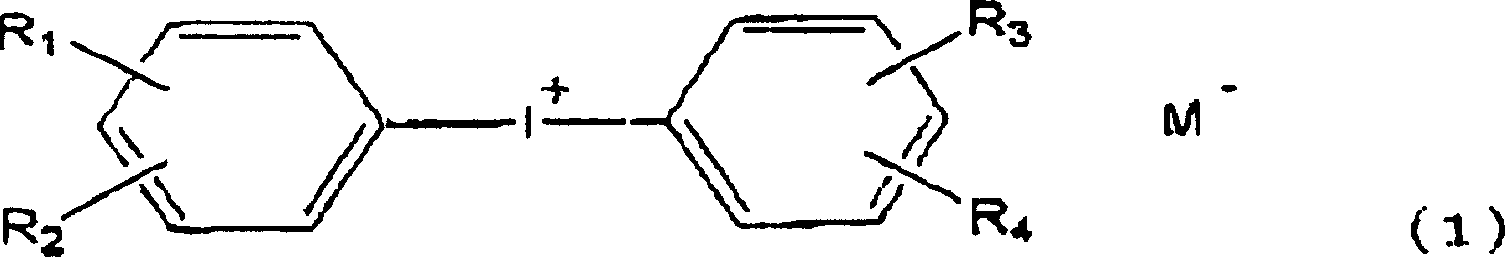
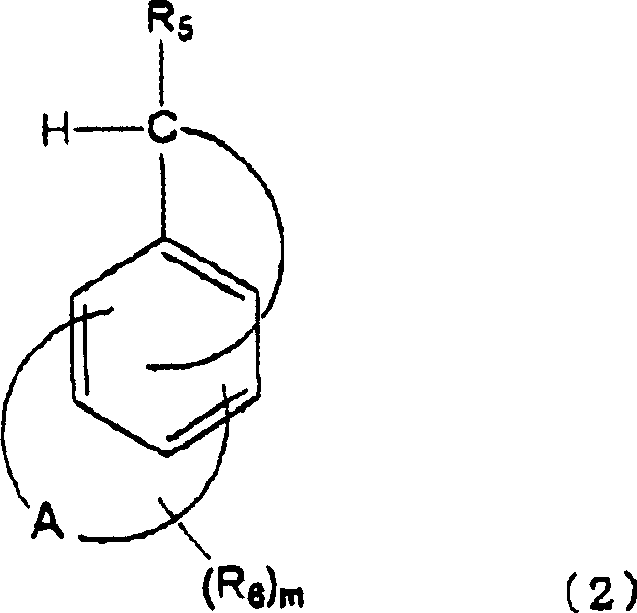
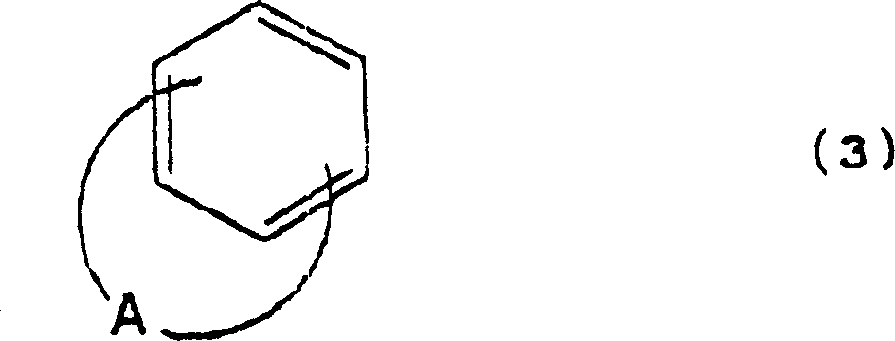
Cation photopolymerization evocator and composition with cation photopolymerization
A photopolymerization initiator, cationic technology, applied in the direction of photosensitive materials, optics, photosensitive materials, etc. for optomechanical equipment, can solve the problems of insufficient curing depth, inability to act as a dental polymerization initiator, and low polymerization rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0119] The present invention will now be specifically described by means of examples, but the present invention is by no means limited by these examples. Described below are the compounds and their abbreviated forms used in the specification and examples.
[0120] (A) Compounds that generate photoacids:
[0121]
[0122] (B) Fused polycyclic aromatic compounds:
[0123]
[0124]
[0125]
[0126] (Note: DOXAn, TCHAn, An, BAn, Pery, and DOAn are not fused polycyclic aromatic compounds for use in the present invention)
[0127] (C) Cationic polymerizable monomers:
[0128]
[0129]
[0130] (D) Other.
[0131] CQ: Camphorquinone
[0132] DMBE: Ethyl N,N-Dimethylaminobenzoate
[0133] Described below are methods for evaluating material properties presented in the specification and examples.
[0134] (1) Gelation time
[0135] A cationically polymerizable monomer solution containing the cationic photopolymerization initiator of the present invention was ad...
Embodiment 1 to 19
[0147] To 100 parts by mass of cationically polymerizable monomers (as shown in Table 1), 0.2 parts by mass of photoacid-generating compounds and 0.05 parts by mass of fused polycyclic aromatic compounds (as shown in Table 1) were added, and then Let it dissolve. The gel time, curing performance and curing depth of the solution are shown in Table 1. In all examples, the solutions gelled rapidly and exhibited good curing properties.
Embodiment 20 to 25
[0194] Solution A was prepared by dissolving 0.8 parts by mass of DPISb and 0.2 parts by mass of DPP into 100 parts by mass of a mixture of OX-2 / EP-1 (95 / 5 by mass) in the dark. Further prepare solution B (the mixture of OX-2 / EP-2 with a mass ratio of 95 / 5), solution C (the mixture of OX-2 / DV with a mass ratio of 95 / 5) and solution D in a similar manner (A mixture of BOE / EP-2 with a mass ratio of 50 / 50 was used).
[0195] Suspend 20 grams of quartz powder (5 microns in particle size) in 80 ml of acetic acid aqueous solution. The pH of the acetic acid aqueous solution is adjusted to 4.0, and 0.8 g of 3-glycidyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane is added thereto under stirring. After stirring for one hour, water was distilled off using an evaporator. The resulting solid was pulverized in a mortar and then dried at 80°C under reduced pressure for 15 hours. After drying, the resulting powder is designated as Inorganic Filler F1.
[0196] Similarly, inorganic filler F2 was prepared using s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com