Method for enhancing anaerobic biodegradation of halogenated phenol by static magnetic field
An anaerobic biology and static magnetic field technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, anaerobic digestion treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve stable properties, reduce treatment costs, and long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
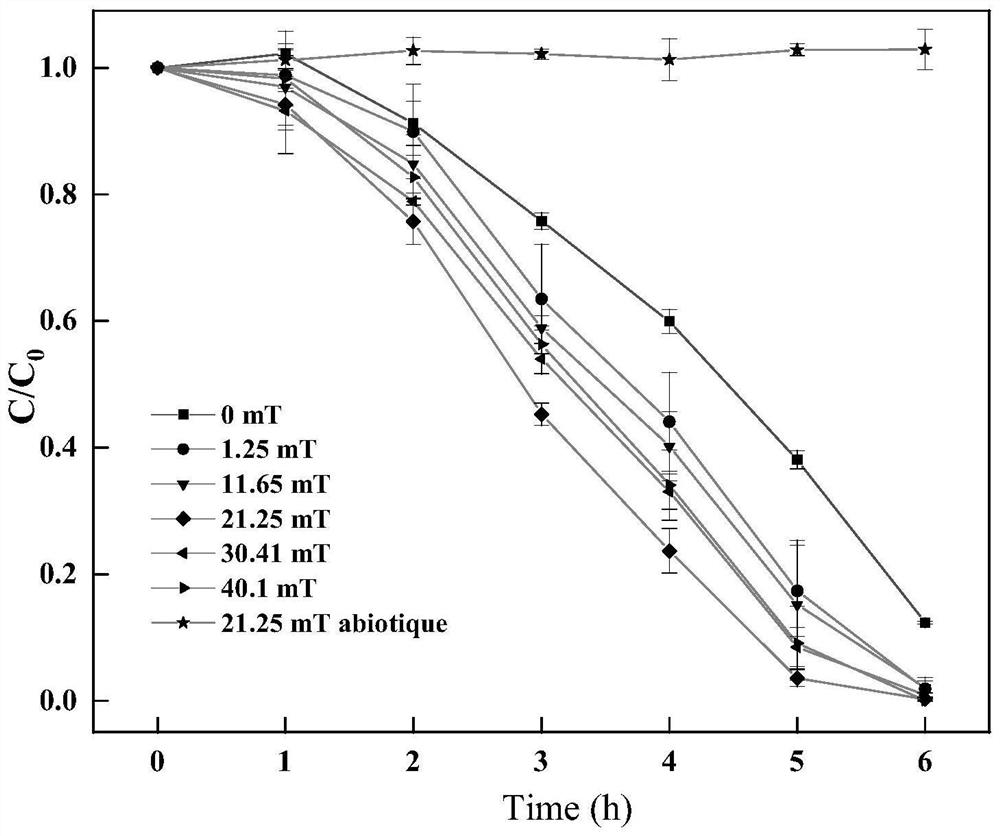
[0030] (1) Sludge domestication: The simulated wastewater was exposed to nitrogen for 15 minutes before use to exhaust the residual oxygen in the wastewater to an anaerobic state. Add the initial simulated wastewater containing 4-BP concentration of 5 mg / L into a 125 mL anaerobic bottle, and add anaerobic sludge with a sludge concentration of 2.47 g / L, and seal the anaerobic bottle. After the 4-BP in the simulated wastewater was completely degraded, the concentration of 4-BP in the wastewater was gradually increased to 50 mg / L, and the sludge domestication was completed after the effluent quality was stable.
[0031] (2) Construct a static magnetic field-anaerobic biological system: Add domesticated sludge into the magnetic field, set the magnetic field strength to 1.25mT, 11.65mT, 21.25mT, 30.41mT and 40.1mT respectively, and pass through the For 50mg / L simulated wastewater, acclimated for 10 days, and constructed a static magnetic field-anaerobic biological system.
[0032]...
Embodiment 2
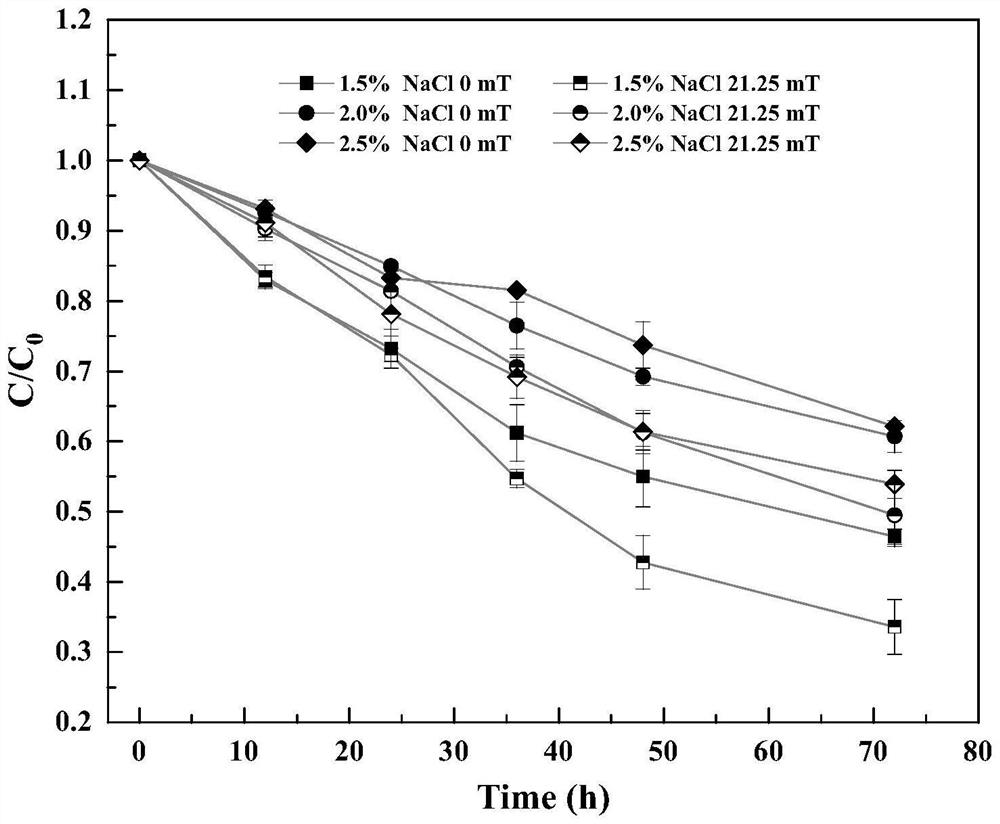
[0037] According to the experimental data of embodiment 1, analyze experiment, select optimal magnetic field strength to be 21.25mT, other conditions are identical with embodiment 1, different salt concentrations (NaCl concentration are respectively 0, 15, 20 and 25g / L) are set, explore Effects of static magnetic field on anaerobic organisms under complex water quality conditions.
[0038] The result is as figure 2 As shown, with the increase of salt concentration, the removal rate of anaerobic organisms to 4-BP is gradually decreasing. When the NaCl concentration is 0g / L and the magnetic field strength is 0mT, the removal rate of 50mg / L 4-BP within 5h It can reach more than 60%; when the salinity increases to 20g / L, the removal rate of 50mg / L 4-BP is only 37.05±2.76%. In contrast, under the action of a static magnetic field of 21.25mT, when the NaCl concentration is 0g / L, the removal rate of 4-BP to 50mg / L has reached more than 95.0% in 5h; 15g / L NaCl and 21.25mT Static ma...
Embodiment 3
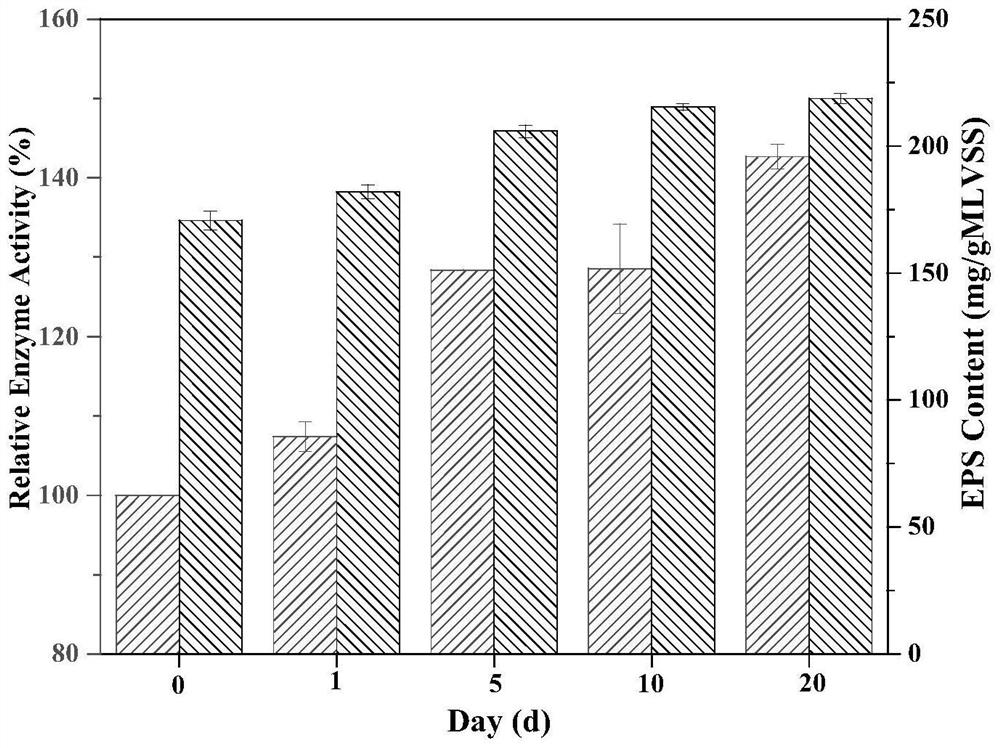
[0040] According to the experimental data of embodiment 1, analyze experiment, select optimum magnetic field strength 21.25mT, other conditions are the same as embodiment 1, research the long-term influence of magnetic field to microorganism, carry out by a definite date 20 days continuous acclimatization degradation experiment, explore static magnetic field to microorganism Secretion of bromophenol dehalogenase and effects of EPS.
[0041] The result is as image 3 As shown, the activity of bromophenol dehalogenase increases with the increase of the magnetic exposure time. Compared with the non-magnetic field exposure on the first day of magnetic exposure, the activity increases by 3.79%. The increase is relatively slow. With the increase of the magnetic exposure time, the magnetic exposure The activity of bromophenol dehalogenase increased by 28.41%, 28.51% and 42.69% respectively at 5d, 10d and 20d. With the increase of magnetic exposure time, the content of EPS also incre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com