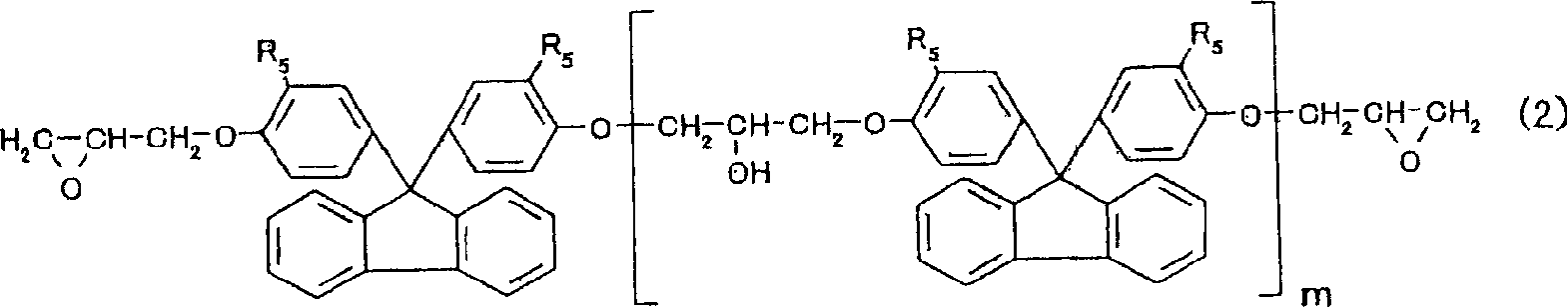
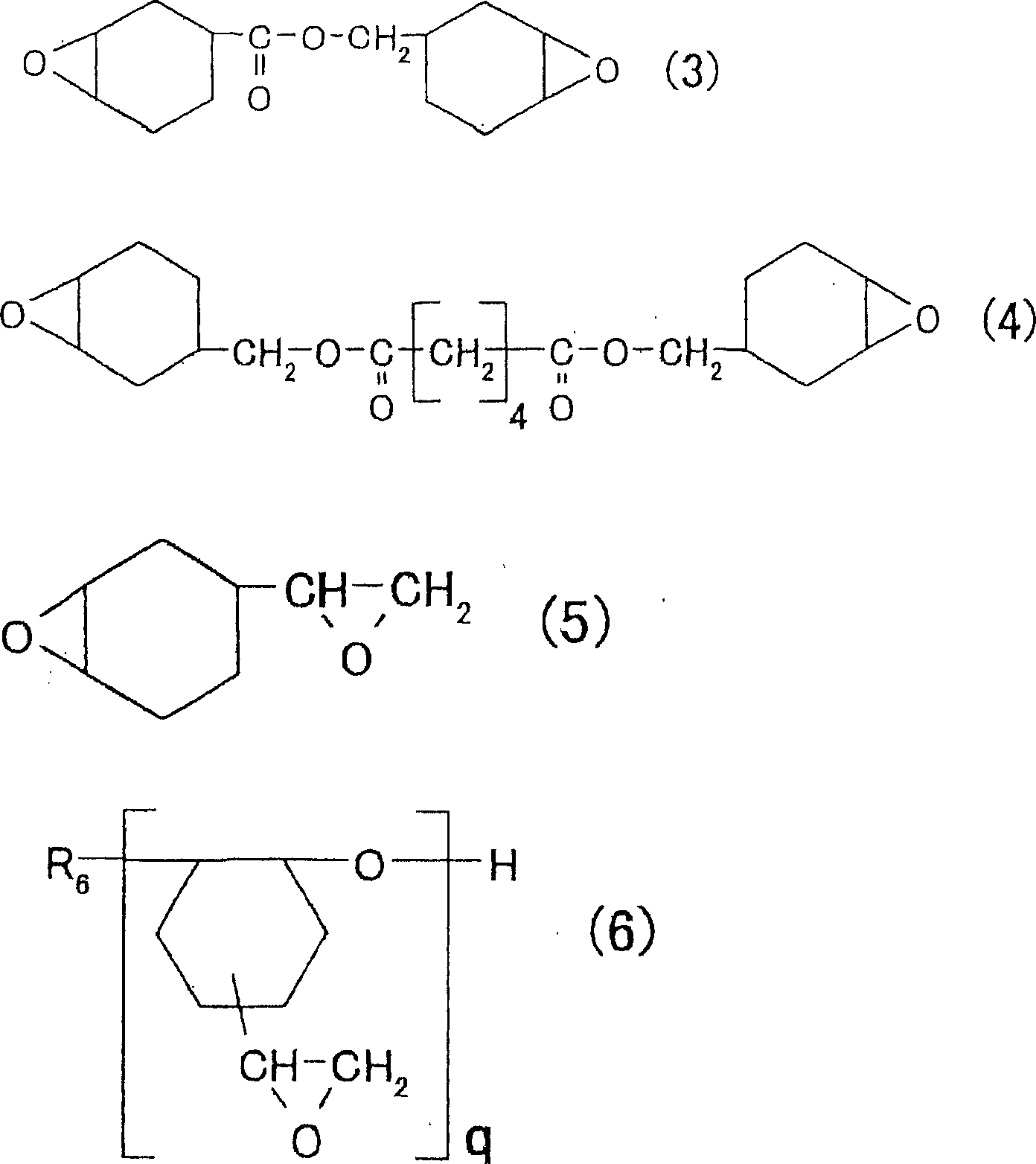
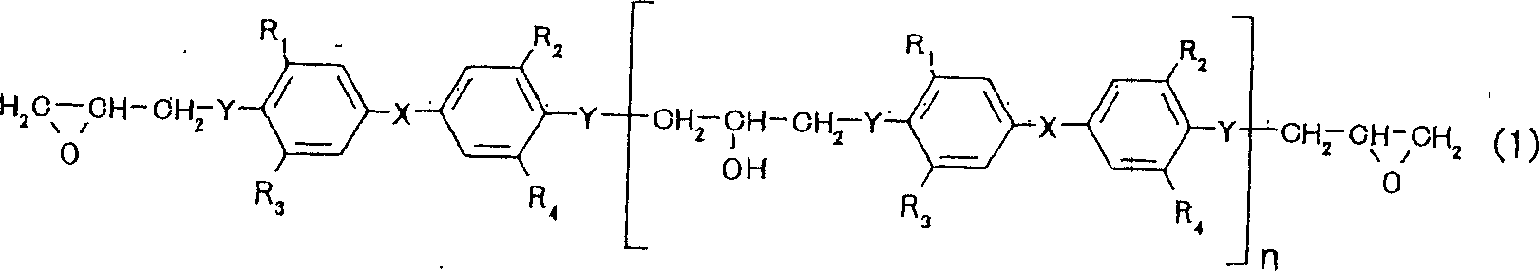Transparent composite composition
A composite material and composition technology, applied in thin material handling, instrumentation, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as damage to the transparency of the substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Organic substances were removed by firing S glass-based glass cloth (thickness 100 μm, refractive index 1.530, manufactured by Unitika Cloth, #2117 type), and then treated with γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (epoxysilane). On this glass cloth, a resin composed of 90 parts by weight of triglycidyl isocyanurate (manufactured by Nissan Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., TEPIC), bisphenol S-type ring, and 110° C. 10 parts by weight of epoxy resin (manufactured by Dainippon Ink Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., EPICLON EXA1514), 170 parts by weight of methyl hydrogenated norbornene diacid anhydride (manufactured by Shin Nippon Chemical Co., Ltd., Rikacid HNA-100), and tetraphenylphosphine bromide (North Xing Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., TPP-PB) 2 parts by weight. The glass cloth is sandwiched between the glass plates that have been released from the mold, and heated in an oven at 100°C for 2 hours, then heated at 120°C for 2 hours, at 150°C for 2 hours, and at 175°C for 2 hours to o...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A resin composed of the following compounds melt-mixed at 110° C. was impregnated on an S-glass-based glass cloth subjected to the same treatment as in Example 1, and defoamed. The above compounds are 62.5 parts by weight of triglycidyl isocyanurate (manufactured by Nissan Chemical Industry, TEPIC), 27.5 parts by weight of bisphenol S-type epoxy resin (manufactured by Dainippon Ink Chemical Industry, EPICLON EXA1514), 27.5 parts by weight of methylhexahydro-ortho 120 parts by weight of phthalic anhydride (manufactured by Shinnippon Chemical Co., Ltd., Rikacid MH-700), and 1.4 parts by weight of tetraphenylphosphine bromide (manufactured by Hokko Chemical Industries, Ltd., TPP-PB). This glass cloth was sandwiched between glass plates subjected to mold release treatment, and heat-treated in an oven under the same conditions as in Example 1 to obtain a transparent sheet with a thickness of 0.1 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0073]Organic matter was removed by burning E glass-based glass cloth (thickness 100 μm, refractive index 1.560, manufactured by Unitika Cloth, #2117 type), and then treated with γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (epoxysilane). A resin composed of the following compounds melt-mixed at 110° C. was dipped and defoamed on the glass cloth. The above compounds are 20 parts by weight of triglycidyl isocyanurate (manufactured by Nissan Chemical Industry, TEPIC), 80 parts by weight of bisphenol S-type epoxy resin (manufactured by Dainippon Ink Chemical Industry, EPICLON EXA1514), methyl hydrogenated 75 parts by weight of bornenedioic anhydride (manufactured by Shinnippon Chemical Co., Ltd., Rikacid HMA-100), and 1 part by weight of tetraphenylphosphine bromide (manufactured by Hokko Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., TPP-PB). This glass cloth was sandwiched between glass plates subjected to mold release treatment, and heat-treated in an oven under the same conditions as in Example 1 to obta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com