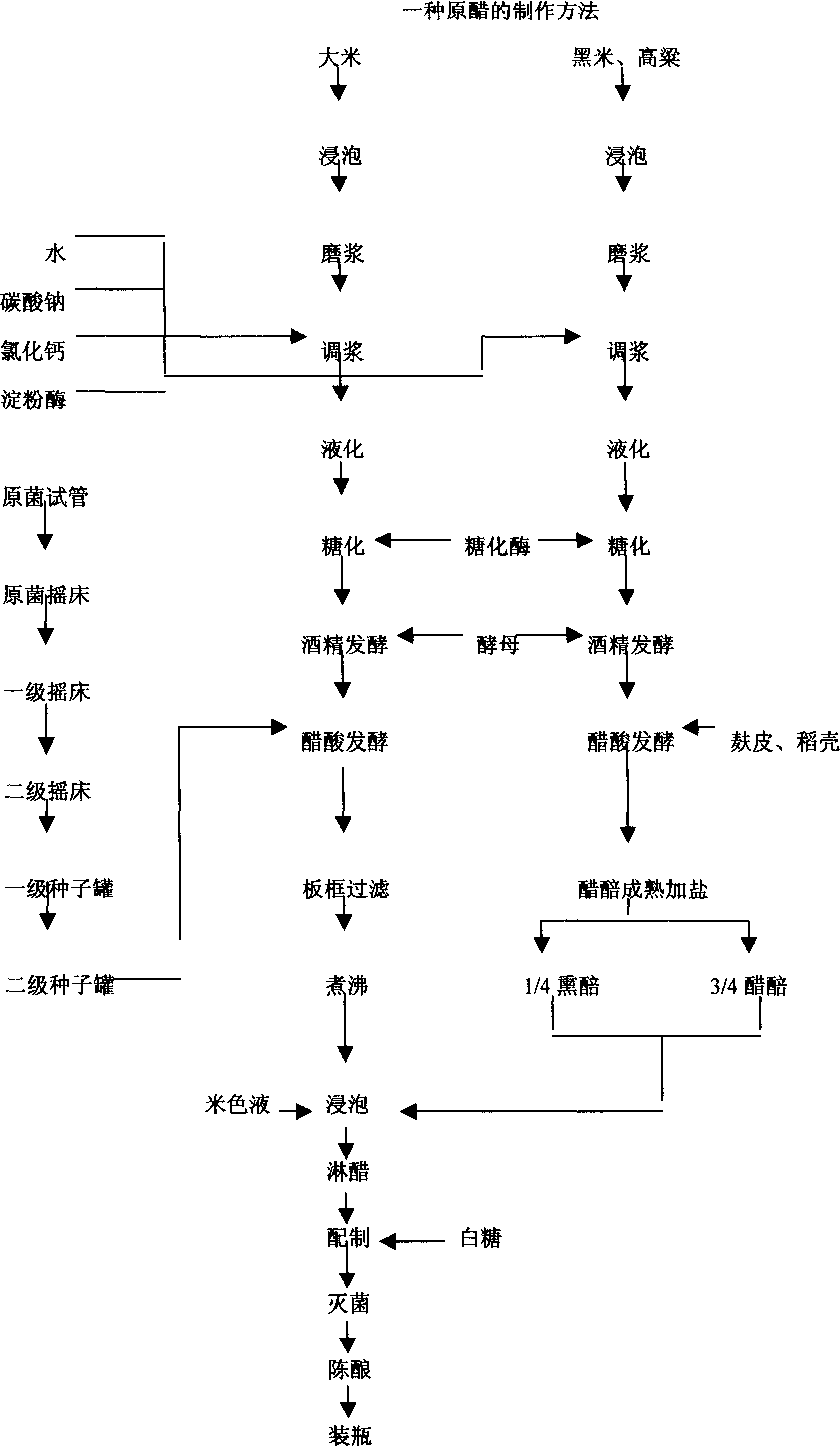
Vinegar making process
A production method and rice technology, which are applied in the preparation of vinegar and other directions, can solve the problems of inability to increase appetite, slightly bitter taste, poor sensory effect and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Rice 1000g Sodium Carbonate 1g
[0028] Salt 50g Calcium chloride 30g
[0029] α-amylase 6g White sugar 1g
[0030] Glucoamylase 130g Yeast 1g
[0031] Water 6000g Rice husk 400g
[0033] The color of the raw vinegar produced is brownish red or dark brown, bright in color, fragrant in smell, soft in sour taste, slightly sweet, without bitterness and astringency, moderate in concentration, free of suspended solids, long aftertaste, total acid (calculated as acetic acid) ≥ 4.0 g / 100ml.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Rice 3000g Sodium Carbonate 3g
[0036] Salt 150g Calcium Chloride 40g
[0037] α-amylase 8g White sugar 3g
[0038] Glucoamylase 185g Yeast 3g
[0039] Water 7000g Rice husk 400g
[0040] Husk bran 6000g
[0041] The color of the raw vinegar produced is brownish red or dark brown, bright in color, fragrant in smell, soft in sour taste, slightly sweet, without bitterness and astringency, moderate in concentration, free of suspended solids, long aftertaste, total acid (calculated as acetic acid) ≥ 4.0 g / 100ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com