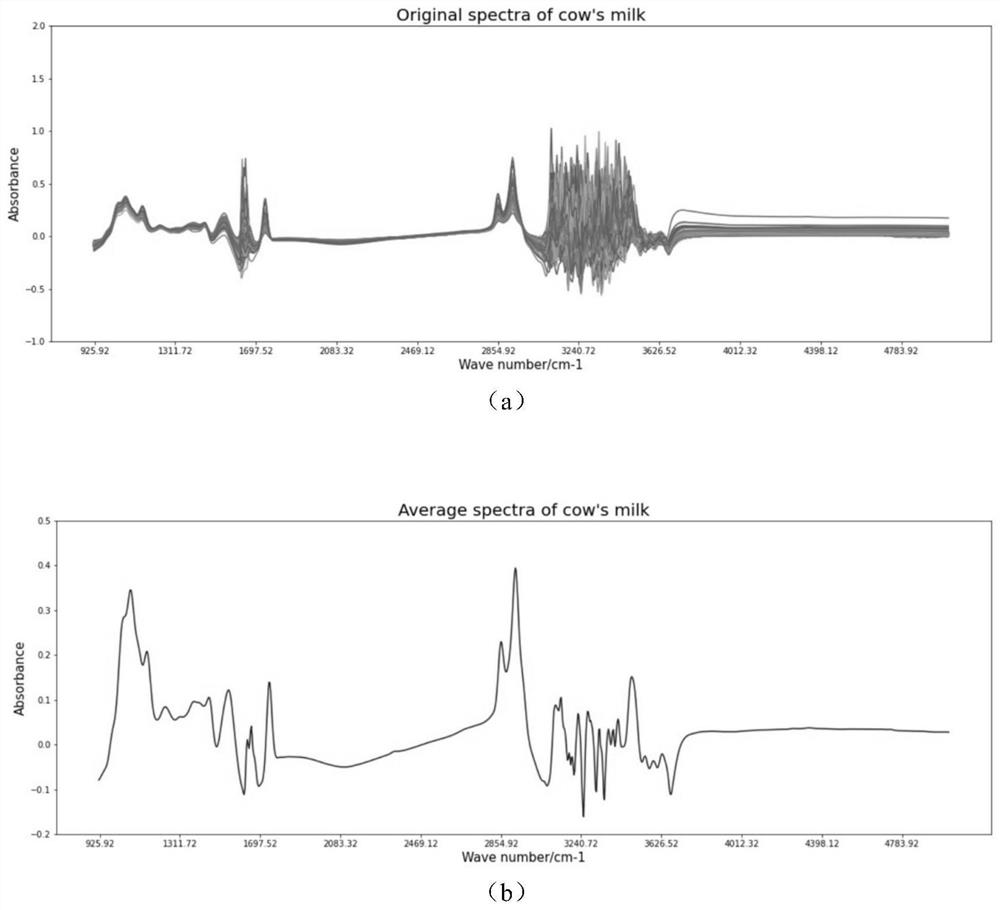
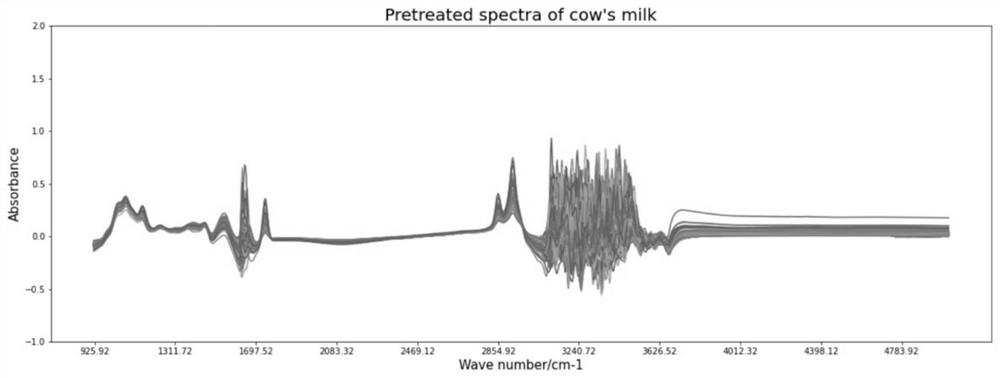
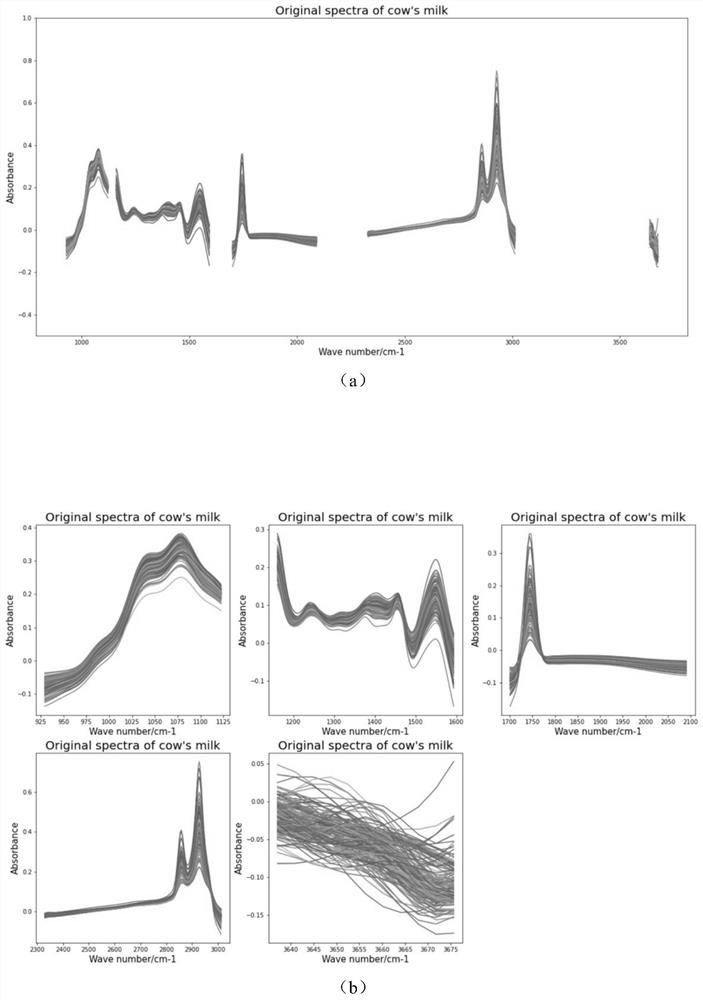
Intermediate infrared rapid batch detection method for content of free lysine in milk
A technology for batch detection and lysine, which is applied in measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of no rapid batch detection model and the inability to effectively obtain milk quality and safety information, and achieve rapid batch detection , low-cost detection, and the effect of improving detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Choice of lysine prediction model algorithm:
[0066] The purpose of this application is to establish a quantitative determination model of lysine, so the modeling algorithm used is a regression algorithm. There are many types of regression algorithms, and this embodiment mainly uses Ridge regression (Ridge) and partial least squares regression (PLSR) [9] Algorithm for model building and comparison, the reasons are as follows:
[0067] Ridge regression is a type of linear regression. Only when the algorithm establishes the regression equation, the ridge regression adds regularization restrictions, so as to achieve the effect of solving over-fitting. There are two types of regularization, namely l1 regularization and l2 regularization. Compared with l1 regularization, the advantages of l2 regularization are: (1) cross-validation can be performed (2) stochastic gradient descent is realized. Ridge regression is a linear regression model after adding l2 regularization, w...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Screening of the number of mid-infrared spectroscopy measurements and how they are used:
[0071] All the samples used in this application have been collected twice in a row. The purpose is to compare the different measurement times of the same sample and the obtained three kinds of MIR data (the first time, the second time, and the second average) to the modeling accuracy. The influence of , and screen out the most effective MIR data for modeling. Because some researchers believe that the average spectral MIR measured twice may improve the modeling accuracy, so in this embodiment, the first, second, and second average spectral MIR are removed from the water band and the area greater than 4000cm -1 Partially modeled and compared the accuracy of the analysis model, the results are shown in the following table:
[0072] Ridge algorithm comparison results:
[0073]
[0074] PLSR algorithm comparison results:
[0075]
[0076] After comprehensive consideration of t...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Establishment of a method for detecting lysine content in milk by mid-infrared spectroscopy:
[0079] 1. Division of modeling data sets
[0080]
[0081] In the division of the modeling data set in this embodiment, 75% is a training set and 25% is a test set. The ratio of the training set to the test set is 3:1. At the same time, the training set is also called the cross-validation set. In the process of training the model, 10-fold cross-validation is performed.
[0082] 2. Screening of modeling MIR data preprocessing methods
[0083] Effective feature screening is the basic operation of spectral data processing, the purpose is to eliminate noise and lay a good foundation for feature extraction. Effective feature screening mainly includes feature extraction, feature preprocessing, and feature dimensionality reduction. This embodiment mainly performs feature preprocessing on the spectral data. First, SG (convolution smoothing), MSC (multiple scattering correction),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com