Sodium purifying process and purification system thereof
A technology of purification process and purification system, which is applied in the field of nuclear grade sodium purification process and its purification system for reactors, and can solve the problems of removal and difficulty in applying industrial scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
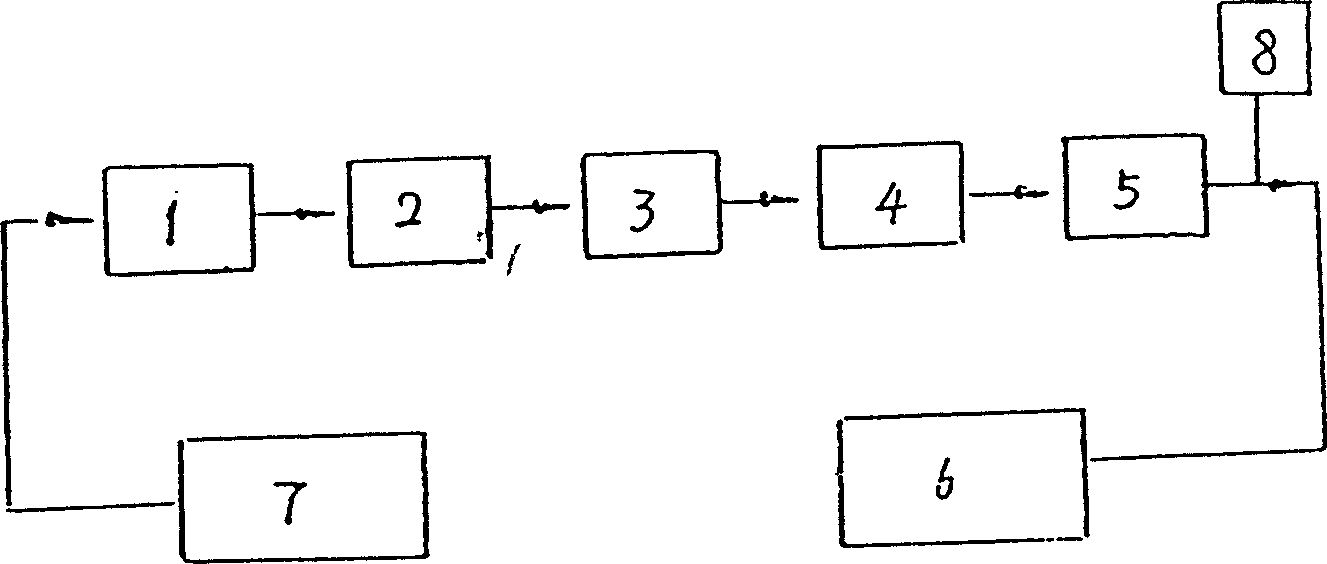
[0039] A kind of sodium purification process, its technological process is:
[0040] Step 1 Calcium removal reaction
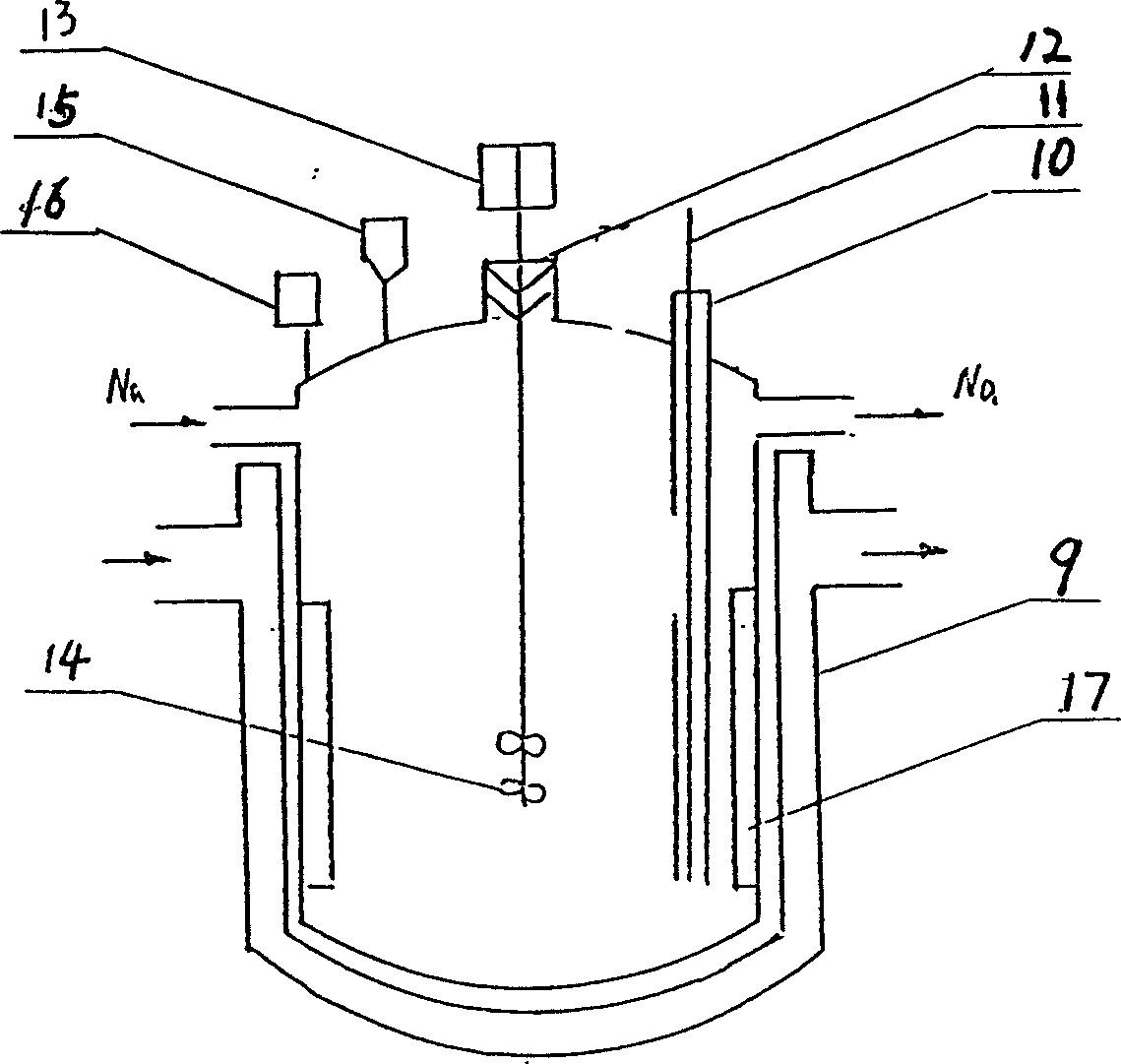
[0041] The reaction reagent Na with an OAC coefficient of 1.4 2 o 2 Add it into the decalcification reactor 1, then press into the industrial sodium to be treated from the sodium receiving tank 7, stir, and maintain the reaction temperature at 350°C for 28 hours.
[0042] Step 2 Primary Settlement
[0043] When the reacted sodium was cooled to 200° C., the valve was opened to enter the primary settler 2 to settle impurities for 45 hours. The low temperature of 140°C is maintained at the bottom of the primary settler 2, and the temperature difference between the upper part and the bottom of the primary settler 2 is maintained.
[0044] Step 3 primary filter
[0045] The precipitated sodium was passed through the wire-filled cold trap 3 at 140° C., and filtered.
[0046] Step 4 Secondary Settlement
[0047] The sodium passing through the screen-filled cold ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A kind of sodium purification process, its technological process is:
[0063] Step 1 Calcium removal reaction
[0064] The reaction reagent Na with an OAC coefficient of 1.2 2 o 2 Add it into the decalcification reactor 1, then press into the industrial sodium to be treated from the sodium receiving tank 7, stir, and maintain the reaction temperature at 300°C for 15 hours.
[0065] Step 2 Primary Settlement
[0066] When the reacted sodium was cooled to 190° C., the valve was opened to enter the primary settler 2 to settle impurities for 40 hours. The low temperature of 130° C. is maintained at the bottom of the first-stage settler 2, and the temperature of the upper part is kept higher than that of the lower part.
[0067] Step 3 primary filter
[0068] The precipitated sodium was passed through the wire-filled cold trap 3 at 135° C., and filtered.
[0069] Step 4 Secondary Settlement
[0070] The sodium passing through the screen-filled cold trap 3 enters the s...
Embodiment 3
[0083] A kind of sodium purification process, its technological process is:
[0084] Step 1 Calcium removal reaction
[0085] The reaction reagent Na with an OAC coefficient of 1.5 2 o 2 Put it into the decalcification reactor 1, then press into the industrial sodium to be treated from the sodium receiving tank 7, stir, and maintain the reaction temperature at 360°C for 30 hours.
[0086] Step 2 Primary Settlement
[0087] When the reacted sodium was cooled to 210° C., the valve was opened to enter the primary settler 2 to settle impurities for 50 hours. The low temperature of 150° C. is maintained at the bottom of the first-stage settler 2 , and the temperature difference between the upper part and the lower part of the first-stage settler 2 is maintained.
[0088] Step 3 primary filter
[0089] The settled sodium was filtered by passing through the wire-filled cold trap 3 at 145°C.
[0090] Step 4 Secondary Settlement
[0091] The sodium passing through the screen-fil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com