Method for changing surface wettability of invar alloy through femtosecond laser
A technology of Invar alloy and femtosecond laser, which is applied in the field of changing the surface wettability of Invar alloy, can solve the problems that micron-level morphology cannot be processed, and it is difficult to reach the ablation threshold of Invar alloy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
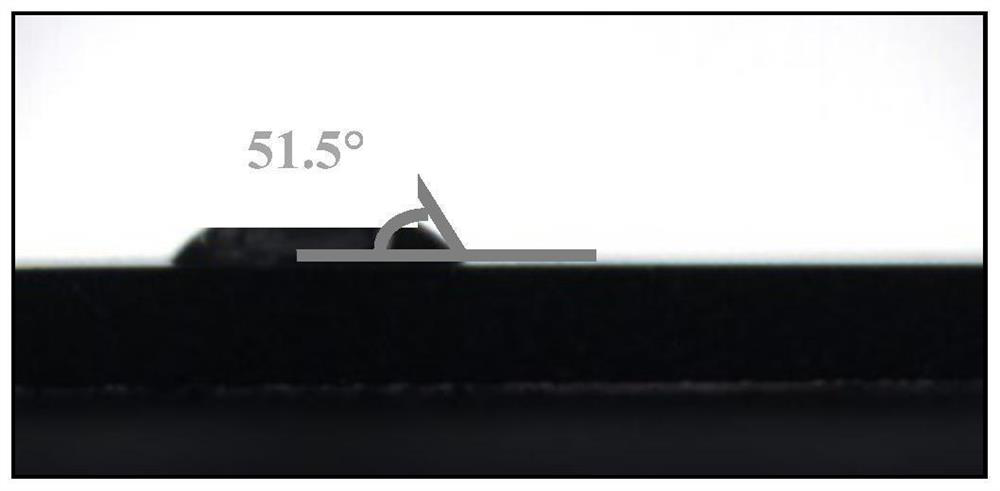
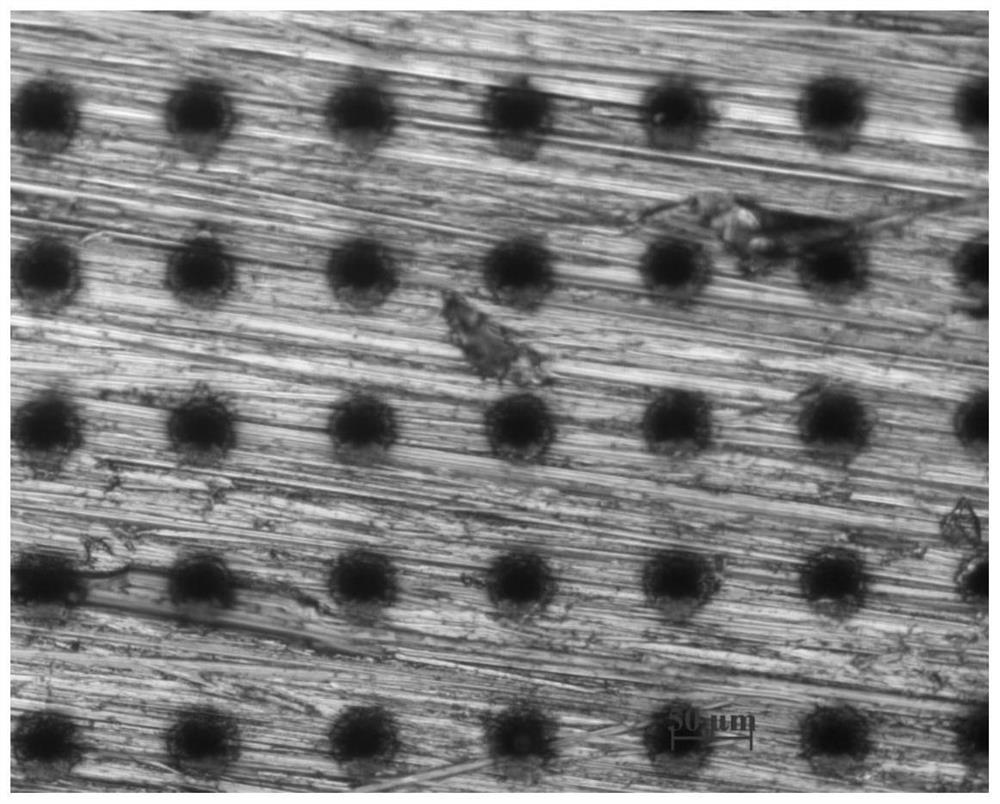
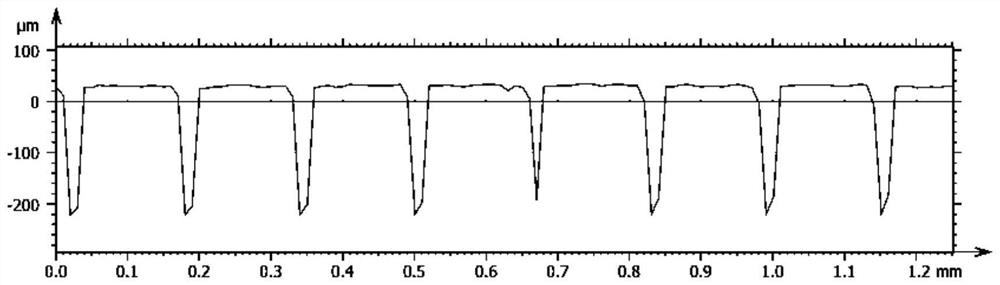
[0046] The invar base material is cut by wire cutting, and the invar base material is polished with 240-grit water-grinding paper until the silver-white metallic luster is exposed. By setting the scanning path of the femtosecond laser as discontinuous non-moving processing, that is, single-point array arrangement, the point spacing is 160 μm, the processing power is 12 W, the number of repetitions is 1, and the single-point dwell time is 10000 μs, and micro-pits are prepared on the surface. shape (such as figure 1 ) shown. Then, the processed Invar alloy was ultrasonically cleaned for 10 minutes, and the in-situ water wetting angle was detected on its surface, and the results were as follows figure 2 shown. The cross section of the micropit is V-shaped (such as image 3 ), that is, the pits have a conical shape (such as Figure 4 ). Compare the original morphology with the wetting angle (e.g. Figure 5 It can be found that the Invar alloy is hydrophilic under this morph...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The invar base material is cut by wire cutting, and the invar base material is polished with 240-grit water-grinding paper until the silver-white metallic luster is exposed. By setting the scanning path of the femtosecond laser to continuous processing, that is, the processing path is a straight line, the line spacing is 160 μm, the processing power is 12 W, the number of scans is 1, and the scanning rate is 1000 mm / s, the microgrooves are prepared on the surface (such as Image 6 ) shown. Then, the processed Invar alloy was ultrasonically cleaned for 10 minutes, and the in-situ water wetting angle was detected on its surface, and the results were as follows Figure 7 shown. The cross-section of the microgroove is V-shaped (such as Figure 8 ), that is, the microgrooves are in the shape of inverted triangular pyramids and inverted triangular strips (such as Figure 9 ). Compare the original morphology with the wetting angle (e.g. Figure 5 ), it can be found that t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com