Boron nitride powder, method for producing same, boron carbonitride powder, composite material, and heat dissipation member
A boron nitride and powder technology, used in the field of composite materials and heat dissipation components, can solve the problem of low thermal conductivity, and achieve the effects of excellent heat dissipation, excellent thermal conductivity and excellent filling.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] [Preparation of hexagonal carbon boron nitride]
[0068] 100 parts by mass of orthoboric acid manufactured by Nippon Denko Co., Ltd. and 35 parts by mass of acetylene black (trade name: HS100) manufactured by Denka Corporation were mixed with a Henschel mixer. The obtained mixture was filled in a graphite crucible, and heated at 2200° C. for 5 hours in an argon atmosphere with an electric arc furnace to obtain block-like boron carbide (B 4 C). The obtained lump was coarsely pulverized with a jaw crusher to obtain a coarse powder. Pass the coarse powder through a ball made of silicon carbide A ball mill is used to further pulverize to obtain pulverized powder. Pulverization by a ball mill was performed at a rotation speed of 20 rpm for 60 minutes. Thereafter, the pulverized powder was classified using a vibrating sieve with a mesh size of 45 μm. The fine powder on the sieve is air-classified with a CLASSIEL classifier to obtain boron carbide powder with a particle ...
Embodiment 2
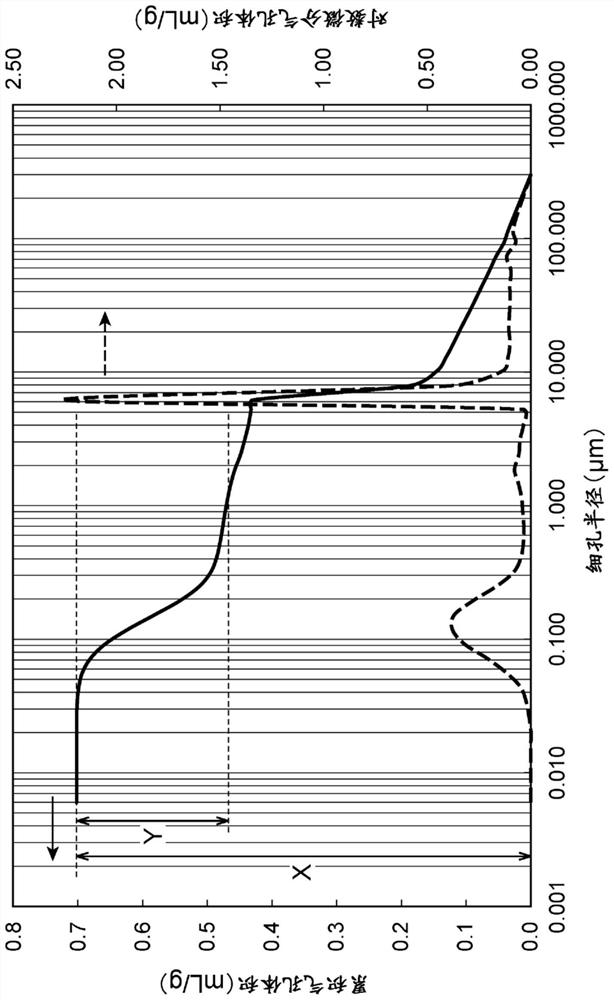
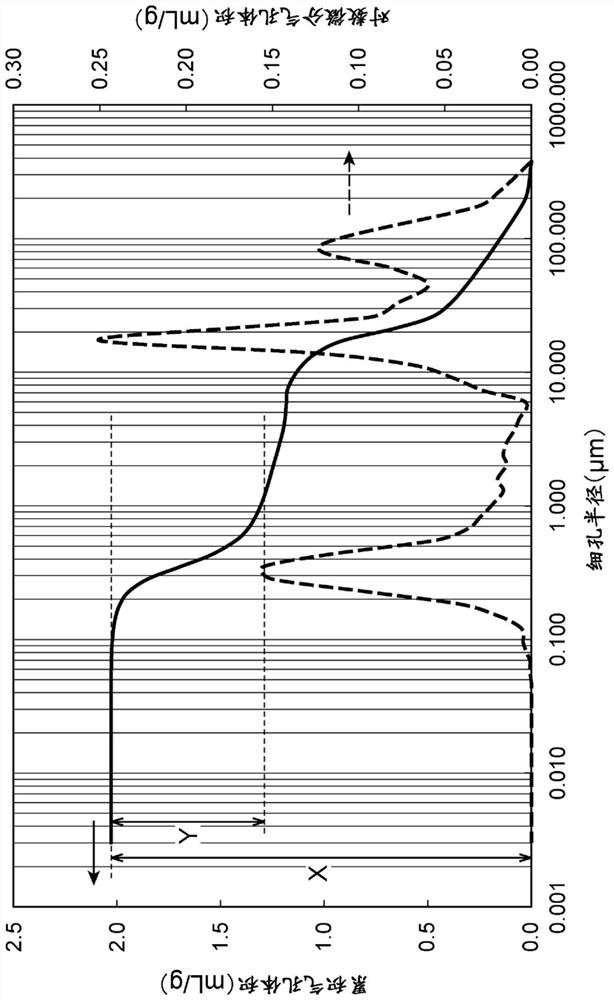
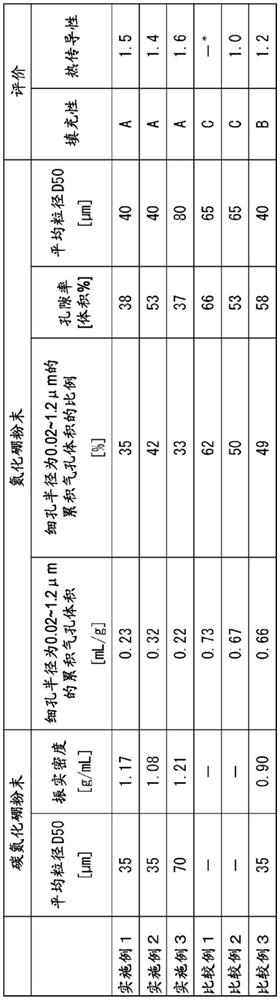
[0085] Except having changed the calcination temperature into 2050 degreeC, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and obtained the boron nitride powder. With respect to the obtained boron nitride powder, the measurement of the cumulative pore volume and the logarithmic differential pore volume, and the evaluation of the fillability and heat dissipation were carried out in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0087]Boron nitride powder was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the pulverization time of boron carbonitride was changed to 0.5 hours to prepare a pulverized product having an average particle diameter of 40 μm. It should be noted that the boron nitride powder was obtained by passing through a vibrating sieve with a mesh size of 150 μm. With respect to the obtained boron nitride powder, the measurement of the cumulative pore volume and the logarithmic differential pore volume, and the evaluation of the fillability and heat dissipation were carried out in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com