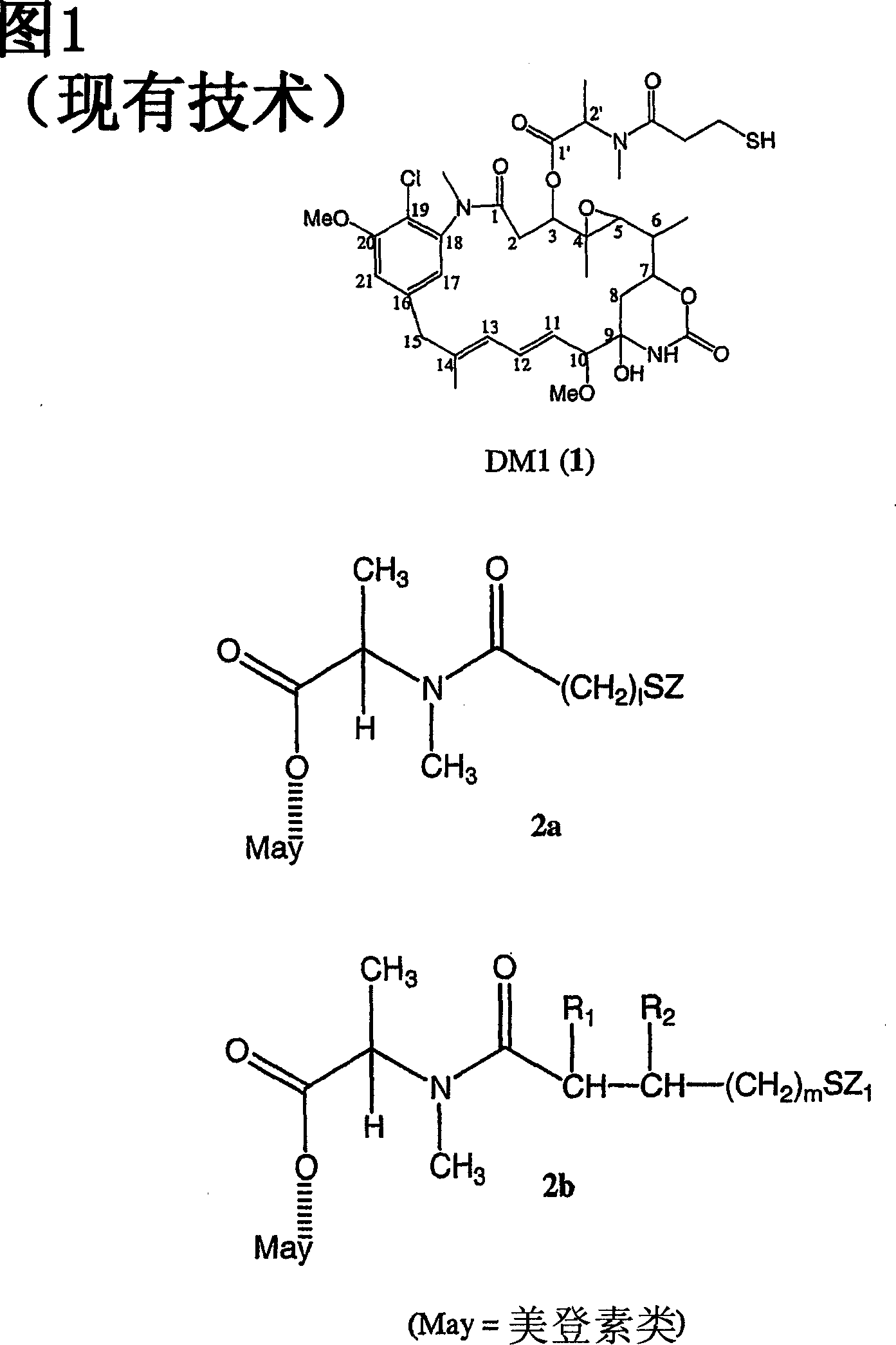
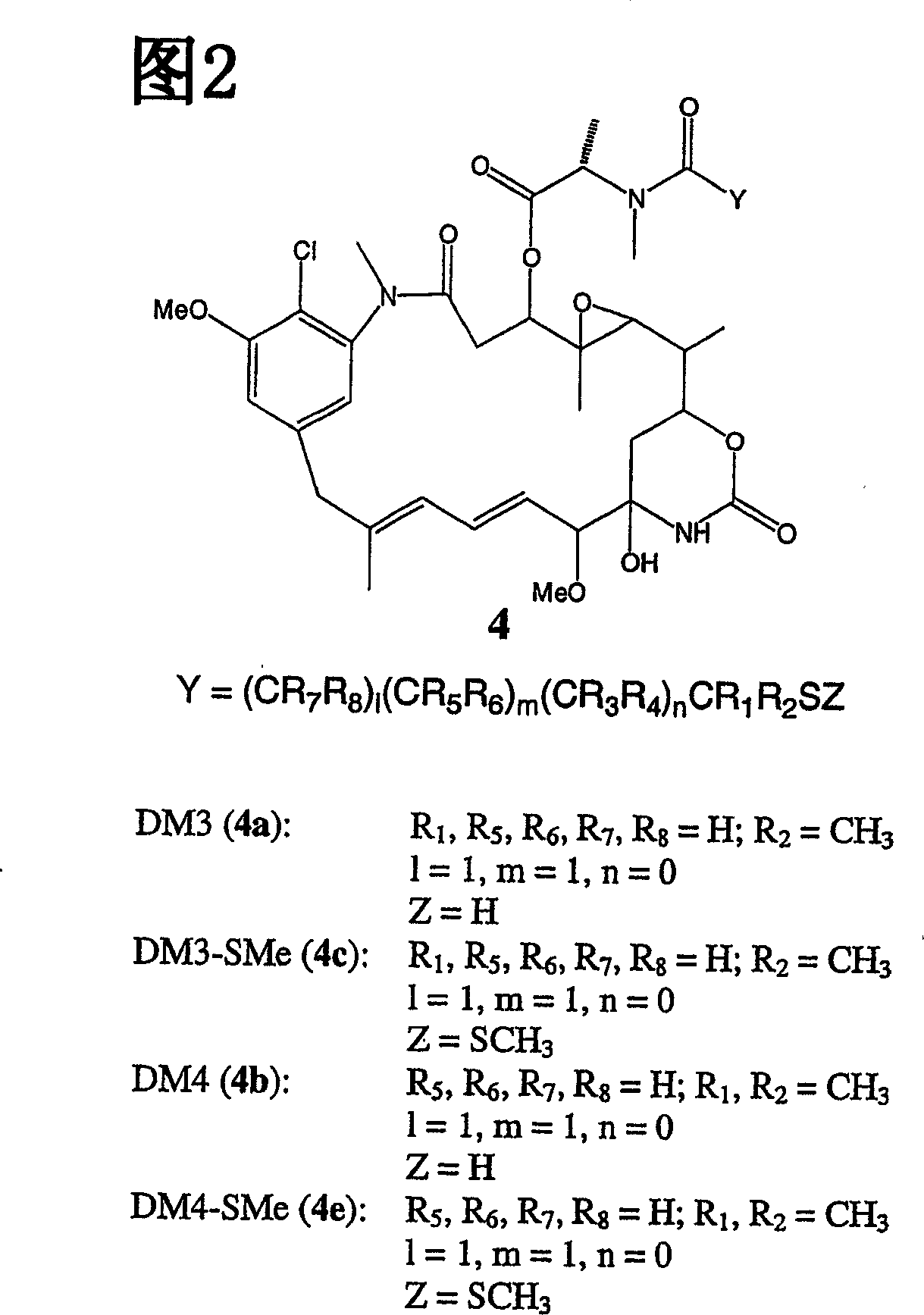
Improved cytotoxic agents comprising new maytansinoids
A technology of maytansine and cells, which is applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, antiviral agents, and medical preparations with non-active ingredients, which can solve problems such as instability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0450] Preparation of cell-binding agents
[0451] [171] The effectiveness of the compounds of the invention as therapeutic agents depends on careful selection of an appropriate cell-binding agent. Cell-binding agents can be of any type currently known, or becoming known, including peptide and non-peptide substances. Typically, they may be antibodies (especially monoclonal antibodies), lymphokines, hormones, growth factors, vitamins, nutrient transport molecules such as transferrin, or any other cell-binding molecule or substance.
[0452] [172] More specific examples of cell-binding agents that may be used include:
[0453] polyclonal antibodies;
[0454] Monoclonal antibodies;
[0455] Antibody fragments such as Fab, Fab' and F(ab') 2 , Fv (Parham, J.Immunol.131:2895-2902 (1983); Spring et al.J.Immunol.113:470-478 (1974); Nisonoff et al.Arch.Biochem.Biophys.89:230-244 ( 1960));
[0456] Interferons (eg, alpha, beta, gamma);
[0457] Lymphokines such as IL-2, IL-3, IL-...
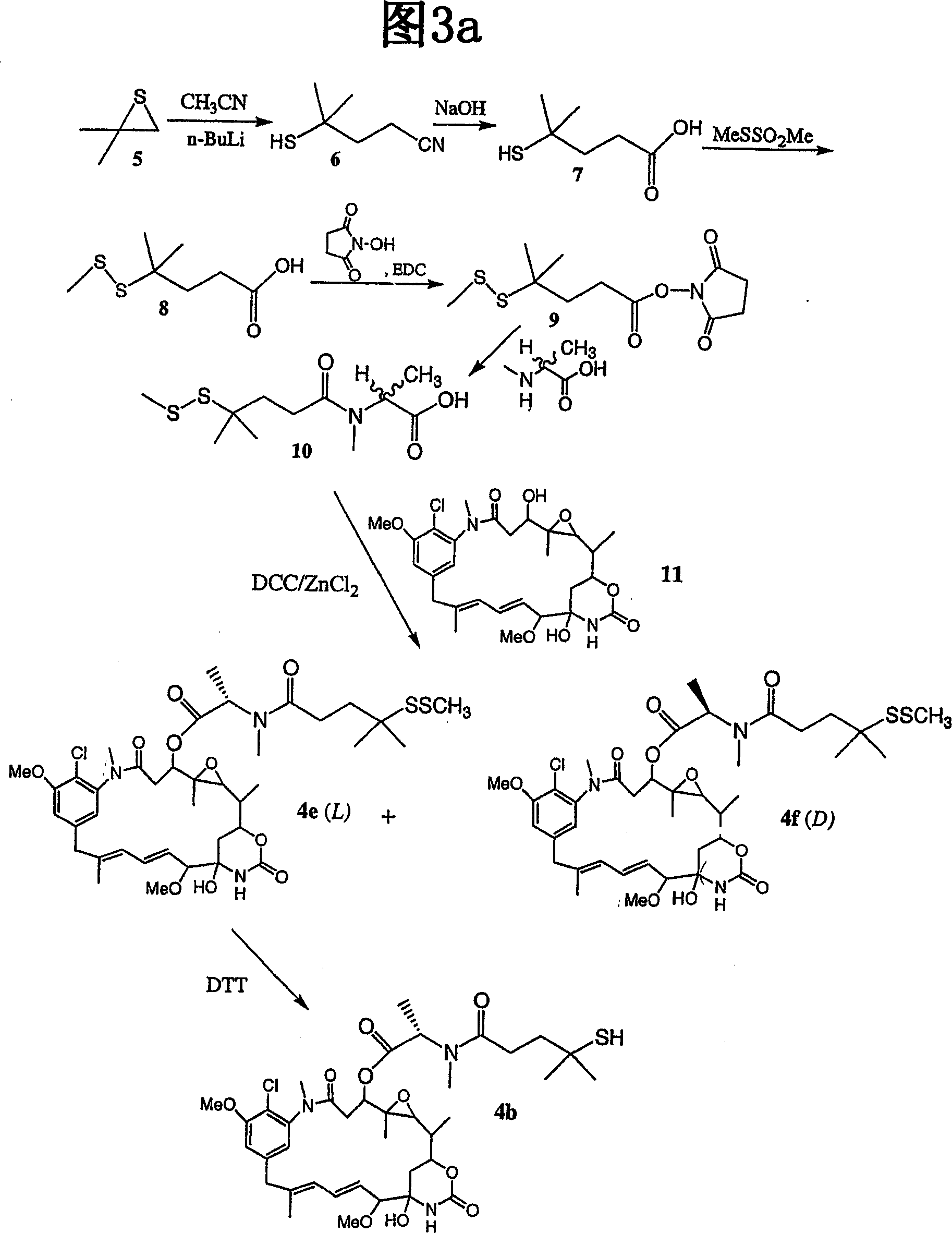
Embodiment 1
[0526] Synthesis of maytansinoid 4b
[0527] [216] 4-Mercapto-4-methylpentanoic acid (7): A 500 ml flask was fitted with a stir bar and a 150 ml addition funnel. The system was placed under nitrogen atmosphere. 150 ml of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (THF) and 75 ml of 2.5M n-BuLi in hexane (18.7 mmol) were added via cannula, and the solution was cooled in a dry ice / acetone bath at -78°C. Acetonitrile (7.3 g, 9.4 ml, 18 mmol) was added dropwise via syringe over a period of approximately 5 minutes. The reaction was stirred for 30 minutes when a white precipitate of lithium acetonitrile formed. Isobutenyl sulfide (15 g, 17 mmol) was dissolved in 100 mL dry THF and added dropwise via the addition funnel over approximately 30 minutes. The cooling bath was removed and the reaction was stirred for 3 hours. 38ml of 0.5M HCl was added dropwise while cooling the flask in an ice / water bath. The THF layer was retained, and the aqueous layer was washed twice with 75 ml of ethyl acetate. ...
Embodiment 2
[0536] Synthesis of Maytansinoid 4a
[0537] [222] 4-Methyldithio-pentanoic acid (13): In a 500 mL flask, a solution of 4-mercaptovaleric acid (12, 16.6 mg, 124 mmol) was dissolved in 350 mL of deionized water. The solution was magnetically stirred while sodium carbonate (19.7 g, 186 mmol) was added to the acid at a rate that did not cause excessive foaming. A 250 ml addition funnel was fitted to the flask containing a solution of methyl methanethiolsulfonate (23.4 g, 186 mmol) dissolved in 220 ml of glass distilled 100% ethanol. The flask was cooled in an ice / water bath and the system was maintained under an argon atmosphere. The methyl methanethiol sulfonate solution was added dropwise to the flask as quickly as possible, but at a rate that did not cause excessive foaming. The cooling bath was removed and the reaction mixture was stirred for an additional 2 hours. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation under vacuum until approximately 250 ml remained. Subsequently...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Extinction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com