Method for separating formic acid and levulinic acid from hydrate molten salt
A technology for the separation of levulinic acid and separation methods, which is applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, chemical instruments and methods, and the preparation of organic compounds. Separation, separation of difficult separation methods and other problems, to achieve good self-catalysis ability, promote the production rate, and enhance the effect of protonation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
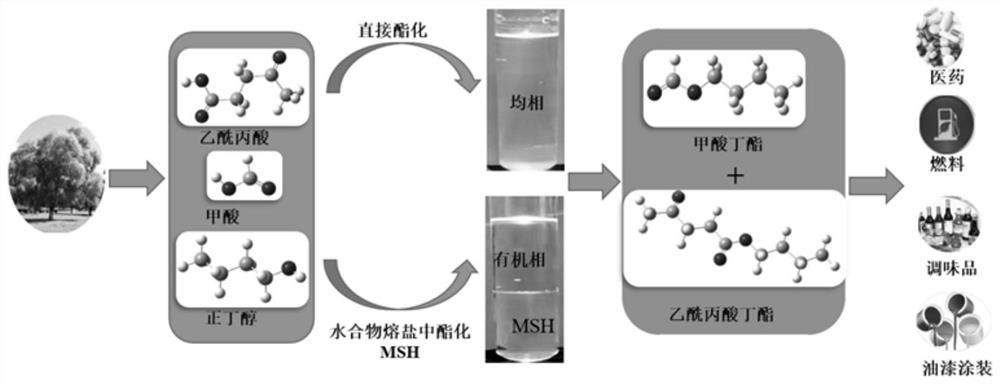
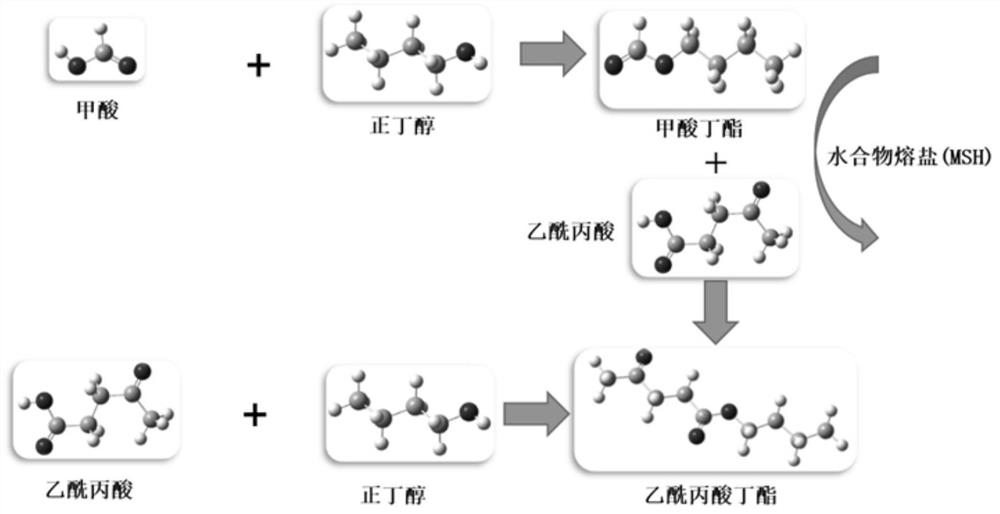
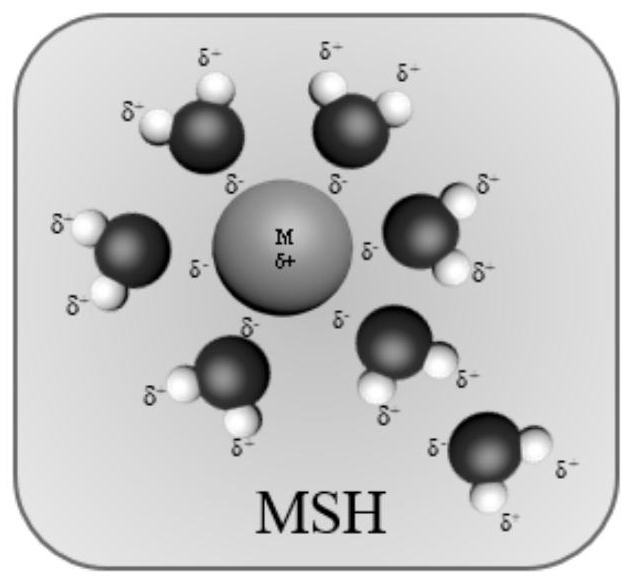
[0043] (1) After the cellulose hydrolyzate is concentrated, the concentrated cellulose hydrolyzate is obtained, and 33g CaCl is added in 30.0g of the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate 2 React with 14.8g of n-butanol at 60°C for 3.0 hours, wherein the concentrated cellulose hydrolyzate consists of 11.6g of levulinic acid, 2.0g of formic acid, 16.0g of water and 0.4g of other biomass hydrolysis by-products;
[0044] (2) After the reaction is completed, the temperature is lowered to 30° C., sedimentation and separation are carried out, and the organic phase is separated, and the mass of the organic phase is 28.1 g;
[0045] (3) the organic phase obtains butyl levulinate and butyl formate respectively through distillation, and the productive rate of butyl formate is 81.0wt.%, and the productive rate of butyl levulinate is 71.1wt.%; Chromatographic analysis, see the results Figure 5 , the two main peaks are as follows: 1, 8.57: butyl formate; 2, 21.587: butyl levulinate;
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) After the cellulose hydrolyzate is concentrated, the concentrated cellulose hydrolyzate is obtained. Add 16.7g LiCl and 14.8g n-butanol to 30.0g of the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate, and react at 80°C for 5.0h. Among them, the composition of the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate 5.8g of levulinic acid, 2.0g of formic acid, 21.8g of water and 0.4g of other biomass hydrolysis by-products;
[0049] (2) After the reaction is completed, the temperature is lowered to 40° C., sedimentation separates the layers, and the organic phase is separated, and the mass of the organic phase is 22.4 g;
[0050] (3) The organic phase was distilled to obtain butyl levulinate and butyl formate respectively, the productive rate of butyl formate was 83.2wt.%, and the productive rate of butyl levulinate was 72.7wt.%.
[0051] (4) Butyl levulinate and butyl formate are hydrolyzed to obtain levulinic acid and formic acid respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) After the cellulose hydrolyzate is concentrated, the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate is obtained, and CaBr is added in 30.0 g of the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate 2 49.0 g and 29.6 g of n-butanol were reacted at 90°C for 2.5 hours, wherein the cellulose concentrated hydrolyzate consisted of 11.6 g of levulinic acid, 4.6 g of formic acid, 13.3 g of water and 0.5 g of other biomass hydrolysis by-products;
[0054] (2) After the reaction is completed, the temperature is lowered to 40° C., sedimentation separates the layers, and the organic phase is separated, and the mass of the organic phase is 45.5 g;
[0055] (3) The organic phase was distilled to obtain butyl levulinate and butyl formate respectively, the productive rate of butyl formate was 81.0wt.%, and the productive rate of butyl levulinate was 73.1wt.%.
[0056] (4) Butyl levulinate and butyl formate are hydrolyzed to obtain levulinic acid and formic acid respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com