Novel gene combinations that alter the quality and functionality of soybean oil
A transgenic, soybean plant technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, edible oil/fat, etc., can solve the problems of unstable liquid oil oxidation and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0128] Preparation of oil from soybeans and analysis of fatty acid composition
[0129]All oils used in these examples were prepared according to the following laboratory scale procedure. Harvested soybeans were heated to 180°F in a microwave oven, cooled to room temperature, and crushed with a Roskamp TRC650-6 crushing roller. The soybean hulls were removed with a Kice aspirator and the remaining substantial portion was heated to 180°C and flaked in Roskamp TRC912 flaking rollers. The crude oil was extracted by heating to 60°C for 45 minutes in a glass water jacketed extraction vessel with a solvent to solid ratio of approximately 4:1. The hexane / oil mixture was collected and the extraction repeated. The mixture was desolvated with a rotary vacuum to leave a crude oil.
[0130] An 85% phosphoric acid solution in a volume equivalent to 0.1% (v / v) of the crude oil was added and the solution was heated to 65-70°C for 10 minutes with stirring. Hot (60° C.) sodium hydroxide (8...
example 2
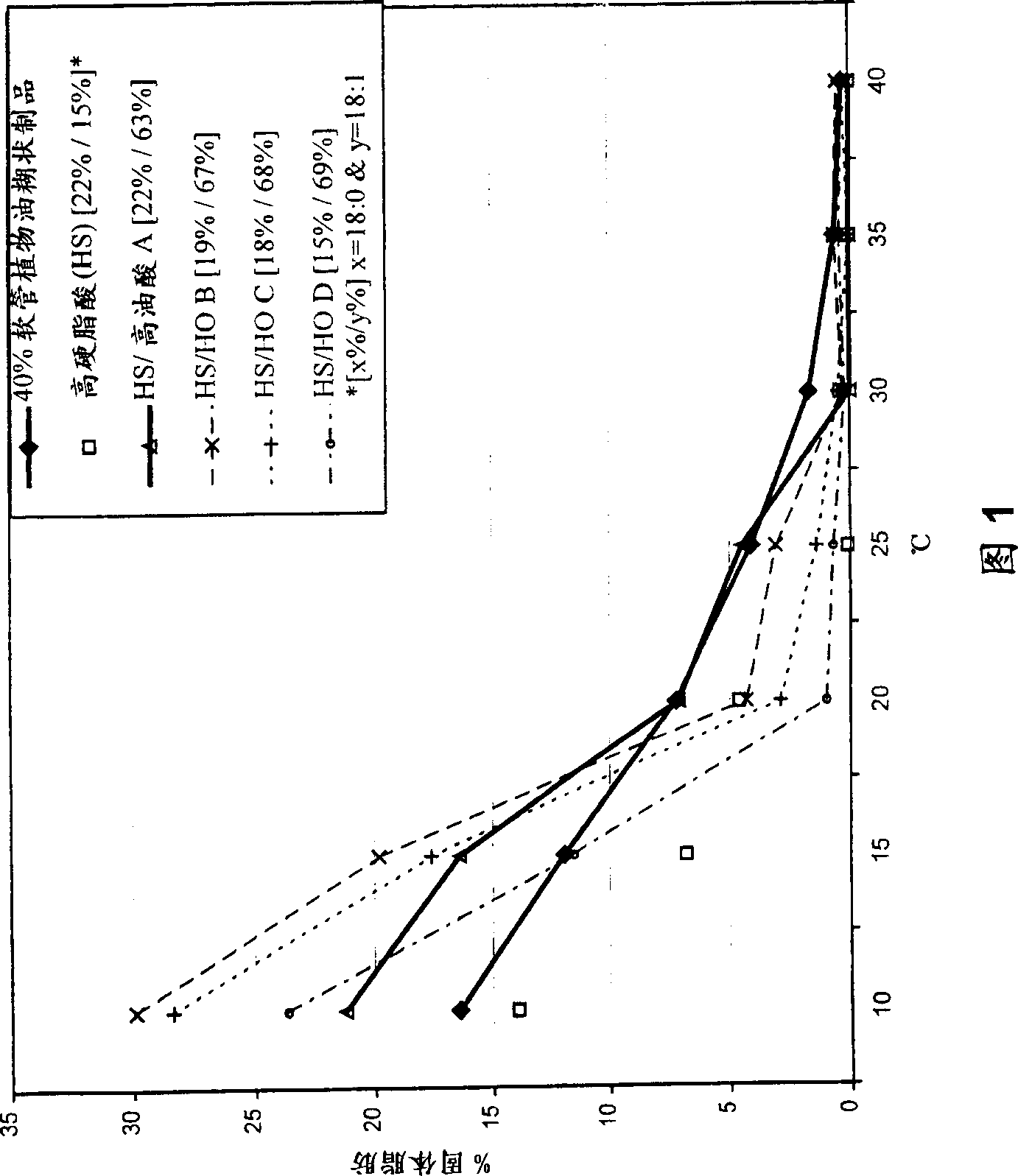
[0136] Solid Fat Content of Commercial Margarine
[0137] Analysis of SFC of commercial margarine samples with different degrees of solidity. Samples were prepared by melting the article at 100°C and removing the aqueous layer. The SFC of the obtained fat fractions was analyzed as a function of temperature, the results of which are given in Table 4. The table represents the different types of margarines and pastes that can be used to produce different types of margarines and pastes depending on the plasticity of the fat and the desired product form (eg tubes, bars, low fat pastes).
[0138] Table 4
[0139] Solid fat content of commercial margarine at different temperatures
[0140] Function Product form 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
[0141] 68% Vegetable Oil Paste Stick 24.2 23.5 16.2 8.5 4.1 0.9 0.5
[0142] 40% Vegetable Oil Paste Stick 22.2 21.7 15 8 3.6 1.1 0.0
[0143] 70% Corn Oil Paste Stick 31.0 25.8 17.6 10.9 5 0.7 0.1
[0144] 40% vegetable oil paste hose 16.4 11.9 7...
example 3
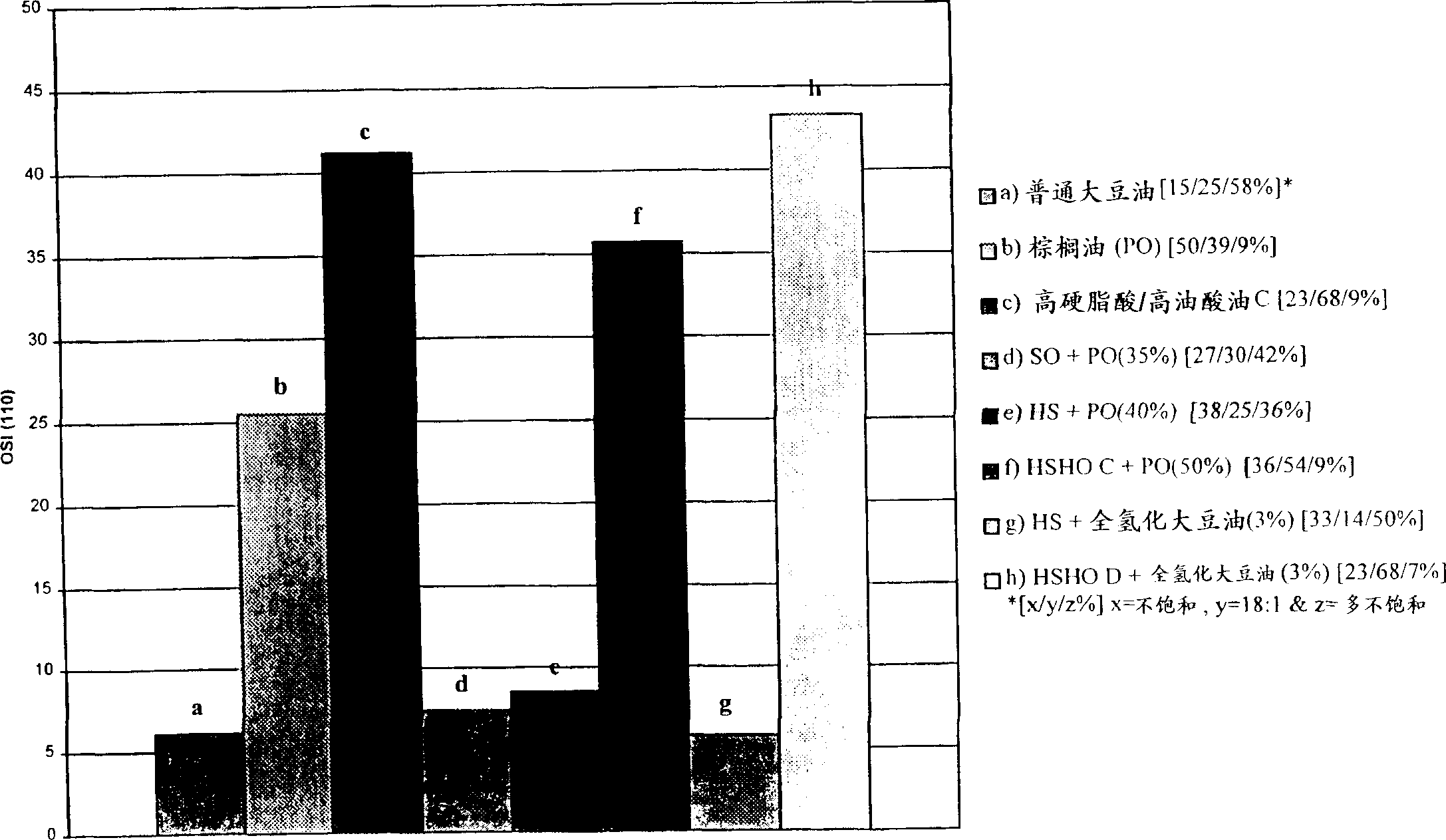
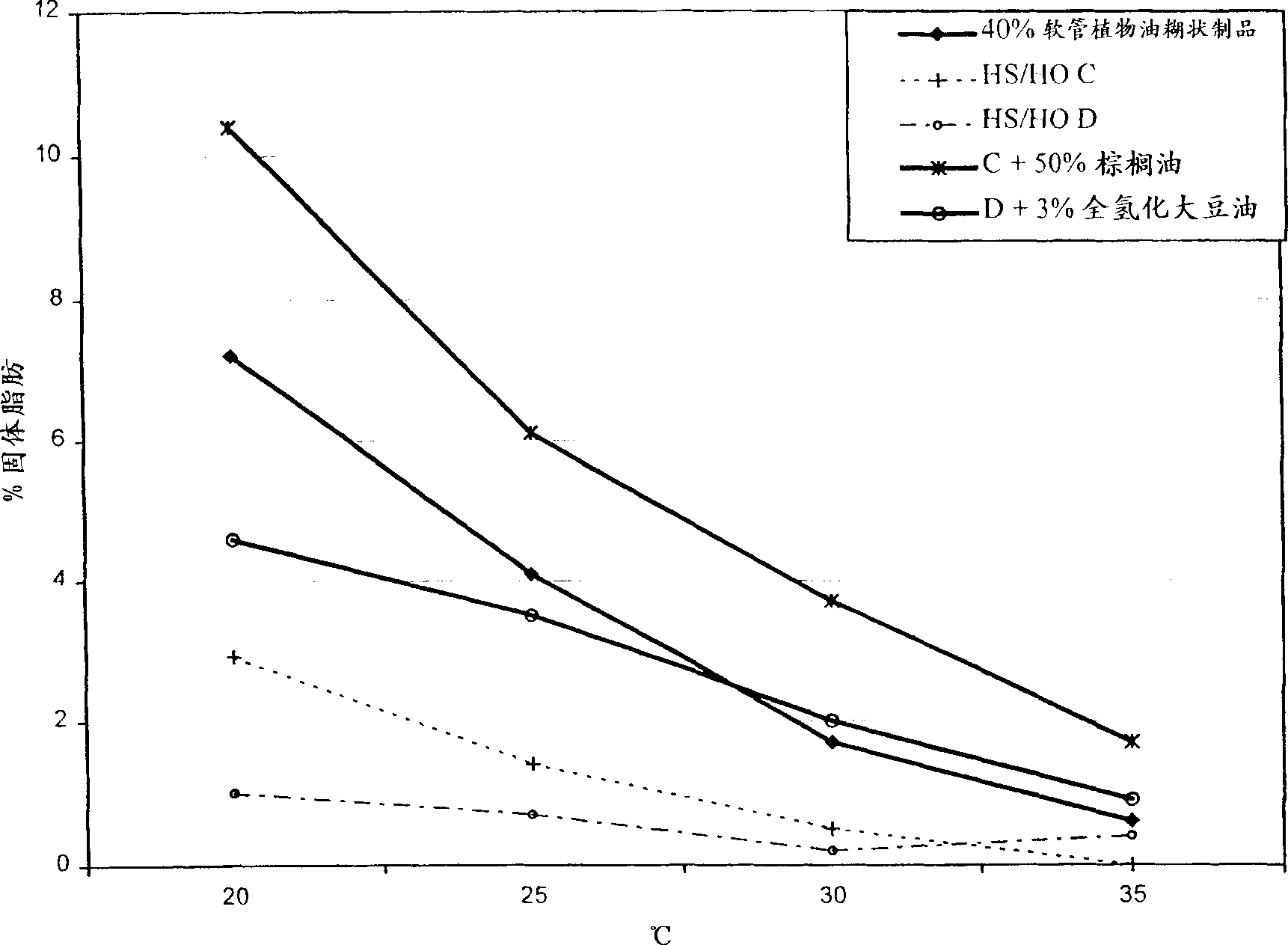
[0152] Solid fat content of high stearic soybean oil
[0153] From a high stearic acid soybean known as L9216116-109, which was produced by DuPont with a pedigree (HST1 * (HO2 * HO4)) * A2506 was bred (which means progeny from the cross HO2 and HO4 were crossed with HST1 and the resulting progeny were crossed with the wild type line A2506 to generate L9216116-109). The resulting seeds have a higher content of stearic acid and a lower content of linolenic acid than conventional soybeans. Parents HST1, HO2 and HO4 (see Table 2) were screened by the mutagenesis method disclosed in US5710365, except that different soybean lines were used as raw materials for mutagenesis, and the screen was based on changes in fatty acid content , rather than carbohydrate content. HST1 is a mutant of N85-2176, which is a high oleic and low linolenic strain, bred by J.W.Burton in North Carolina, USA (Kuhr et al., N85-2124, N85-2131 and N85 on March 26, 1987 - Sales Announcement for 2176. USDA A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com