N-formyl peptide receptor complex with a G-protein kinase signal pathway modification agent
A G protein and complex technology, applied in hormone receptors, peptide/protein components, animal/human proteins, etc., can solve unexplained and unanswered questions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
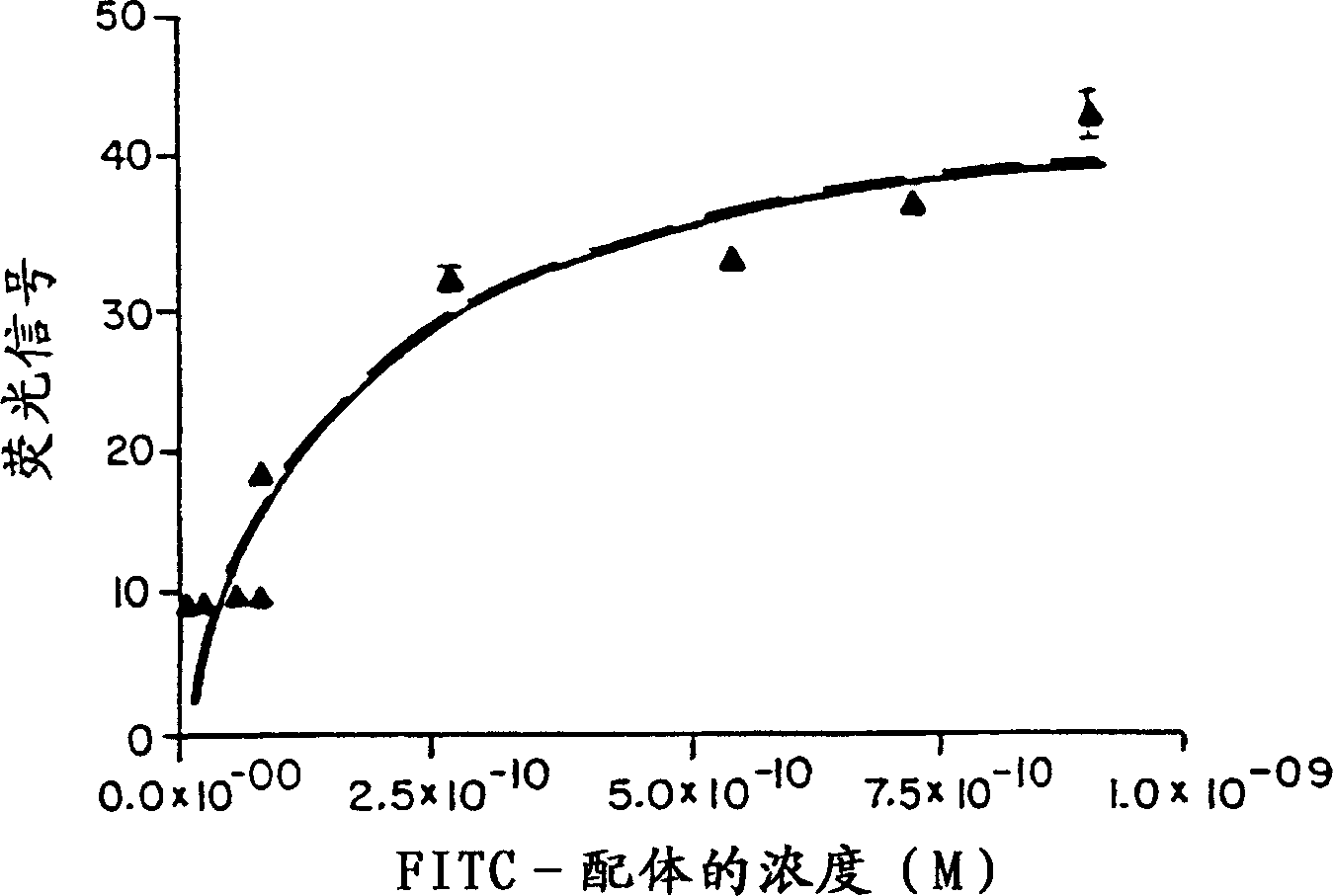
[0065] Example 1: Binding of labeled HK-X to peripheral blood nucleated cells
[0066] Kd and Bmax (saturation binding) of HK-X ("f-Met-Leu-Phe-Phe") on peripheral blood nucleated cells were determined. 2 × 10 of the various fractions (monocytes, lymphocytes, granulocytes) prepared by density centrifugation in 100 μl of the solution were pre-washed in 1% BSA-PBS solution containing 0.1% sodium azide. 5 cells. According to Table 1, add 100 μl of FITC-labeled HK-X (dissolved in 1% BSA-PBS solution) at the following molar concentration to each group of test tubes:
[0067] pipe number
FITC-labeled HK-X molar concentration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9.06×10 -12
2.71×10 -11
5.43×10 -11
7.25×10 -11
9.06×10 -11
2.71×10 -10
5.43×10 -10
7.25×10 -10
9.06×10 -10
[0068]The tubes were mixed and vortexed for 30 seconds. The tubes were then placed at 4-8°C for 30 minutes. Then add 100 μl Cal-Lyse and incubate for 5 minutes,...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2: Binding of HK-X to activated receptors
[0071] At 24 or 120 hours of culture, peripheral blood lymphocytes were stimulated with the mitogen Concanavalin A (ConA). These cells were then either exposed or not exposed to 100 nM FITC-labeled HK-X. Cells were stained with DAPI to determine the cell cycle. Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry.
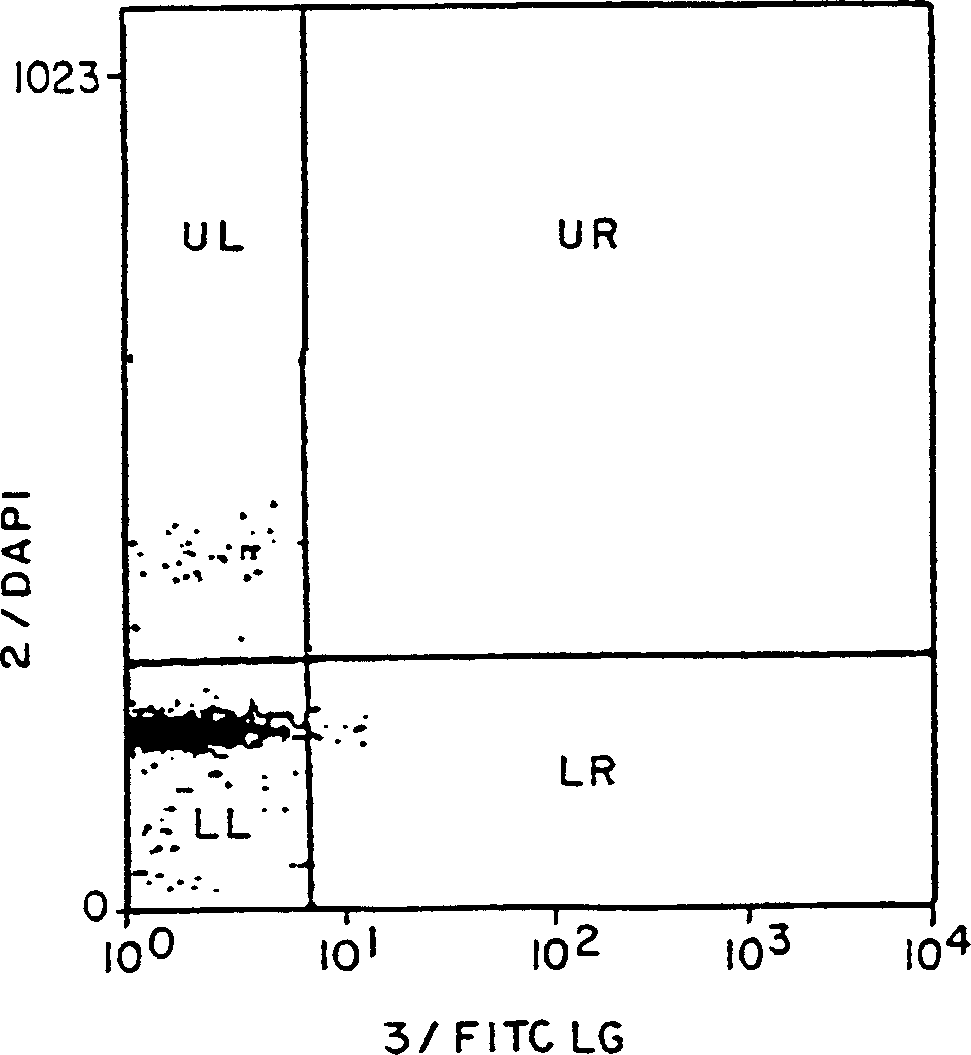
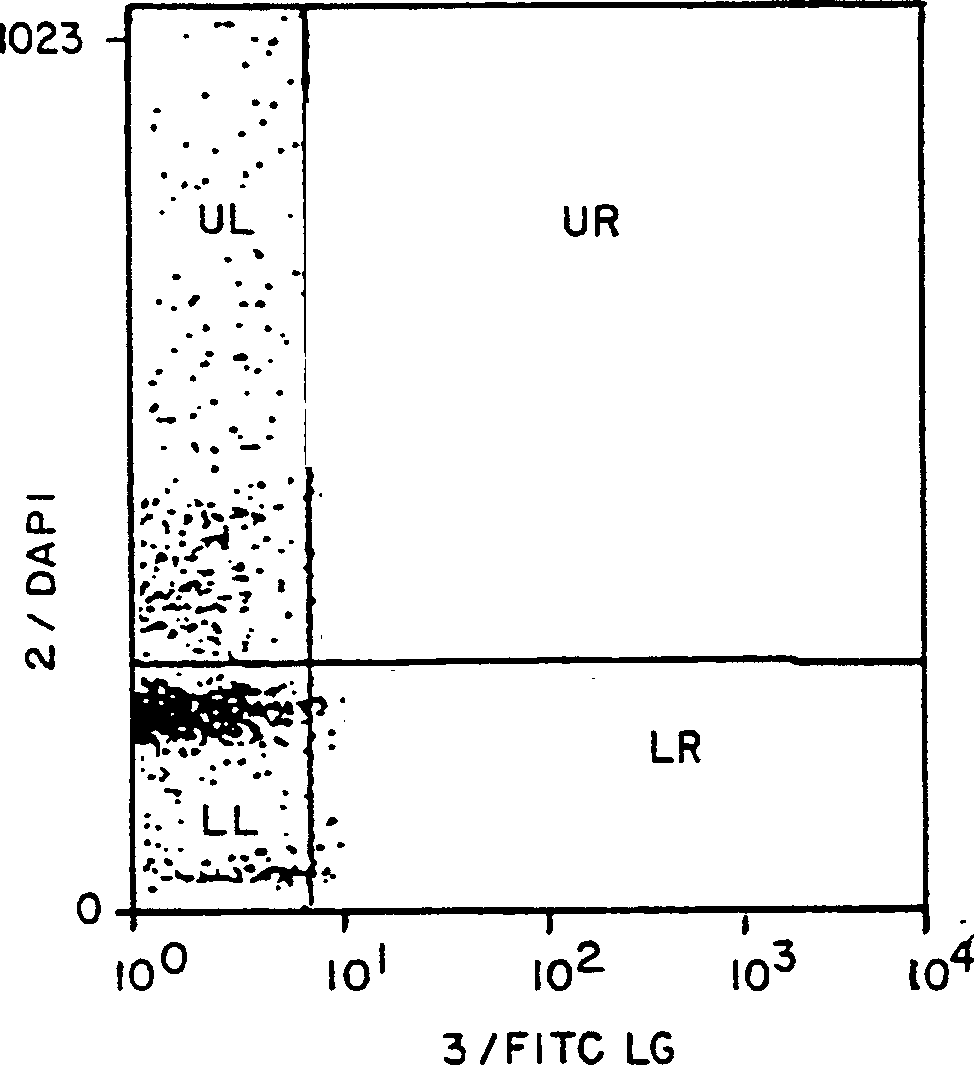
[0072] Figures 2A-2C The relationship between ConA-activated lymphocytes and the appearance of binding sites for FITC-labeled HK-X is shown. These four quadrants display the following characteristics:
[0073] Upper left quadrant represents DNA content above 1n with background levels (using figure 1 Cells with increased FITC HK-X binding levels above as determined by the distribution curve of
[0074] The upper right quadrant represents cells with DNA content exceeding 1n and FITC-ligand binding above background;
[0075] The lower right quadrant contains cells with 1 n DNA content but bound FITC-ligand above...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3: Identification and Characterization of HK-X Receptors
[0083] Isolation and characterization of receptors that bind HK-X and other N-formyl peptides from murine peritoneal mast cells, human polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cell populations. Moreover, G protein activation of FCεR receptors acts as an increase in PKC, PI3 and Ca 2+ As a downstream consequence of mobilization, FCε receptors become downstream effector receptors of interfering G proteins.
[0084] Cells that bind HK-X include mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils, as evidenced by changes in bioreactivity upon exposure to HK-X, and binding to fluorescently or radioactively labeled HK-X cell. A receptor for HK-X has not been identified. In contrast, neutrophils express formyl peptide receptors on their surface. However, blood lymphocytes and monocytes appear to bind HK-X less than neutrophils.
[0085] Detailed Materials and Methods
[0086] 1. Isolation of Cells - Rat peritoneal mast cells...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com