Real-time detector for laser beam quality factor M2
A laser beam quality and real-time detection technology, applied in the field of detectors, can solve the problems of difficult phase distribution measurement, inability to realize real-time detection, cumbersome operation, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient manufacture, compact structure and small volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
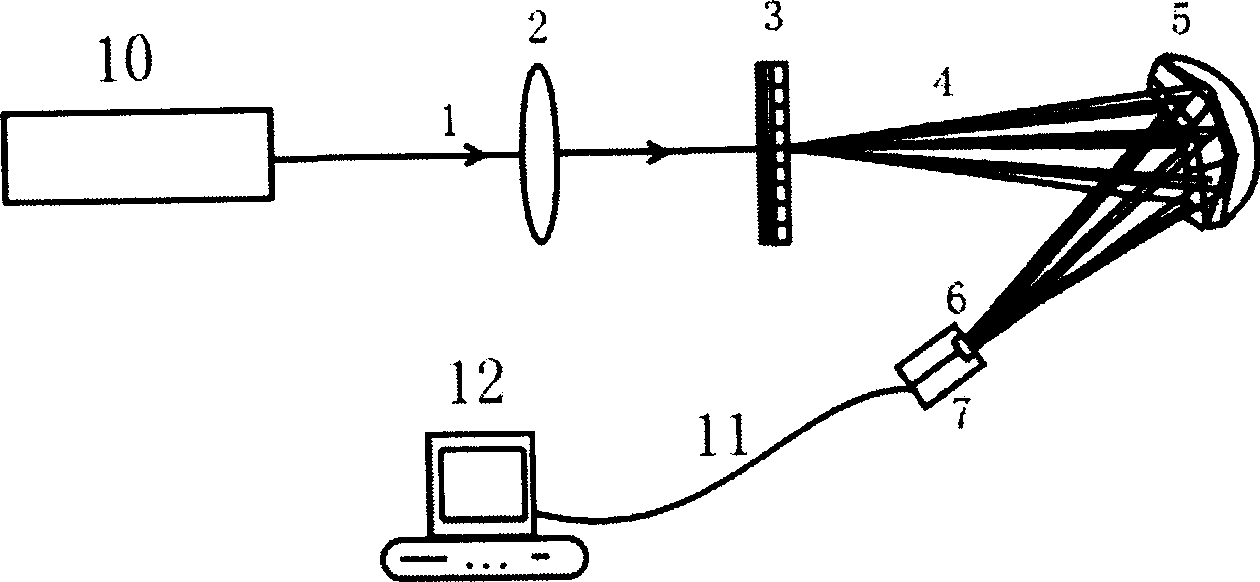
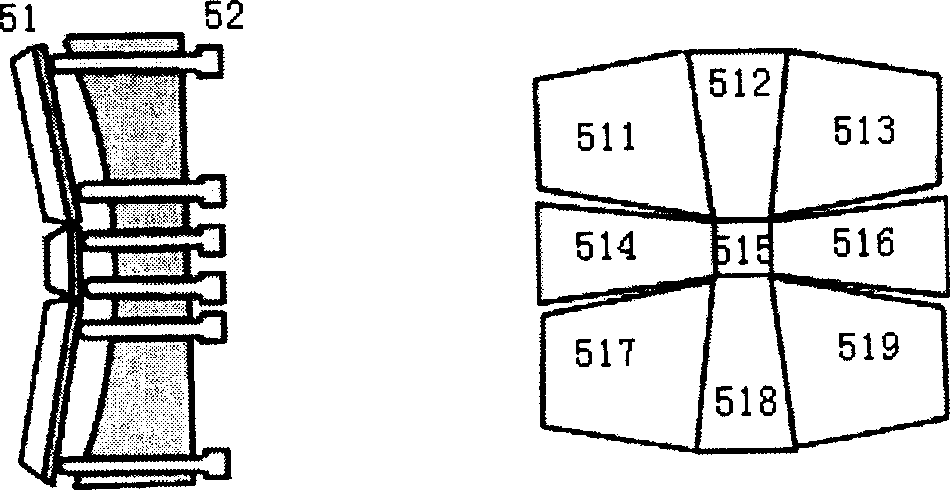
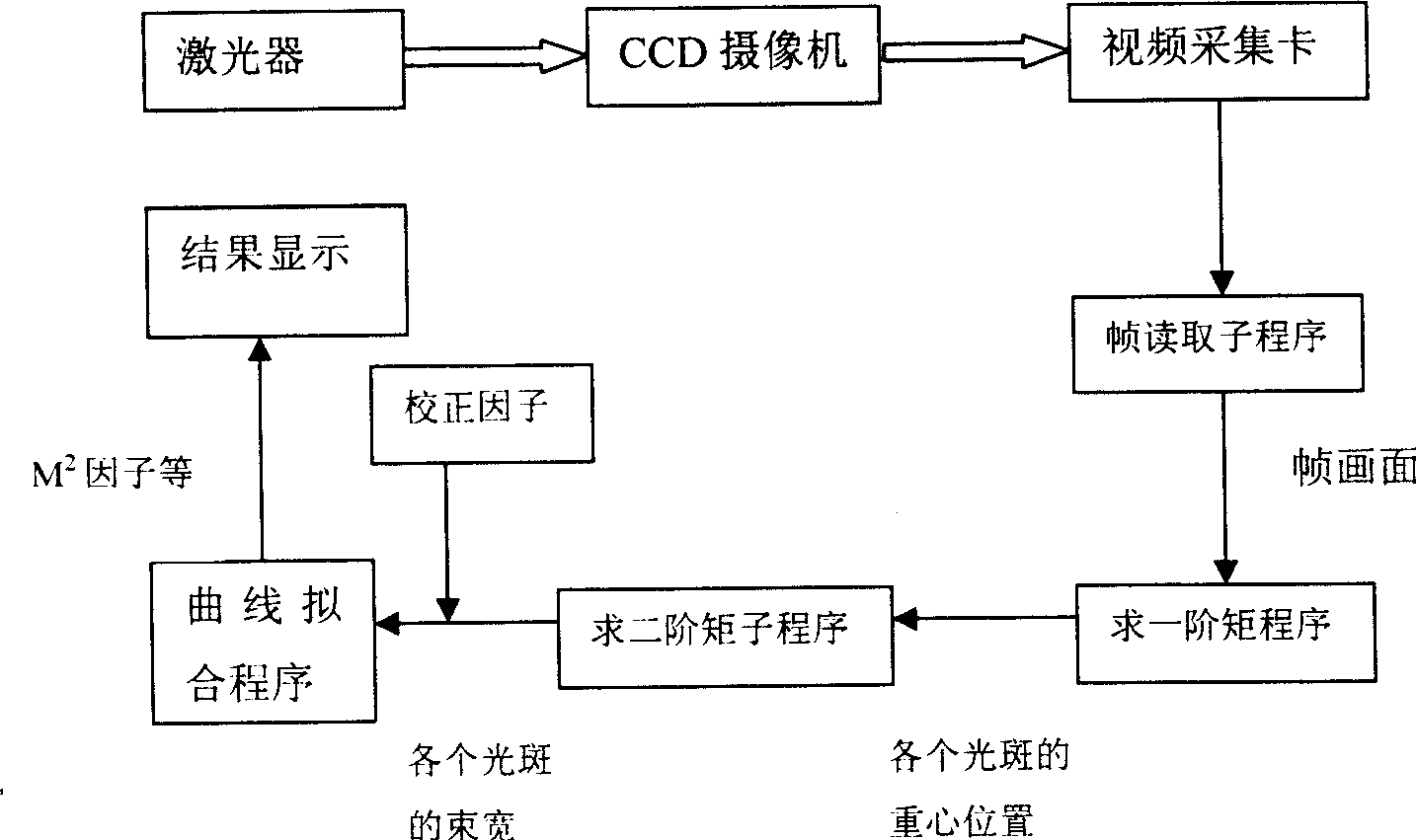
[0020] see first figure 1 , figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the laser beam quality factor real-time detector of the present invention. As can be seen from the figure, the composition of the laser beam quality factor real-time detector of the present invention is: a focusing lens 2, a grating group 3, an optical path adjuster 5, and a CCD 7 that are sequentially arranged on the same optical path in the advancing direction of the laser beam 1 to be measured that the laser 10 emits , the output end of the CCD7 is connected to the computer 12 through the signal line 11, the focal length of the focusing lens 2 is f, and the diameter is D, and the grating group 3 is composed of two gratings placed close to each other in an orthogonal manner The compact grating ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com