Fabric and clothes for atopic dermatitis patients
A technology for patients with atopic dermatitis, applied in the field of cloth and clothing, can solve the problems of unable to exert the characteristics of silk protein, no description of the relationship, limitations of thermoplastic resin, etc., to reduce or cure atopic dermatitis, high production efficiency, small stimulating effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 and comparative example 4 and 5
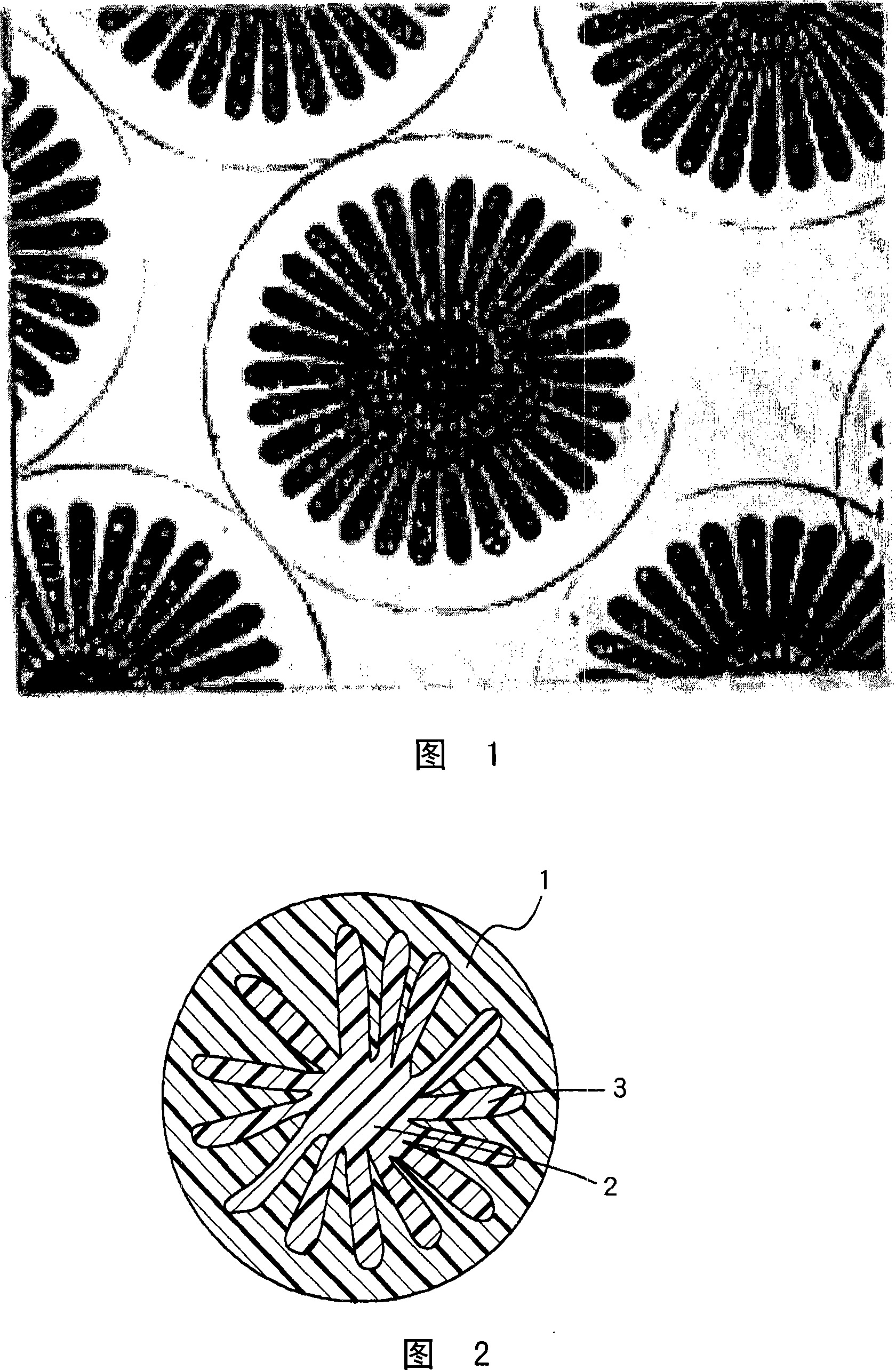
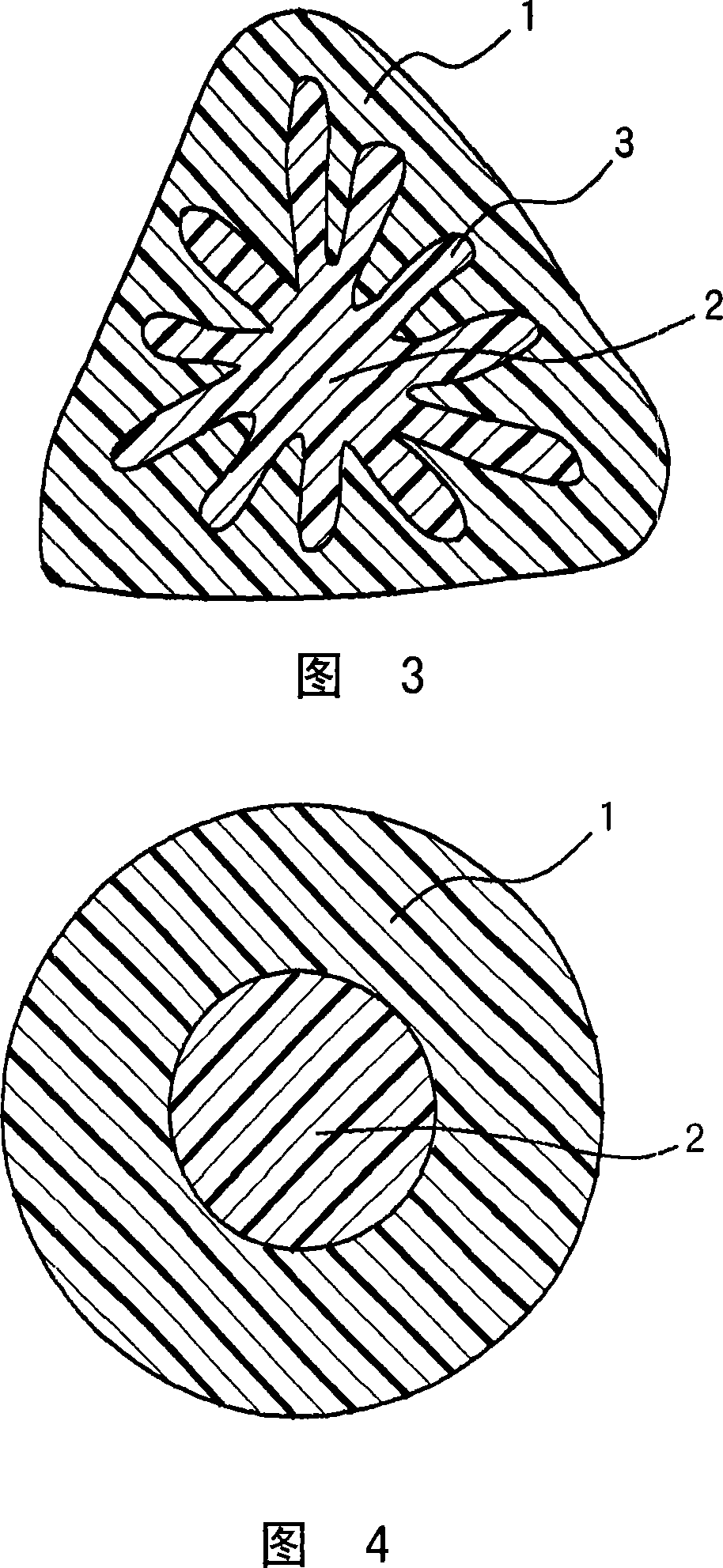
[0104] Free-radical polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate to produce a random copolymer with a copolymerization ratio of 44 mol% of ethylene, and then saponification treatment with sodium hydroxide to obtain an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer with a saponification degree of 99 mol% or more Saponification (EVOH). Using this polymer as the A polymer (forming the sheath), on the other hand, using ethylene terephthalate (PET) as the B polymer (forming the core), the composite ratio of the A polymer and the B component Under the condition of 50:50, carry out melt composite spinning with spinning temperature 285 ℃, take-up speed 3500m / min, the cross-sectional shape of obtaining each fiber is the multifilament fiber of the shape shown in Figure 1 (total thickness is 83dtex 24 multifilaments (hereinafter referred to as "83dtex / 24 monofilament")). Before the fiber is produced, the pellets in a wet state as polymer A are washed with a large amount of pure aqueous solution conta...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 is an example of fiberization using commercially available polyamide 6 as the B polymer. That is, except that polyamide 6 was used as the B polymer, long fibers were produced in the same manner as in the examples, and knitted materials were formed into T-shirt-shaped underwear, and a wearing test was carried out. The results are shown in Table 1. From the results in Table 1, it can be seen that the itching reduction effect in patients with atopic dermatitis is remarkable.
Embodiment 3
[0120] In Example 1 and the same ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer, 20% of the polyamide resin synthesized by the following production method was melt-kneaded, and the extruded product was used as the A polymer, and commercially available polyamide 6 was used as the B polymer. Polymer, at a spinning temperature of 285 ° C, a core-sheath composite fiber (core-sheath ratio = 1: 1) containing A polymer as the sheath component and B polymer component as the core component is discharged through the nozzle. / min take-off speed for can winding. The obtained fiber bundles were stretched, crimped, and sheared by common methods to obtain chemical fiber staple fibers with a single fiber thickness of 1.2 dtex, a fiber length of 38 mm, and a cross-sectional composite shape as shown in Figure 1. The average size of islands containing polyamide resin in polymer A is about 70 nm, and the number of islands is about 50 / μm 2 .
[0121] The elastic modulus of raw cotton is 15cN / dtex. 70% of the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com