Use of tmem236 gene in the preparation of neoadjuvant radiotherapy resistance markers for diagnosing rectal cancer
A rectal cancer and multipurpose technology, applied in the field of biology, can solve problems such as few researches, achieve high technical value, wide application potential, and efficient and convenient experimental methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Tumor regression grade (TRG) in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer neoadjuvant radiotherapy
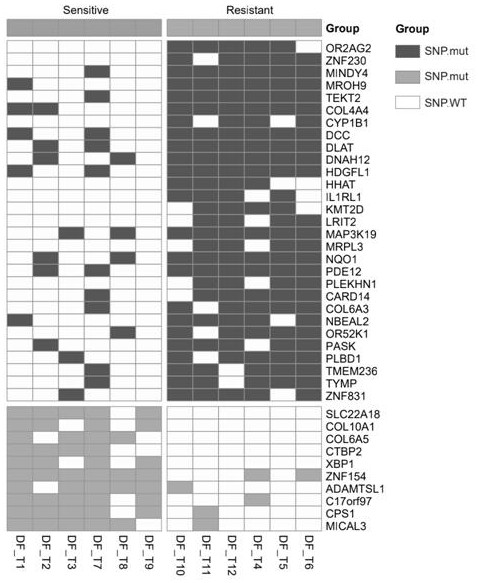
[0041] A total of 12 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer who had received neoadjuvant radiotherapy were collected. A total of 12 cases of tumor tissue and normal tissue samples were matched before and after radiotherapy. The patients were divided into radiosensitive group (TRG=0+1) and radiotherapy resistant group (TRG= 2+3), with normal tissue as the control. Among them, 6 patients were radiosensitive and 6 were radioresistant. Table 1 below presents the raw data of 12 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer neoadjuvant radiotherapy.
[0042] The specific methods are as follows: (Grading is carried out with reference to the AJCC version of TRG grading)
[0043] AJCC version of tumor regression grade (Tumor Regression Grade, TRG)
[0044]
[0045] Table 1 Tumor regression grades in patients with neoadjuvant radiotherapy for rectal cancer (T...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 Whole exome sequencing of paired tissue samples before and after radiotherapy
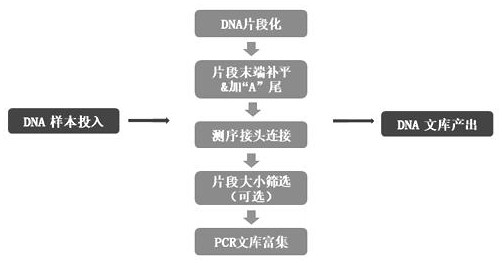
[0048] According to the 12 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer in Example 1, the tumor tissue was taken for colonoscopy biopsy before neoadjuvant radiotherapy, and the paired normal tissue was used as a control for whole-exome sequencing. The specific experimental process is as follows: (eg figure 1 , 2 shown)
[0049] Genomic DNA was extracted from the tissue, cut into short fragments by ultrasonic waves, and then connected to the library building adapter for the first amplification. Two rounds of amplification, purified and sequenced on a sequencer.
[0050] Human Whole Exome Sequencing Experimental Process
[0051] 1. Materials and methods
[0052] 1.1 Main instruments
[0053]
[0054] 1.2 Main reagent consumables
[0055]
[0056] 1.3 Enrolled patients and specimen collection
[0057] A total of 12 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer in the Depar...
Embodiment 3
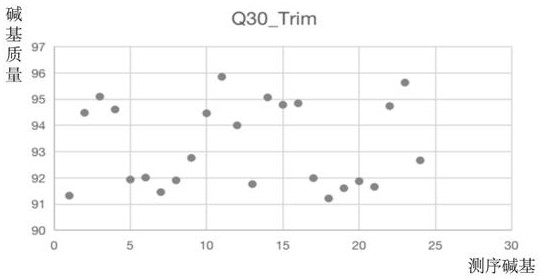
[0208] Example 3 Quality control analysis of whole exome sequencing raw data
[0209] 1. Preprocessing of sequencing raw data
[0210] First, the original image data file obtained by sequencing was used for base calling using the Base Calling software IllunimaCasava 1.8 and converted to obtain the original base sequence (Raw Data), and the result was exported as a FASTQ file. To remove low-quality reads and adapter sequence data, we preprocessed the raw FASTQ sequences to obtain clean reads and ensure the accuracy of subsequent analysis work.
[0211] The data preprocessing and filtering operations are as follows:
[0212] 1) Use Trimmomatic tools (v 0.36) software to process the raw sequencing data with the following options: TRAILING: 20, MINLEN: 235 and CROP: 235 to remove tailing sequences with a phred quality score lower than 20 and obtain sequencing of uniform length fragments data for subsequent analysis.
[0213] 2) Use FastQC software to check the quality of the se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com