Construction method and application of lung injury animal model
A lung injury and animal model technology, applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formulation, biological testing, and preparation of test samples, can solve the problems of decreased respiratory compliance of mice, affecting the intensity of lung injury, and not meeting the respiratory rate of mice, etc. , to reduce research costs, avoid stray into the esophagus or nasal cavity, and avoid hidden dangers of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Model of acute pulmonary inflammation induced by non-exposed tracheal perfusion CS
[0046] 1. Preparation before the experiment:
[0047] Preparation of CS suspension: Weigh CS granules, add an appropriate amount of normal saline to prepare CS suspension with a final concentration of 60 mg / mL, sterilize by ultrasonic and autoclave before use (need to shake well before administration to make CS in suspension Evenly distributed).
[0048] 2. Tracheal intubation (experimental group)
[0049] 2-1. The mice were weighed before anesthesia, and the mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% sodium pentobarbital at a dose of 10 mL / kg.
[0050] 2-2. After confirming that the mouse is successfully anesthetized by the tail clamp, use ordinary adhesive tape to fix the mouse limbs on the foam board, and then use rubber bands to fix the mouse upper incisors on the foam board, so that the head and neck of the mouse are in contact with the operator. Keeping...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Construction of LPS-induced acute pulmonary inflammation model in mice
[0071] 1. Preparation before the experiment:
[0072] Prepare LPS solution: Add physiological saline to the LPS powder to a final concentration of 0.4 mg / mL. Ready to use after autoclaving.
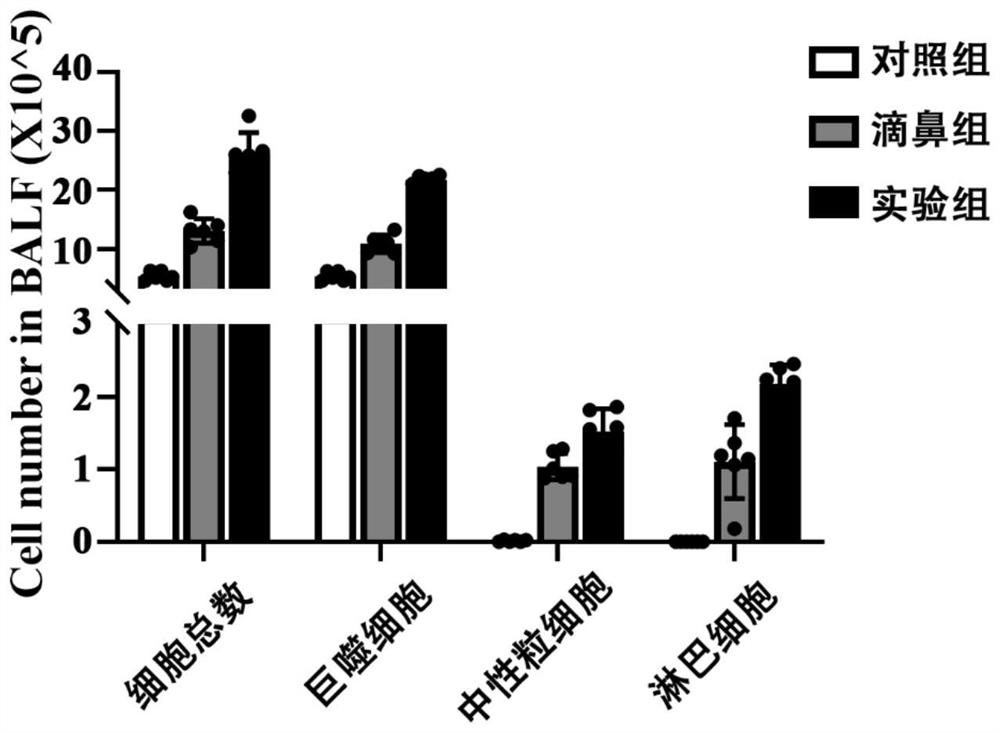
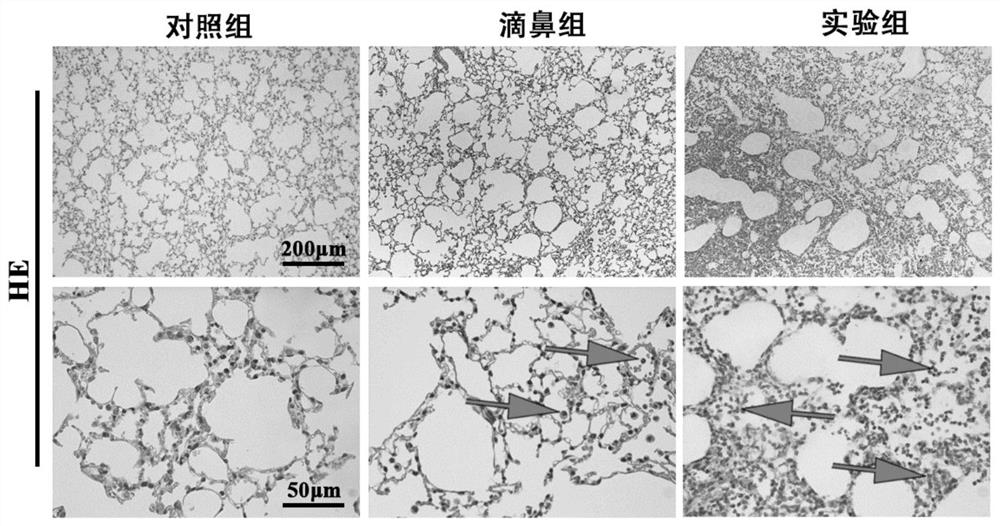
[0073] 2. The operation methods of each group were referred to in Example 1, except that the administered drug was LPS solution, the mice were anesthetized and sacrificed 24 hours after perfusion, the mortality was recorded, and lung tissue was collected.
[0074] 3. Experimental results
[0075] 3-1. The mortality data of mice are shown in Table 2:
[0076] Table 2
[0077]
[0078] Conclusion: At the end of the experiment, only one mouse died in the present invention, and the mortality rate was only 5%, while the mortality rate of the tracheotomy group was as high as 30%, and the mortality rate of the injection group was also as high as about 20%. are significantly higher than the present i...
Embodiment 3
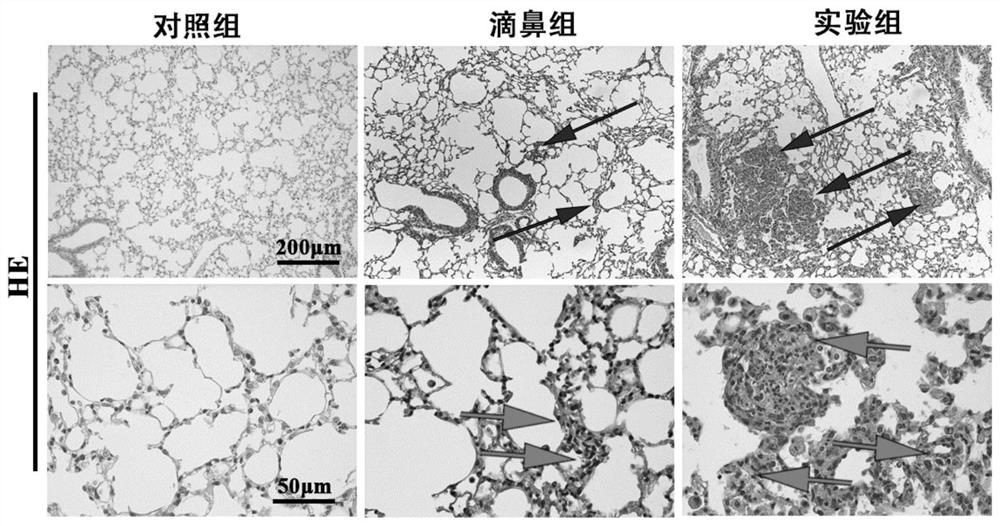
[0081] Example 3 Construction of CS-induced pulmonary fibrosis model in mice
[0082]1. Preparation before the experiment with reference to Example 1
[0083] 2. The operation method of each group was referred to in Example 1, except that after the mice were returned to the SPF animal breeding room by tracheal perfusion, the mice were anesthetized and sacrificed on the 48th day, the mortality was recorded, and the lung tissue was collected for pathological experiments.
[0084] 3. Experimental results
[0085] 3-1. The comparison data of mouse mortality is shown in Table 3
[0086] table 3
[0087]
[0088] Conclusion: At the end of the experiment, the number of dead mice in the present invention was only 3, and the mortality rate was only 15%, while the mortality rates of the tracheotomy group and the injection group were as high as 45% and 25%, respectively, which was significantly higher than that of the present invention. .
[0089] 3-2. See H&E staining results F...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com