Rapid detection method and detection kit for number of bacteria in food
A detection method, food technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem that cannot meet the needs of simple, fast and accurate detection, and cannot meet the requirements of the food field. The need for rapid detection and the increase in production costs have achieved the effect of improving the bacterial interception rate, eliminating the process of colony counting, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
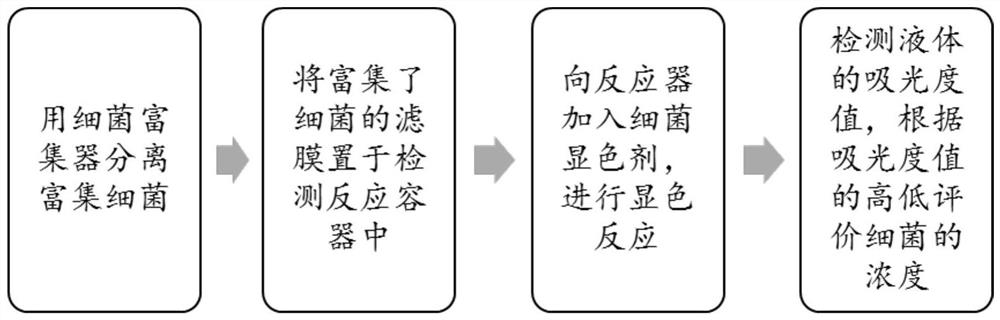
[0047] A rapid detection method for bacterial content of liquid food, comprising the following steps:
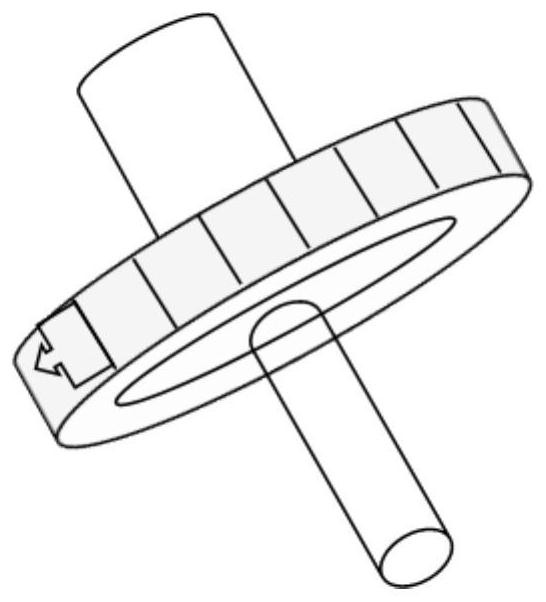
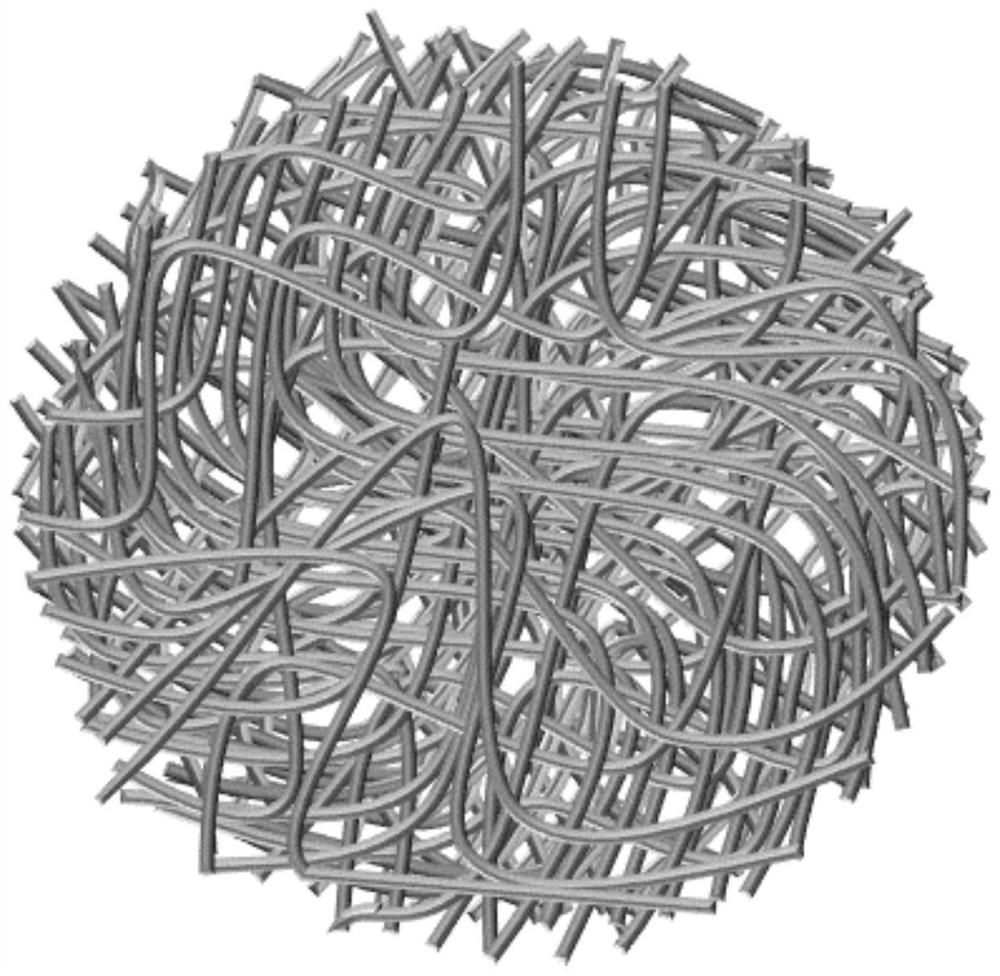
[0048] S1. Use a fiber separation membrane to enrich bacteria in liquid food, beer, etc.; the fiber separation membrane is made of two-layer fiber membranes of cation-modified nanofiber membrane and fluorosilane surface-modified superhydrophobic microfiber membrane by hot pressing; The cationic modified molecules are as follows:
[0049]
[0050] where n is 6.
[0051] S2. Take out the fiber separation membrane enriched with bacteria, put it into a centrifuge tube, make three groups in parallel with the same concentration, and add 4 mL (to ensure that the filter membrane is completely immersed in the solution) CCK-8 solution (with PBS at a ratio of 1:3) Dilution), react in a constant temperature incubator at 35.5 °C for 2 h, and then measure the absorbance value at 450 nm;
[0052] S3. Obtain the bacterial content in the food according to the absorbance value.
Embodiment 2
[0054] A method for rapid detection of bacterial content in solid food is different from Example 1 in that step S1 includes: breaking and dispersing the solid food in water, and then enriching the bacteria in the solid food with a fiber separation membrane. Others are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and are not repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0056] A method for rapid detection of bacterial content in liquid food, compared with Example 1, the difference is that step S1 includes: the first layer is a cation-modified nanofiber membrane, and the second layer is a non-superhydrophobic structure modification. The microfiber film is hot-pressed. Others are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and are not repeated here.
[0057] Whether the liquid food contains bacteria can be judged by the absorbance value of this embodiment, and the bacterial content can be qualitatively judged. If the liquid food contains a small amount of bacteria, the number of bacteria will increase after culture, and then the enrichment detection will have higher sensitivity and higher judgment accuracy. Overcome the problem of not being able to detect directly without culturing when the bacterial content is too low.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com