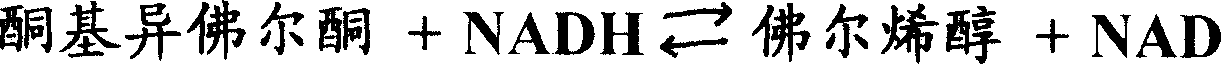Process for producing phorenol
A technology of phorenol and ketoisophorone, which is applied in the field of producing phorenol, and can solve the problems of low optical purity of the product and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0027] Column: ULBON HR-20M (Shinwa, Japan) 0.25mmφ×30m
[0028] Column temperature: 160°C (constant)
[0029] Syringe temperature: 250°C
[0030] Carrier gas: He (about 1ml / min)
[0031] After the reaction, Forsenol in the reaction mixture can be recovered, for example, by extraction with a water-immiscible organic solvent that readily dissolves Forsenol, such as ethyl acetate, n-hexane, toluene, or n-butyl acetate. Finish. Further purification of forsenol can be done by concentrating the extract to directly crystallize forsenol or by a combination of various chromatography (such as thin-layer chromatography, adsorption chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography or high-performance liquid chromatography). phase chromatography) to achieve.
[0032] The following examples further illustrate the invention.
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Production of Forsenol using Corynebacterium aquaticus AKU611 (FERM BP-6448)
[0034] Corynebacterium aquaticus AKU611 (FERM BP-6448) was inoculated in 1.0g / L yeast extract, 15.0g / L Bacto-peptone (Difco laboratories, U.S.A), 0.2g / LMgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 3.0g / LK 2 HPO 4 , 2.0g / L NaCl and 22.4g / L glucose·H 2 O seed medium (100 mL, in a 500 mL flask), and cultivated at 30° C. with rotary shaking for 24 hours. Part (100ml) of the seed culture was inoculated with 8.0g / L yeast extract, 0.2g / L MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.01g / L MnSO 4 ·4-5H 2 O, 2.0g / L NaCl and 11.1g / L glucose·H 2Production medium for O (3.0 L, in a 5-L scale fermenter; type MJ-5-6, L.E. Marubishi, Japan). Culture was performed at 30°C with agitation at 600 r.p.m. and aeration at 1.0 vvm. The pH was maintained at 7.0 by using ammonium solution. After approximately 9 hours of incubation, glucose supplementation was started at a feed rate of 20 g / hour. After 24 hours from the start of fermentation, each con...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: Clone L-diketone reductase gene from Aquatic Corynebacterium AKU611 (FERM BP-6448) genomic DNA
[0036] Genome DNA of Corynebacterium aquaticus AKU611 (FERMBP-6448) was prepared using Genome Isolation Kit (BIO101). Using the prepared genomic DNA as a template, a thermal cycler (Perkin elmer 2400, U.S.A.) was used to amplify the full-length coding sequence of the L-diketone reductase gene without redundant flanking regions by PCR amplification. The two synthetic primers used are as follows:
[0037] LV-ORF(+): (5'-GGAGGC GAATTC ATGACCGCAACCAGCTCC-3') (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0038] (The underlined sequence is the position of the EcoRI site)
[0039] LV-ORF(+): (5'-GGGCTG CTGCAG TCAGTACGCGGCGGA-3') (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0040] (The underlined sequence is the position of the PstI site)
[0041] The PCR mixture (0.02 ml) contained 5 pmol of each primer, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, and 1 U of LA Taq (Takara Shuzo co. LTD / Kyoto, Japan). The initial template denaturation ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com