Injectable hydrogel preparation of pegylated medicament
A technology of polyethylene glycol and hydrogel, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulation, drug delivery, and medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., to achieve the effect of easy use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Add 20g of polyethylene glycol (PEG, number average molecular weight 1500) into a 250ml three-necked flask, heat the oil bath to 150°C, and vacuum filter for three hours under stirring to remove the residual moisture in the PEG, and then add a molar ratio of 10 : 1 lactide (37.7g) and glycolide (3.0g), after heating under vacuum to make it melt completely, add 100μl of stannous octoate, the oil bath is heated up to 160 ℃, and continue to react under an argon atmosphere for 8 Hour. After the reaction was completed, vacuum filtration was performed for two hours to remove unreacted monomers and low-boiling products. Then dissolve the initial product in cold water (5°C-8°C). After it is completely dissolved, the solution is heated to 80°C. The product precipitates, and the upper solution is removed. Repeat the above steps once to obtain the product. The remaining water is frozen It was removed by drying with a yield of about 85%. pass 1 H-NMR determination of PLGA copoly...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Add 20g of polyethylene glycol (PEG, 1500) into a 250ml three-necked flask, then add 31.2g of DL-lactide and 6.3g of glycolide, heat it under vacuum to make it melt completely, add 100μl of stannous octoate, and put it in an oil bath The temperature was raised to 160° C., and the reaction was continued for 8 hours under an argon atmosphere. After the reaction was completed, vacuum filtration was performed for two hours to remove unreacted monomers and low-boiling products. Then dissolve the initial product in cold water (5°C-8°C). After it is completely dissolved, the solution is heated to 80°C. The product precipitates, and the upper solution is removed. Repeat the above steps once to obtain the product. The remaining water is frozen It was removed by drying with a yield of about 85%. Then under argon atmosphere, in 250ml there-necked flask, add the block copolymer of 10g, after 100ml dichloromethane solution dissolves, add equimolar succinic anhydride and anhydrous p...
Embodiment 3
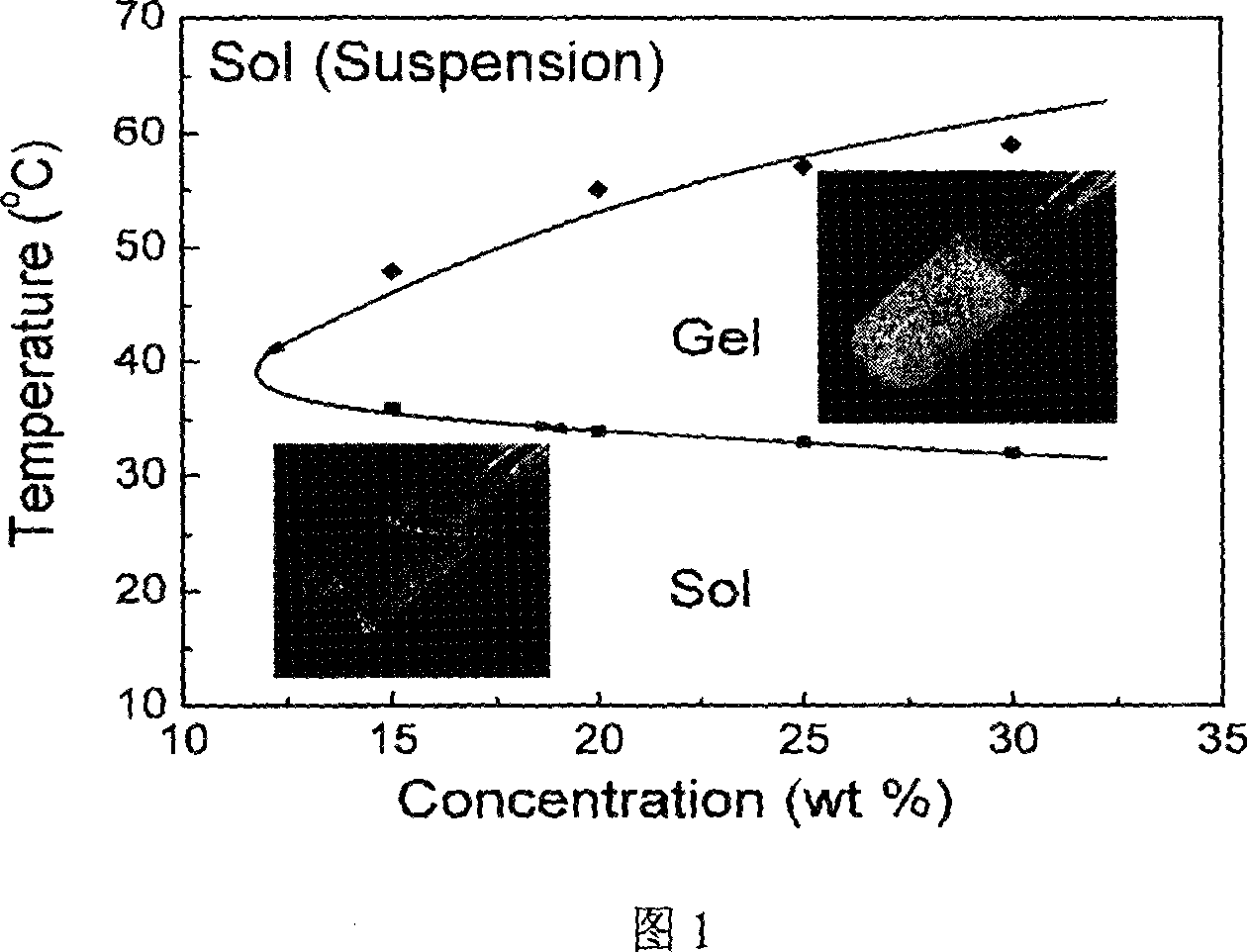
[0042] The gelation behavior of the block copolymer in Example 1 in aqueous solutions with different concentrations was studied. Copolymer aqueous solutions with different weight percent concentrations from 10% to 30% were prepared, and the viscosity changes between 0°C and 60°C were measured. Gelation was defined by observing that no flow occurred within 30 seconds when the tube was inverted. Figure 1 is the phase diagram of the block copolymer in Example 1 with different concentrations of aqueous solution as the temperature changes. The reversibility of its gelation process can be clearly seen, and its gelation at human body temperature is very useful for injectable drug sustained-release systems.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com