Antipathogenic synthetic piptides and compositions comprising them
A technology of pathogens and mixtures, which can be used in antiviral agents, drug combinations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as lack of antibacterial activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0106] (v) Preparation of lipid vesicles
[0107] Small unilamellar vesicles (SUV) were prepared by sonication of PC / cholesterol (10:1, w / w) or PC / PS (1:1, w / w) dispersions. Briefly, dry lipid and cholesterol (10:1, w / w) were dissolved in CHCl 3 / MeOH mixture (2:1, V / V). The solvent was then evaporated in a nitrogen stream, and the lipid (concentration: 7.2 mg / ml) was treated in vacuo for 1 hour, then re-dissolved in a suitable buffer with vigorous shaking. The obtained lipid dispersion was sonicated for 5-15 minutes in a tank-type ultrasonic instrument (G1125SP1 ultrasonic instrument, Laboratory Supplies Company Inc. NY) until clear. Lipid concentrations in the resulting preparations were determined by phosphorus analysis (Bartlett, 1959). Vesicles were observed with a JEOL JEM 100B electron microscope (Japen Electron Optics Laboratory Co., Tokyo, Japan) as follows. A drop of vesicles was placed on a carbon-coated grid and negatively stained with uranyl acetate. Examinat...
Embodiment 1
[0127] Example 1 Synthesis and biological activity of diastereomers derived from pardaxin
[0128] 1.1 Synthesis
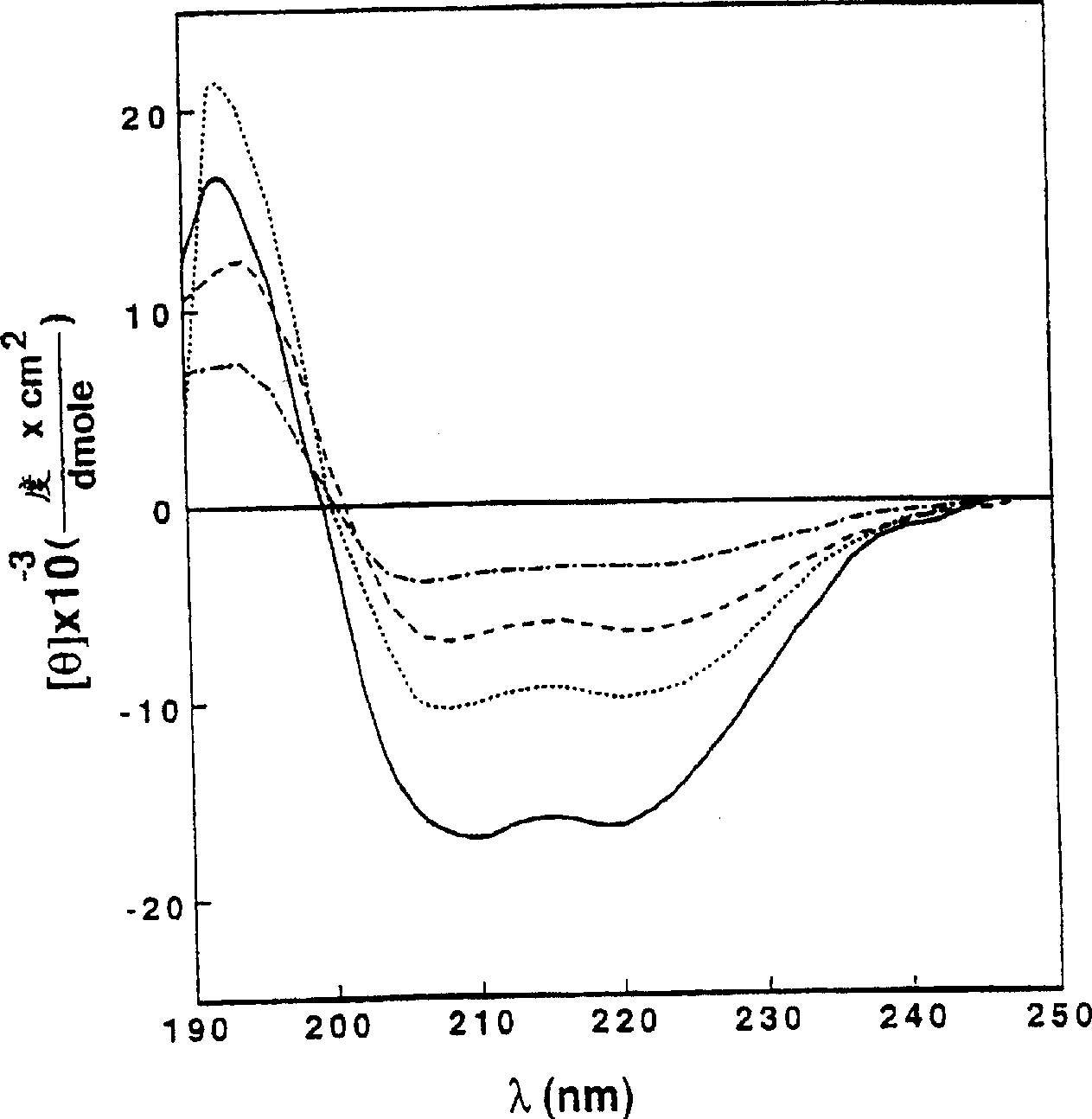
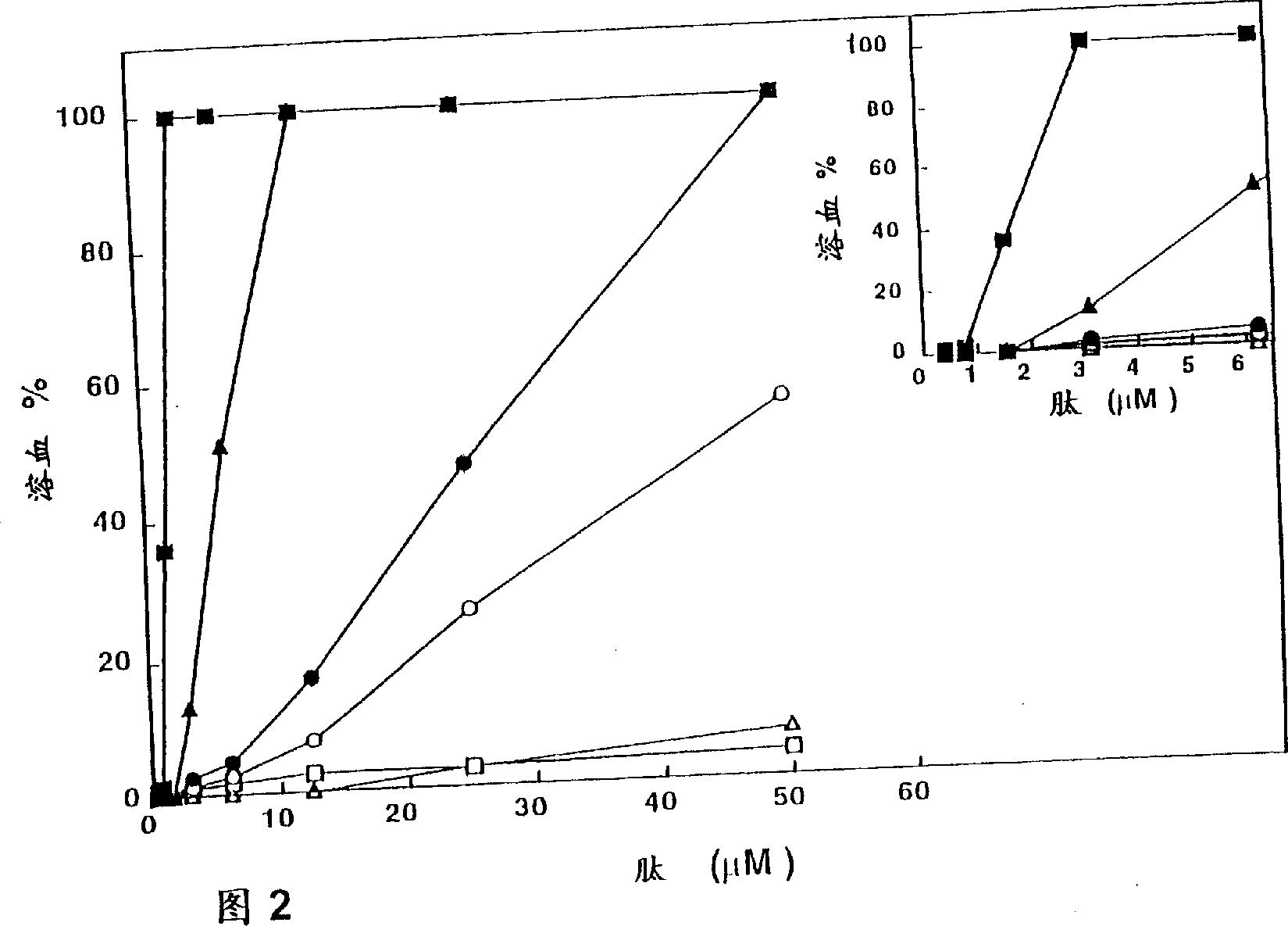
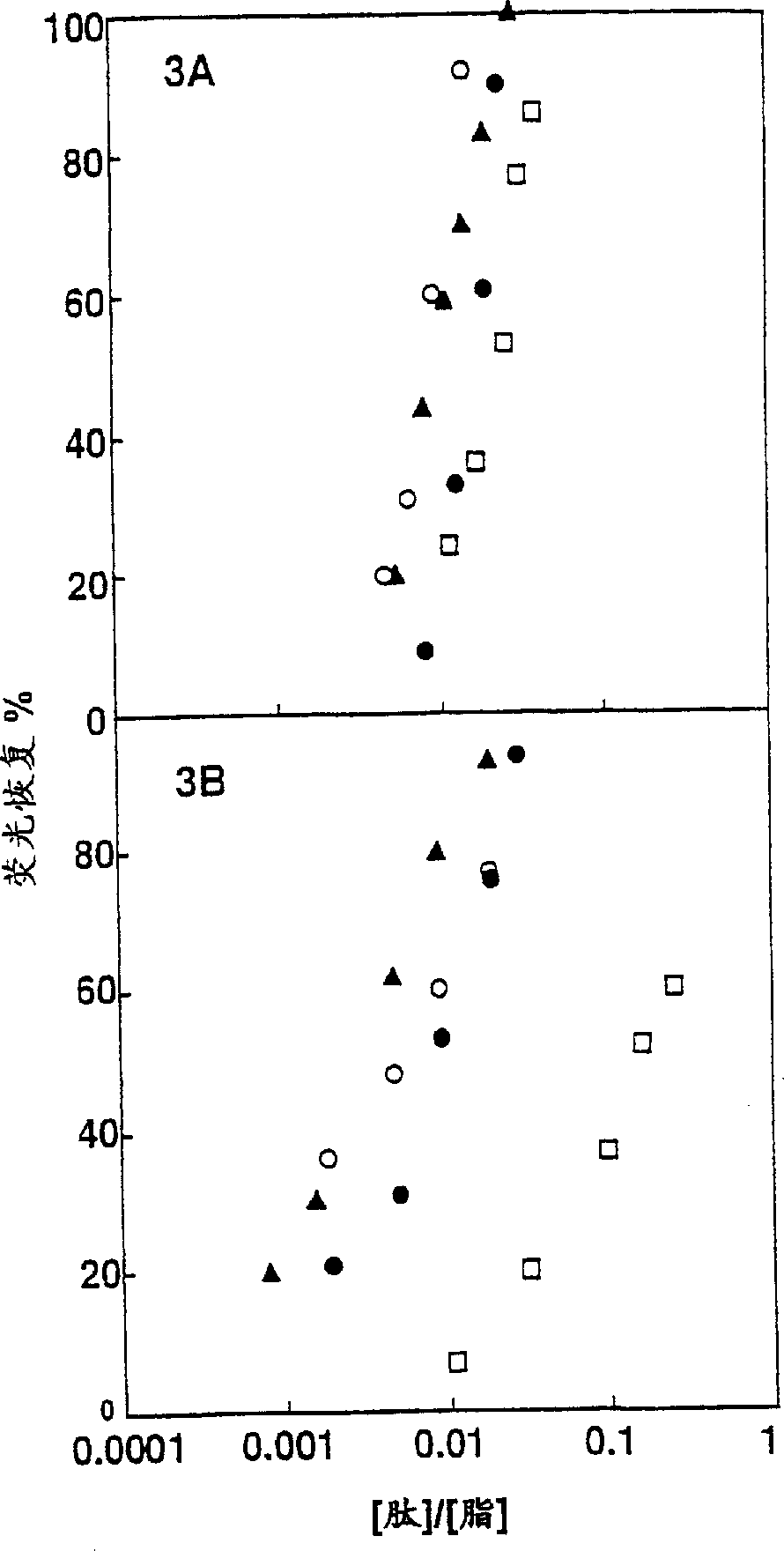
[0129] To examine the role of the α-helical structure of polycationic cytolysins in their cytotoxicity against mammalian cells and bacteria, we synthesized a series of pardaxins as described in Experimental Methods (ii) and (iii) The derived peptides were analyzed for their structure, hemolytic activity on hRBC, antibacterial activity and effect on bacterial morphology.
[0130] pardaxin (par) is a 33-mer peptide with the following sequence
[0131] Gly-Phe-Phe-Ala-Leu-Ile-Pro-Lys-Ile-Ile-Ser-
[0132] Ser-Pro-Leu-Phe-Lys-Thr-Leu-Leu-Ser-Ala-Val-
[0133] Gly-Ser-Ala-Leu-Ser-Ser-Ser-Gly-Gly-Gln-Glu
[0134] To introduce a positive charge, the modification of the pardaxin molecule is carried out by deleting the acidic C-terminus of pardaxin, or converting the acidic C-terminus of pardaxin or its fragments to be positively charged by placing the carboxyl group o...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Example 2 Synthesis and biological activity of diastereomers derived from melittin
[0178] 2.1 Synthesis
[0179] In order to further examine the role of the α-helical structure of cytolysin in its cytotoxicity to mammalian cells and bacteria, and to understand the inner mechanism of this action, we synthesized four diastereomers of melittin (mel).
[0180] melittin is a 26-mer peptide with the following sequence Gly-Ile-Gly-Ala-Val-Leu-Lys-Val-Leu-Thr-Thr-Gly-Leu-Pro-Ala-Leu-Ile-Ser-Trp-Ile -Lys-Arg-Lys-Arg-Gln-Gln-NH 2
[0181] To introduce a positive charge, melittin is modified by converting the acidic C-terminus of melittin or fragments thereof to be positively charged by reacting the C-terminal carboxyl group with ethylenediamine. In melittin diastereomers, the N-helix and C-helix are replaced by D-Val, D-Ile and D-Lys, respectively, of the two Val residues at positions 5 and 8 of melittin, the Ile residue at position 17, Lys residue at position 21 to change ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com