Malaria plasmodium antigen polypeptide se36, method of purifyng the same and vaccine and diagnostic with the use of the thus obtained antigen
a technology of plasmodium plasmodium and polypeptides, which is applied in the field of purifying the same and vaccines with the use of the thus obtained antigen, can solve the problems of insufficient antigenicity and purity of these vaccine antigens, unsatisfactory purification process, and inability to meet the needs of mass production. safety, efficacy or homogeneity,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of SE36 Expression System
[0146] The DNA base sequence of the full length SE36 gene that had been armchair-converted from Pf codons to Escherichia coli codons was divided into 8 fragments. For each divided fragment, a sense (+) strand and an antisense (-) strand were synthesized to obtain 16 single stranded DNA fragments in total (8 pairs), which were annealed to give 8 pairs of double-stranded DNAs. These sequences were ligated each other to give the full length of SE36 gene, from which an expression vector was constructed. In this operation, the basic procedure for cloning and ligation of the synthetic DNA fragments were conducted in accordance with the method of Sambrook et al. (Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989).
[0147] The above respective single-stranded DNA fragments were synthesized using a DNA / RNA synthesizer "Applied Biosystem Model 392" [PE Co., USA]. These synthesized fragments were purified by elect...
example 2
Expression and Purification of SE36
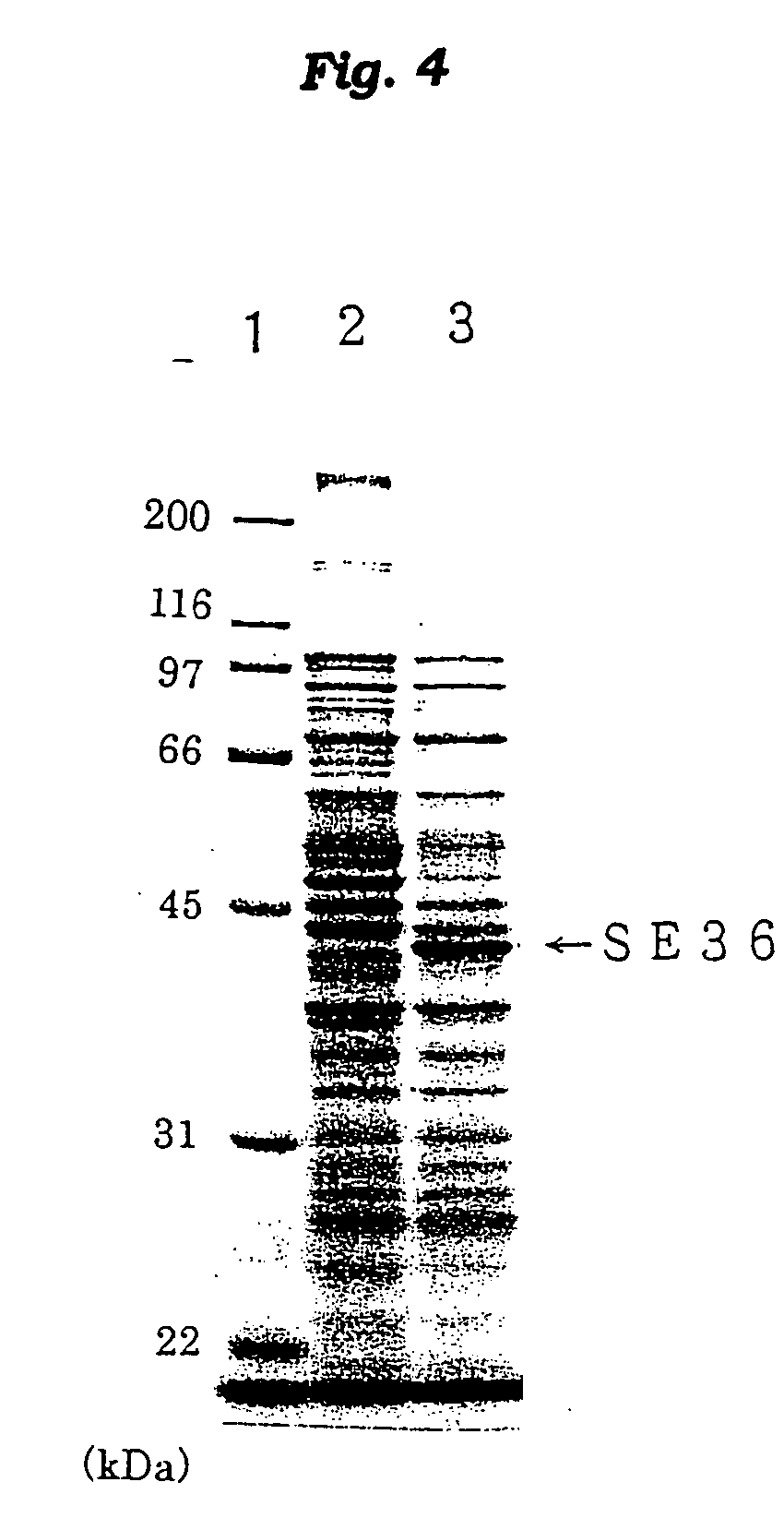
[0149] Escherichia coli BL / SE36 prepared in Example 1 was incubated on an LB medium [Bacto-trypton 1% (w / v), Bacto-yeast extract 0.5% (w / v), and NaCl 1% (w / v)] containing 50 .mu.g / ml of ampicillin at 37.degree. C. for 18 hours to give seeds. The seeds (50 ml) were inoculated on the above fresh LB medium (5 L) and incubated at 37.degree. C. When the cell number reached 1.times.10.sup.8 / ml, IPTG (isopropyl-1-thio-.beta.-D-galactopyran-oside) was added at the final concentration of 50 .mu.g / ml, and further incubated at 37.degree. C. for 3 hours. After termination of the incubation, the mixture was centrifuged (5,000 rpm, 10 minutes) to collect the cells as 3.2 g of cell paste. The paste was suspended into 9.6 ml of an ice-cold lysis buffer solution (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, and 1 mM EDTA). Then, the procedure (1) to (6) was conducted at 4.degree. C. in order as described.
[0150] (1) Sonication The above-described paste cells were treated with ultrasonic...
example 3
Determination of the Amino Acid Sequence
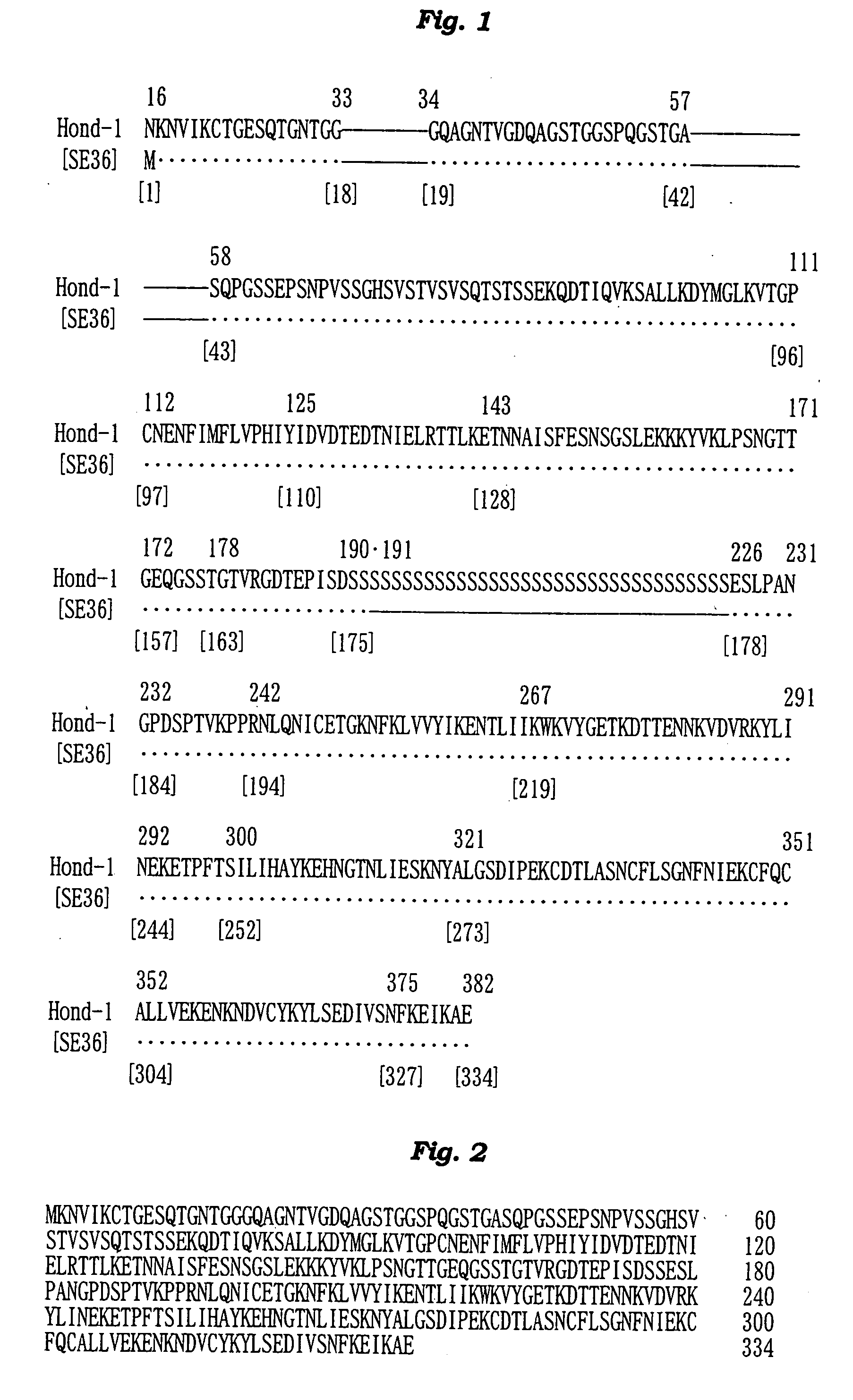
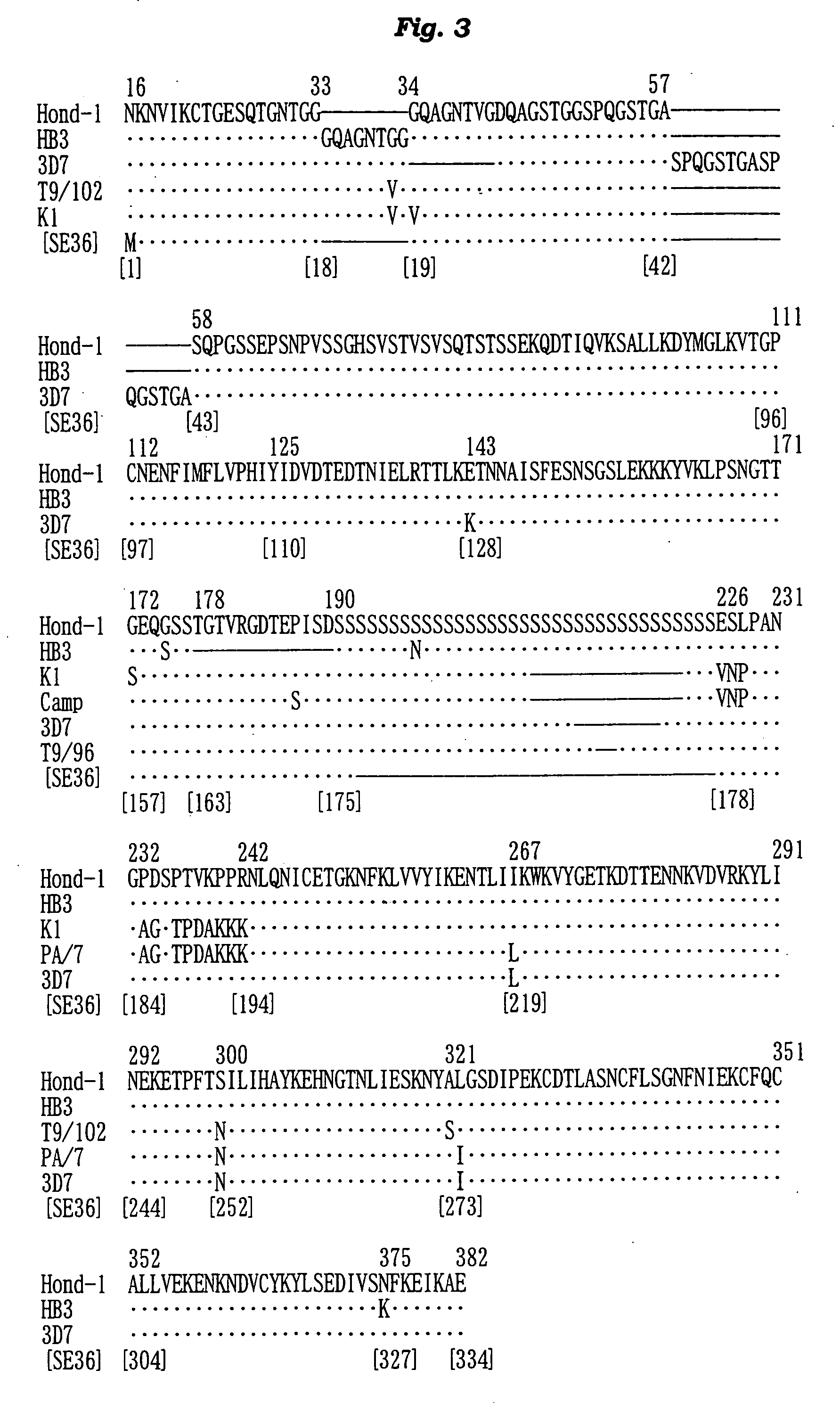
[0162] The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the SE36 protein prepared in Example 2 was determined by the Edman degradation using a protein sequencer Applied Biosystems 473A [PE Co., USA]. The results are shown in FIG. 2 and SEQ ID NO: 4 of Sequence Listing.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com