Method of stable labelling liver cancer cell
A technology for liver cancer cells and human liver cancer cell lines, applied in the field of stable labeling of liver cancer cells, can solve the problems of high cost, complicated operation, and poor practicability, and achieve the effect of convenient operation, simplified steps, and strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The present invention is to the fluorescent labeling of human liver cancer cell HCCLM6, and the steps are as follows:
[0035] A. Cell culture The human liver cancer cell line HCCLM6 was cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma, Saint Louis, Missouri, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone, Utah, USA). Culture conditions: 37°C, 5% CO 2 / 95% air, saturated humidity. Replace the culture medium every other day, and subculture once every 4-6 days.
[0036] B. Treatment of cell culture slides and culture dishes, wash the 20mm×20mm cover glass and the glass culture dish with a diameter of 9cm with clean water, soak in 2% (vol / vol) hydrochloric acid solution overnight, soak in clean water, and use a soft brush Gently scrub, dry in an oven, control the temperature at 50-70°C, soak in 100ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, potassium dichromate cleaning solution, and 1000ml of distilled water in the acid tank for 1-3 days, rinse with tap water 20 times, wash with distilled wa...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The specificity test of the marker liver cancer cells of the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0051] A.~G. The same as in Example 1, divide the sealed hepatoma cell slides into two groups, one group uses specific mouse anti-human AFP antibody as the primary antibody, and one group uses PBS (same as in Example 1, step D) as the primary antibody. Primary antibody, according to the steps of Example 1
[0052] H. Operation.
[0053] I.~K. are the same as embodiment 1
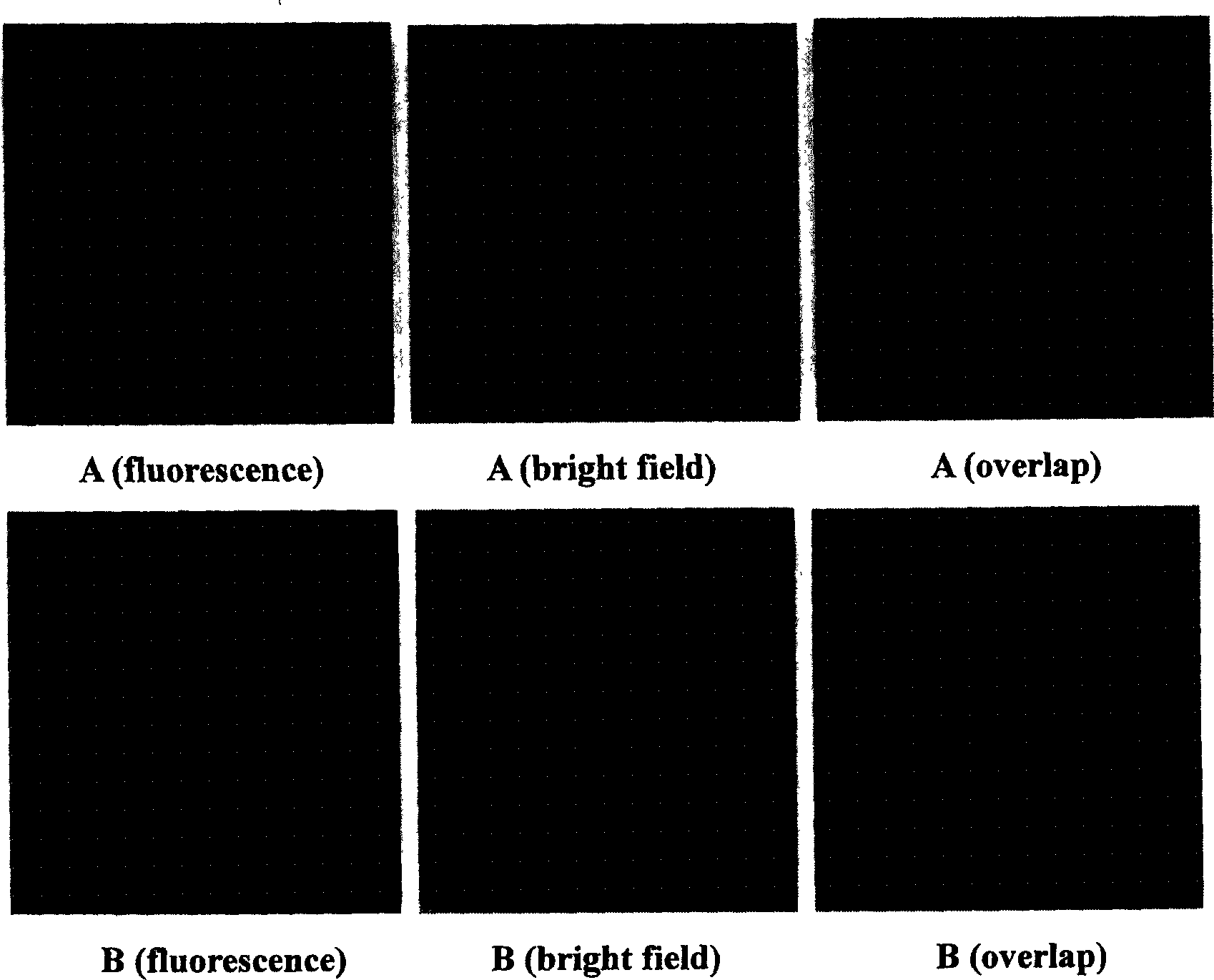
[0054] L. The slides were mounted in buffered glycerol and observed under a confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscope. see results figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0056] The fluorescence stability test of labeled liver cancer cells of the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0057] A.~I. Same as Example 1, the liver cancer cell slices that have been washed are divided into two groups, and one group is divided into QD s -IgG complex probe was used as the secondary antibody, and one group used FITC-IgG as the secondary antibody, and operated according to step J. of Example 1.
[0058] K. same as embodiment 1
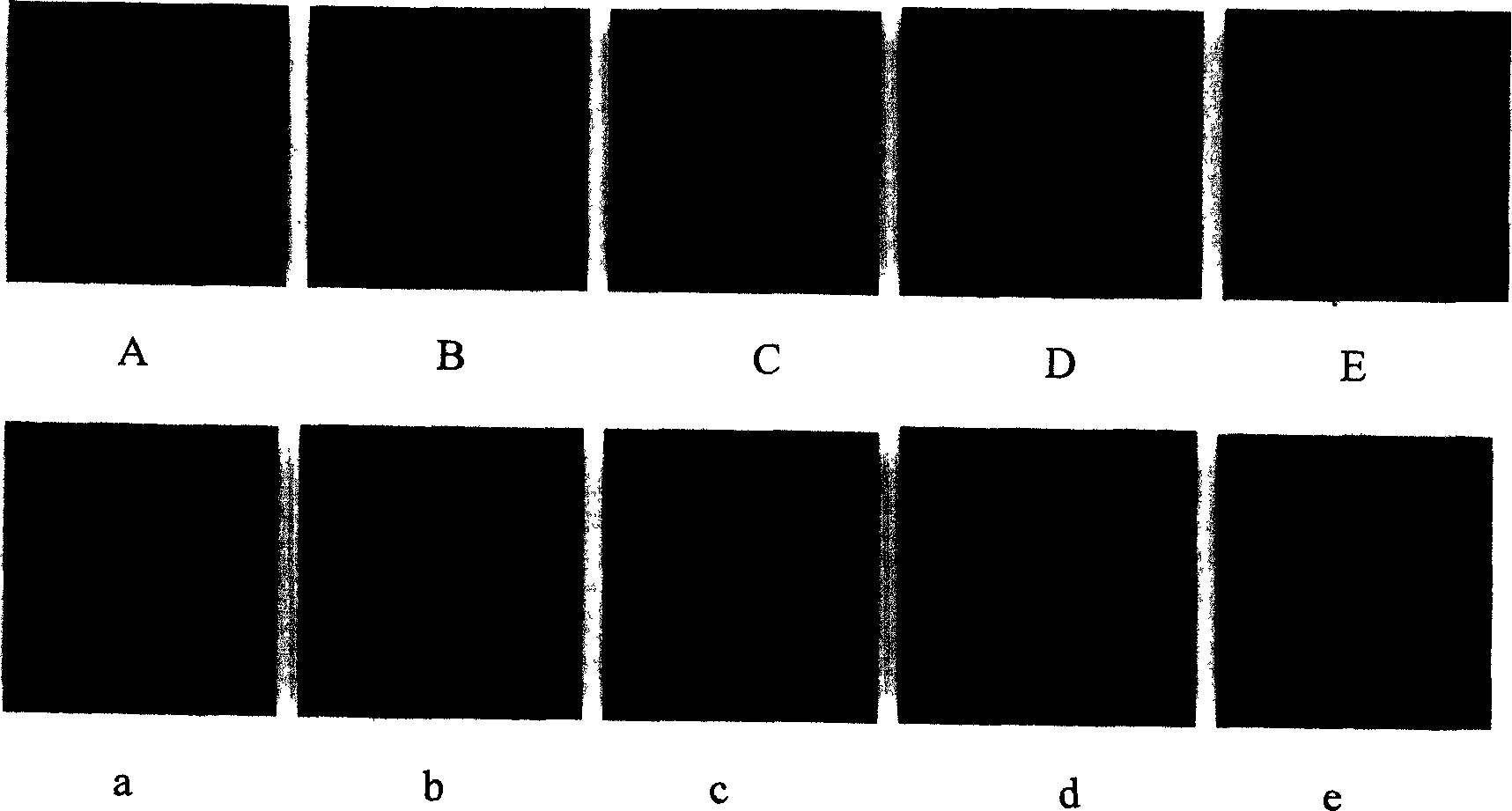
[0059] L. The slides were mounted in buffered glycerol and observed under a confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscope. see results image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com